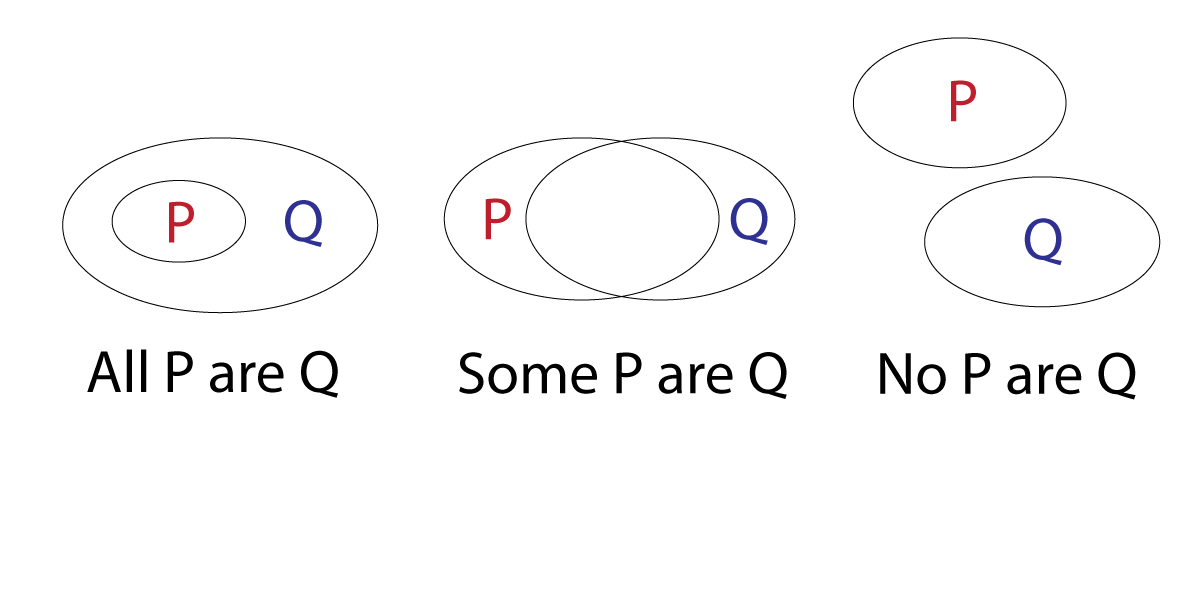
12.3 EULER 图表
章节大纲
-
Consider the following argument:
::考虑以下论点:Dogs learn fast. Frank does not learn fast. Frank is a cat.
::狗学得很快 弗兰克不会学得很快 弗兰克是只猫How could you use a diagram to help you evaluate the validity of this argument?
::您如何使用图表来帮助您评估此论点的有效性 ?
Euler Diagrams
::Euler 图图You may not immediately associate art with Reason and Logic, but sometimes drawing diagrams can greatly simplify the process of evaluating a statement for validity or soundness.
::您可能不会立即将艺术与理性和逻辑联系起来,但有时绘图图表可以大大简化对声明的有效性或正确性进行评价的过程。Euler (sounds like “oiler”) diagrams look very much like Venn Diagrams, but Euler was using them to describe mathematical concepts a very long time before the classic was recognized. The purpose of Euler diagrams is to create a visual representation of each of the aspects in a logical argument so that the conclusion may be clearly evaluated.
::欧勒(Euler)图表(听起来像“锅炉 ” ) , 看上去非常像文恩图表,但欧勒在经典被认可之前很久就用它们来描述数学概念。 欧勒图表的目的是在逻辑论证中直观地描述每个方面,以便明确评估结论。Generally, one oval is constructed to represent each set described in the argument, and an “X” is used to represent solitary units. Possible relationships can be expressed by the location of the ovals and “X’s”.
::一般说来,一个oval是用来代表论点中描述的每一组,一个 " X " 用来代表单独单元,可能的关系可以用oval和 " X " 的位置来表示。Expressing Arguments Using an Euler Diagram
::使用 Euler 图表表达参数Express the argument using an Euler diagram .
::使用Euler图表表达这一论点。All trucks are vehicles. I drive a truck. Therefore I drive a vehicle.
::所有卡车都是车辆,我开卡车,所以我开汽车The set “all trucks” is a subset of the set “vehicles”. My truck is a member of the set “all trucks”, so my truck is also within the set “vehicles”.
::一套“所有卡车”是一套“车辆”的子集,我的卡车是一套“所有卡车”的成员,因此,我的卡车也在一套“车辆”之内。Evaluating Validity
::评价有效性1. Evaluate the validity of the argument using an Euler diagram.
::1. 使用Euler图表评估论点的有效性。Boots are a type of footwear. I wear footwear. Therefore, I wear boots.
::靴子是一种鞋,我穿鞋,所以穿靴子The set “boots” is a subset of the set “footwear”. My footwear is in the set “footwear”, but we do not know if it is in the set “boots” or not.
::这套“装置”是一套“脚装”的子集,我的鞋在一套“脚服”内,但我们不知道这是否在一套“装置”内。We can see from the diagram that this argument cannot be valid, since both statements may be true but I might be wearing sandals, making the conclusion false.
::我们从图表中可以看出,这一论点是站不住脚的,因为两种说法可能都是真的,但我可能穿着凉鞋,使结论虚假。2. Evaluate the validity of the argument using an Euler diagram.
::2. 使用Euler图表评估论点的有效性。All teachers are cool. Some guys are teachers. Some guys are cool.
::所有的老师都很酷 有些人是老师 有些人很酷The set “teachers” is a subset of the set “cool people”. The set “guys” intersects with the set “teachers”. The set “cool people” intersects with the set “guys” where “guys” includes “teachers”.
::一套“教师”是一套“酷人”的子集,一套“人”与一套“教师”交叉,一套“酷人”与一套“人”交叉,其中“人”包括“教师”。If the premises are true, the conclusion must be. The only way for there to be no cool guys is for one of the premises to be false. The argument is valid.
::如果房舍是真实的,那么结论必须是真实的。 没有酷男的唯一办法就是其中一处房舍是虚假的。 论点是有道理的。Earlier Problem Revisited
::重审先前的问题Consider the following argument:
::考虑以下论点:All dogs learn fast. Frank does not learn fast. Frank is a cat.
::弗兰克不会学得很快 弗兰克是只猫How could you use a diagram to help you evaluate the validity of this argument?
::您如何使用图表来帮助您评估此论点的有效性 ?Create an Euler diagram to illustrate the argument:
::创建 Euler 图表以说明参数 :“Dogs” are a subset of “things that learn fast”. Frank is not a member of the set “things that learn fast”, so he is not a member of “dogs” either. However, that does not mean he must be a member of “cats”. It is possible for both premises to be true, while the conclusion is false. The argument is invalid.
::“狗”是“学得快的东西”的子集,Frank不是一套“学得快的东西”的成员,因此他也不是“狗”的成员,但这并不意味着他必须是“猫”的成员,两个前提都有可能是真实的,而结论是虚假的,论点是无效的。Examples
::实例Use the Euler diagram below to answer Examples 1-3:
::使用下面的 Euler 图回答示例1-3:Example 1
::例1Which pair of premises could be illustrated by the Euler diagram?
::欧勒图可以说明哪些房舍?a. All bald people are cooks. Mr Jones is bald.
::a. 所有秃头者都是厨师,琼斯先生是秃头者。b. Some cooks are bald. Mr Jones is a cook.
::b. 有些厨师秃头,琼斯先生是厨师。c. Mr Jones is a cook. Mr Jones is bald.
::琼斯先生是厨师 琼斯先生是秃头The correct answer is "b: Some cooks are bald. Mr Jones is a cook". The set of bald people intersects with the rest of cooks, but neither is a subset of the other. Mr. Jones is somewhere within the set of cooks, but may or may not be within the set of bald people.
::正确的答案是“b:有些厨师是秃头的。琼斯先生是一名厨师 ” 。 一群秃头的人与其他厨师交织在一起,但其他厨师中也没有一个分支。 琼斯先生在厨师队伍内,但也可能不在秃头的人队伍内。Example 2
::例2Given the premises from Example 1, what conclusion is illustrated as being incorrect by the diagram?
::鉴于例1的房地情况,图表说明哪些结论不正确?The conclusions that Mr Jones is/is not bald is shown to be incorrect by the diagram, since he could be in either set, based on the given premises.
::图表显示,Jones先生不是秃头/不是秃头的结论是不正确的,因为他可以依据特定前提,在两组中任选一个。Example 3
::例3Is the argument valid? Why or why not?
::论点是否有效?为什么或为什么不能呢?The argument is not valid, since both premises could be true while the conclusion remains false.
::这一论点是站不住脚的,因为两个前提都可能是真的,而结论仍然是虚假的。Example 4
::例4What valid conclusion could be drawn from the given premises?
::从上述房地可以得出什么有效结论?The only possible conclusion is that Mr Jones may be bald, which is the case regardless, so the premises are weak.
::唯一可能的结论就是琼斯先生可能是秃头的,不管怎样,情况都是如此,所以房舍很虚弱。Review
::回顾Create Euler diagrams to represent each of the situations in questions 1-7:
::创建 Euler 图表以代表问题 1-7 中的每一种情况:1. All are .
::1. 所有P均为Q。2. Some are .
::2. 有些P是Q。3. All are not .
::3. 所有问题都不是问题。4. Some are not .
::4. 有些P不是Q。5. All are . is a member of . is a member of .
::5. 所有议员均为Q.R.,是P.R.的成员。6. All are . is not . is not .
::6. 所有P为Q. R不是Q. R不是P.7. All are . All are . All are .
::7. 所有P均为Q。 所有Q均为R。 所有P均为R。8. Create a Euler diagram to represent the following argument:
::8. 创建Euler图以代表以下参数:If a bull has been gelded, it is a steer. Ferdinand is not a steer. Therefore, Ferdinand is not a gelded bull.
::公牛 被 凝胶 的 、 就 是 公牛 . 费迪南不是 公牛 . 因此 、 费迪南不是 凝胶 的 公牛9. Is the argument in question 8 valid or invalid? Why?
::9. 问题8中的论点是否有效或无效?为什么?10. Create an Euler diagram to represent the following argument:
::10. 创建欧勒图以代表以下参数:Ignoring problems makes them go away. I ignore my problems. My problems go away.
::我忽视我的问题,我的问题就消失。11. Is the argument in question 10 valid or invalid? Why?
::11. 问题10中的论点是否有效或无效?为什么?12. Create an Euler diagram to represent the following argument:
::12. 创建代表下列参数的Euler图:Arguments must be valid or invalid. This argument is invalid. This argument is valid.
::参数必须有效或无效。 此参数无效。 此参数有效 。13. Is the argument is question 12 valid or invalid? Why?
::13. 问题12是否有效或无效?为什么?14. Create an Euler diagram to represent the following argument:
::14. 创建Euler图以代表以下参数:If you study Reason, you will better understand Logic. If you better understand Logic, you will make better use of Statistics. Therefore if you study Reason, you will be better at math.
::如果你学习理性,你会更好地理解逻辑。如果你更好地理解逻辑,你会更好地利用统计。因此,如果你学习理性,你会在数学上做得更好。15. Is the argument in question 14 valid or invalid? Why?
::15. 问题14中的论点是否有效或无效?为什么?Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。