3.16 遗传疾病
章节大纲
-
When is a cold not just a cold?
::什么时候感冒不只是感冒?At some point in your life, you're bound to catch a cold. And there are ways to prevent catching a cold. But what if you couldn't prevent an illness? What if you were born with a disease? What if having a disease was actually due to your ? These are genetic diseases, and they can be very serious.
::在你生命的某个时刻,你注定要感冒。有办法防止感冒。但是如果你不能预防疾病呢?如果你生来就患有一种疾病呢?如果疾病实际上是由你造成的呢?这些是遗传疾病,它们可能非常严重。Human Genetic Disorders
::人类遗传疾病Many genetic disorders are caused by in one or a few genes . Others are caused by chromosomal mutations. Some human genetic disorders are X-linked or Y-linked, which means the faulty gene is carried on these sex chromosomes . Other genetic disorders are carried on one of the other 22 pairs of chromosomes ; these chromosomes are known as autosomes or autosomal (non-sex) chromosomes. Some genetic disorders are due to new mutations, others can be inherited from your parents.
::许多遗传疾病是由一种或几种基因引起的,另一些是由染色体突变引起的,有些人类遗传疾病与X相关或Y相关,这意味着这些性染色体携带了有缺陷的基因,其他遗传疾病则由另外22对染色体中的一种染色体造成,这些染色体被称为异体或异体(非性)染色体,有些遗传疾病是由新的变异引起的,另一些则可能由父母继承。Autosomal Recessive Disorders
::自动溶性衰退紊乱Some genetic disorders are caused by recessive alleles of a single gene on an autosome. An example of autosomal recessive genetic disorders are Tay-Sachs disease and cystic fibrosis . Children with cystic fibrosis have excessively thick mucus in their lungs , which makes it difficult for them to breathe. The inheritance of this recessive allele is the same as any other recessive allele, so a can be used to predict the probability that two carriers of the disease will have a child with cystic fibrosis. Recall that carriers have the recessive allele for a trait but do not express the trait. What are the possible genotypes of the offspring in the following table ( Table )? What are the possible phenotypes ?
::一些遗传障碍是由一个单基因的休眠异象引起的。自动休眠遗传障碍的一个例子是Tay-Sachs病和细胞纤维化。患有细胞纤维化的儿童肺部有超厚的粘结,这使得他们难以呼吸。这种休眠异象的遗传传承与任何其他的休眠异象相同,因此可以用来预测两种疾病携带者将有一个患细胞纤维化子的概率。回顾母体有休眠异象的特性,但不表示其特性。下表(表)中后代的可能基因类型是什么?可能的苯型是什么?F f F FF
::FF FF(normal)
:正常)
Ff
::Fff ff ff(carrier)
:载体)
f Ff
::Fff ff ff(carrier)
:载体)
ff
::ff 时(affected)
:受影响)
According to this Punnett square, two parents that are carriers ( Ff ) of the cystic fibrosis gene have a 25% chance of having a child with cystic fibrosis ( ff ). The affected child must inherit two recessive alleles. The carrier parents are not affected.
::根据Punnett广场的说法,双亲是囊肿纤维化基因的携带者(Ff),有25%的生子患囊肿纤维化(ff)的几率。 受影响儿童必须继承两个休眠异形,承生者的父母不受影响。Tay-Sachs disease is a severe genetic disorder in which affected children do not live to , so the gene is not passed from an affected individual. Carriers of the Tay-Sachs gene are not affected. How does a child become affected with Tay-Sachs?
::Tay-Sachs疾病是一种严重的遗传疾病,受影响儿童无法存活,因此该基因不会从受影响的个人传承。 Tay-Sachs基因的携带者不会受到影响。 一个儿童如何受到Tay-Sachs的影响?Autosomal Dominant Disorders
::自动共控主力紊乱Huntington’s disease is an example of an autosomal dominant disorder . This means that if the dominant allele is present, then the person will express the disease. A child only has to inherit one dominant allele to have the disease.
::亨廷顿的疾病是自闭症占支配地位的一个例子。 这意味着如果占支配地位的异灵存在,那么这个人就会表达这种疾病。 一个孩子只要继承一个占支配地位的异灵就可以有这种疾病。The disease causes the brain’s cells to break down, leading to muscle spasms and personality changes. Unlike most other genetic disorders, the symptoms usually do not become apparent until middle age. You can use a simple Punnett square to predict the inheritance of a dominant autosomal disorder, like Huntington’s disease. If one parent has Huntington’s disease, what is the chance of passing it on to the children? If you draw the Punnett square, you will find that there is a 50 percent chance of the disorder being passed on to the children.
::疾病导致大脑细胞破裂,导致肌肉抽搐和人格变化。 与其他大多数遗传疾病不同,症状通常直到中年才会显现出来。 您可以使用简单的Punnett广场来预测占支配地位的自闭症(比如亨廷顿病 ) 的遗传性。 如果父母一方患有亨廷顿病,那么将病传给孩子的几率会有多大?如果绘制Punnett病方形,你就会发现50%的病症会传给孩子。Can you have too many chromosomes?
::你能有太多染色体吗?Yes, it's not a good thing to have extra chromosomes. An extra chromosome can be fatal to an embryo , in fact. In the case of a few chromosomes, however, a baby may be born with an extra chromosome. This child will have a chromosomal disorder.
::是的,增加染色体并不是一件好事。额外的染色体对胚胎来说是致命的。事实上,额外的染色体对胚胎来说是致命的。但是,在少数染色体的情况下,婴儿可能与额外的染色体一起出生。这个孩子会患染色体紊乱。Some children are born with genetic defects that are not carried by a single gene. Instead, an error in a larger part of the chromosome or even in an entire chromosome causes the disorder. Usually the error happens when the egg or is forming. Having extra chromosomes or damaged chromosomes can cause disorders.
::有些儿童出生时遗传缺陷不是由单一基因携带的。相反,染色体中较大部分的错误甚至整个染色体中的错误导致疾病。通常错误发生在卵子或形成时。染色体外加染色体或受损染色体可能造成疾病。Extra Chromosomes
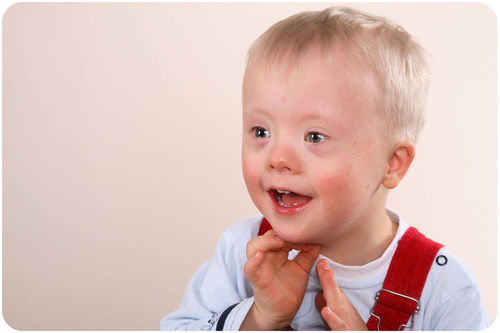
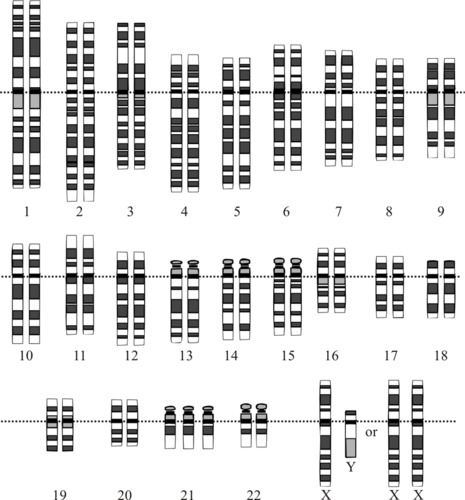
::外染色体One common example of an extra-chromosome disorder is Down syndrome ( Figure ). Children with Down syndrome are mentally disabled and also have physical deformities. Down syndrome occurs when a baby receives an extra chromosome 21 from one of his or her parents. Usually, a child will receive one chromosome 21 from the mother and one chromosome 21 from the father. In an individual with Down syndrome, however, there are three copies of chromosome 21 ( Figure ). Therefore, Down syndrome is also known as Trisomy 21. These people have 47 total chromosomes.
::超染色体紊乱的一个常见例子是唐氏综合症(Figure),患有唐氏综合症的儿童是智障儿童,身体也畸形,当婴儿从父母一方收到额外的21个染色体时,就会出现唐氏综合症;通常,儿童从母亲处收到21个染色体,从父亲处收到21个染色体;但是,在患有唐氏综合症的人中,有3个21个染色体(Figure),因此,唐氏综合症也称为Trisomy 21,这些人共有47个染色体。A child with Down syndrome. Chromosomes of a person with Down Syndrome. Notice the extra chromosome 21. Another example of a chromosomal disorder is Klinefelter syndrome , in which a male inherits an extra “X” chromosome. These individuals have an XXY genotype. They have underdeveloped sex organs and elongated limbs. They also have difficulty learning new things.
::染色体紊乱的另一个例子是Klinefelter综合症,在这个综合症中,男性继承了额外的“X”染色体,这些人有20Y基因型,性器官发育不足,四肢长,也难以学习新东西。Outside of chromosome 21 and the sex chromosomes, most embryos with extra chromosomes do not usually survive. Because chromosomes carry many, many genes, a disruption of a chromosome can cause severe problems with the development of a fetus . Individuals with one (or more) fewer chromosome usually don't survive either. Can you explain why?
::在21个染色体和性染色体之外,大多数带有额外染色体的胚胎通常不会存活下来。 因为染色体含有许多许多基因,染色体的中断会给胎儿发育造成严重问题。 染色体少一个(或更多)的人通常也无法存活下来。 你能解释为什么吗?Damaged Chromosomes
::损伤染色体Chromosomal disorders also occur when part of a chromosome becomes damaged. For example, if a tiny portion of chromosome 5 is missing, the individual will have cri du chat (cat’s cry) syndrome. These individuals have misshapen facial features, and the infant’s cry resembles a cat’s cry.
::当染色体的一部分受损时,染色体也会出现染色体紊乱。 比如,如果染色体五分之一的一小部分缺失,个人将患有credi du talk (Cat's cry)综合症(Cat's cry) 。 这些人有错位面部特征,婴儿的哭声类似于猫的叫声。Summary
::摘要-
Autosomal recessive genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, are caused by recessive alleles of a single gene on an autosome.
::诸如cyctic Fibroisis等自动休眠性遗传障碍,是由一个单基因的休眠通灵导致的,这种失常性遗传障碍是由一个机体上的单一基因的休眠通灵引起的。 -
Autosomal dominant genetic disorders, such as Huntington's disease, are caused by dominant alleles of a single gene on an autosome.
::诸如亨廷顿病等自闭症主要遗传障碍,是由一种自闭症上单一基因的支配性异变引起的。 -
Changes in chromosome number can lead to disorders like Down syndrome.
::染色体数的变化可能导致唐氏综合症等疾病。 -
Chromosomal disorders also occur when part of a chromosome becomes damaged.
::当部分染色体受损时,也会出现染色体紊乱。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。I. What are Genetic Disorders? at
::一、什么是遗传疾病?-
What are multifactorial disorders? What is an example of a multifactorial disorder?
::什么是多因素障碍?多因素障碍的例子是什么?多因素障碍的例子是什么? -
What are single-gene disorders? What is an example of a single-gene disorder?
::什么是单基因疾病?单基因疾病的例子是什么?单一基因疾病的例子是什么? -
What causes galactosemia? How is it diagnosed? How is it treated?
::是什么导致甘蓝贫血?如何诊断?如何治疗? -
What causes Colon Cancer? What is a tumor suppressor gene?
::是什么导致科隆癌?什么是肿瘤抑制基因? -
What is newborn genetic screening? How is it carried out?
::什么是新生儿基因筛选?如何进行?
II. Cracking the Code: Rare Chromosome Disorders at
::二. 破坏《守则》:-
What do all people diagnosed with a chromosome disorder share?
::所有被诊断患有染色体紊乱的人 都分享了些什么? -
What is a clinical geneticist?
::什么是临床遗传学家? -
What are they trained to do that is different from a regular doctor?
::他们受过什么训练才能这样做? 这与普通医生有什么不同? -
What is a karyotype? Do chromosomal disorders always involve extra genetic material? Explain your answer.
::染色体紊乱总是涉及额外的遗传物质吗?
Review
::回顾-
Can you be a carrier of an autosomal recessive genetic disorder?
::您是否可成为自动休眠基因紊乱的携带者? -
Can you be a carrier of an autosomal dominant genetic disorder?
::您是否可携带一种自给性主要遗传疾病? -
One parent is a carrier of the cystic fibrosis gene, while the other parent does not carry the allele. Can their child have cystic fibrosis?
::父母一方是囊性纤维化基因的携带者,而另一方则不携带止痛剂。 他们的孩子有囊性纤维化吗? -
What is a chromosomal disorder?
::什么是染色体紊乱? -
Explain what causes Down Syndrome.
::解释导致唐氏综合症的原因 -
When do chromosomal defects occur?
::何时出现染色体缺陷? -
What happens to most embryos with extra chromosomes? Explain your answer.
::大部分带有额外染色体的胚胎会怎么样?
-
Autosomal recessive genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, are caused by recessive alleles of a single gene on an autosome.