5.2 细菌特征
章节大纲
-
Are living things?
::活着的东西吗?Bacteria are individual living . Bacteria cells are similar to your cells in many ways; yet, they also have distinct differences. Bacteria have many unique adaptations allowing them to live in many different environments.
::细菌是个体生物。细菌细胞在许多方面与你的细胞相似;然而,它们也有不同的差异。细菌有许多独特的适应性,允许它们生活在许多不同的环境中。Characteristics of Bacteria
::细菌的特性Bacteria are the most successful organisms on the planet. They lived on this planet for two billion years before the first eukaryotes and, during that time, evolved into millions of different .
::细菌是地球上最成功的生物。它们在这个星球上生活了20亿年, 在那之前的第一颗苏卡利奥特, 在那个时期,它们演变成数以百万计的不同生物。Size and Shape
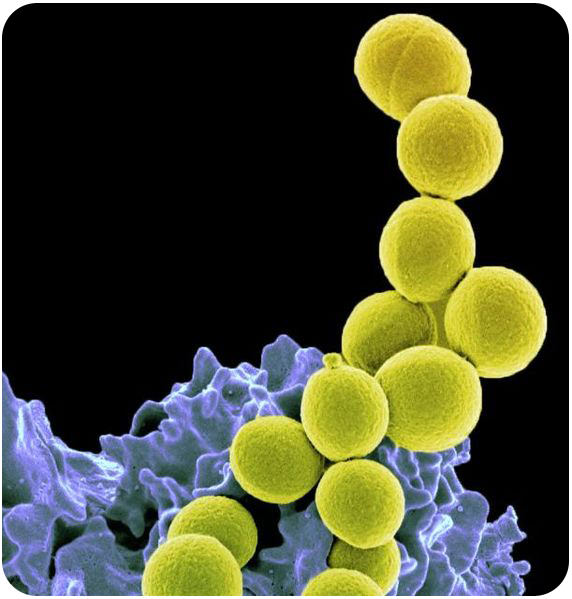
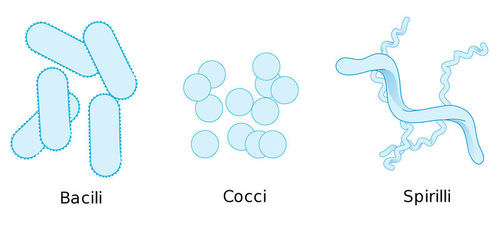
::大小和形状Bacteria are so small that they can only be seen with a . When viewed under the microscope, they have three distinct shapes ( Figure ). Bacteria can be identified and classified by their shape:
::细菌小到只能用显微镜来观察它们。当在显微镜下观察它们时,它们有三个不同的形状(图示)。细菌可以按它们的形状来辨别和分类:-
Bacilli
are rod-shaped.
::Bacilli是棒形的。 -
Cocci
are sphere-shaped.
::Coccci是球形的。 -
Spirilli
are spiral-shaped.
::螺旋状螺旋状的螺旋状。
Bacteria come in many different shapes. Some of the most common shapes are bacilli (rods), cocci (spheres), and spirilli (spirals). Bacteria can be identified and classified by their shape. Similarities to Eukaryotes
::与Eukaryotes相似Like eukaryotic cells , bacterial cells have:
::与衣体细胞一样,细菌细胞有:-
Cytoplasm
, the fluid inside the cell.
::细胞内流体 -
A plasma or
, which acts as a barrier around the cell.
::等离子体或,作为细胞周围的屏障。 -
, in which
are put together.
::中,它们被组合在一起。 -
. By contrast though, bacterial DNA is contained in a large, circular strand. This single
is located in a region of the cell called the
nucleoid
. The nucleoid is not an
, but a region within the cytoplasm. Many bacteria also have additional small rings of DNA known as
plasmids
.
::。相反,细菌DNA则包含在大型圆形链条中。这一链条位于细胞中一个叫做核素的区域。核素不是细胞内的一个区域,而是细胞内的一个区域。许多细菌还增加了一个称为颗粒的小型DNA环。
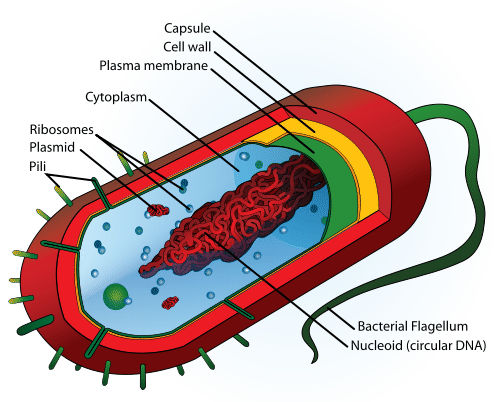
The features of a bacterial cell are pictured below ( Figure ).
::细菌细胞的特征图示如下(图)。The structure of a bacterial cell is distinctive from a eukaryotic cell because of features such as an outer cell wall, the circular DNA of the nucleoid, and the lack of membrane-bound organelles. Unique Features
::独特特点Bacteria lack many of the structures that eukaryotic cells contain. For example, they don't have a . They also lack membrane-bound organelles, such as or . The DNA of a bacterial cell is also different from a eukaryotic cell. Bacterial DNA is contained in one circular chromosome, located in the cytoplasm. Eukaryotes have several linear chromosomes. Bacteria also have two additional unique features: a cell wall and flagella . Some bacteria also have a capsule outside the cell wall.
::细菌缺乏许多包含在单体细胞结构中的结构。 例如, 它们没有 。 它们也缺少诸如 或 。 细菌细胞的DNA也不同于 单体细胞。 细菌DNA包含在一个圆形染色体中, 位于细胞图拉斯姆。 Eukaryotes 有几种线性染色体。 细菌还有另外两种独特的特征: 细胞墙和旗状体。 有些细菌在细胞墙外也有胶囊 。The Cell Wall
::牢房墙墙Bacteria are surrounded by a cell wall consisting of peptidoglycan . This complex molecule consists of sugars and amino acids . The cell wall is important for protecting bacteria. The cell wall is so important that some antibiotics , such as penicillin , kill bacteria by preventing the cell wall from forming.
::细菌环绕在由peptidoglycan组成的细胞墙上。 这个复杂的分子由糖和氨基酸组成。 细胞墙对保护细菌非常重要。 细胞墙非常重要, 以至于一些抗生素, 如青霉素, 通过防止细胞墙形成而杀死细菌。Some bacteria depend on a host organism for energy and nutrients . These bacteria are known as parasites . If the host starts attacking the parasitic bacteria, the bacteria release a layer of slime that surrounds the cell wall. This slime offers an extra layer of protection.
::有些细菌的能量和养分依赖宿主有机体。这些细菌被称为寄生虫。如果宿主开始攻击寄生虫细菌,细菌就会释放一层粘液,在细胞墙周围。这种粘液提供了额外的保护层。Flagella
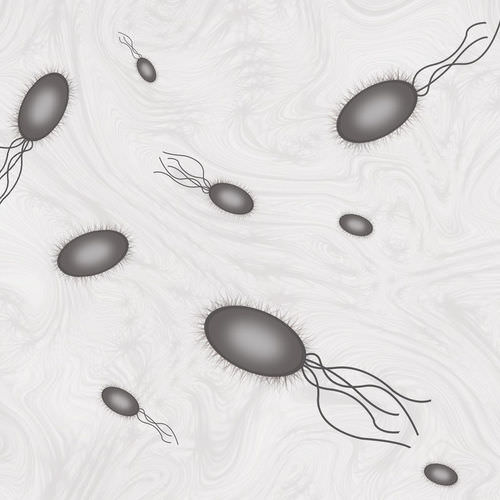
::国旗Some bacteria also have tail-like structures called flagella ( Figure ). Flagella help bacteria move. As the flagella rotate, they spin the bacteria and propel them forward. It is often said the flagella looks like a tiny whip, propelling the bacteria forward. Though some eukaryotic cells do have a flagella, a flagella in eukaryotes is rare.
::有些细菌也有尾部相似的结构,叫做旗子(Figure ) 。 旗子帮助细菌移动。 当旗子旋转时,它们会旋转细菌,并把它们推向前进。 人们常说,旗子看起来像小鞭子,将细菌推向前进。 尽管有些乌卡利细胞确实有旗子,但乌卡利奥特的旗子却很少。The flagella facilitate movement in bacteria. Bacteria may have one, two, or many flagella—or none at all. Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要-
Bacteria can be classified by their shape, including bacilli (rods), cocci (spheres), and spirilli (spirals)
::细菌可按其形状分类,包括bacilli(阴茎)、coccci(球形)和spirilli(螺旋) -
Bacteria are like eukaryotic cells in that they have cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a plasma membrane.
::细菌就像衣原体细胞, 因为它们有细胞托盘、血清和血浆膜。 -
Features that distinguish a bacterial cell from a eukaryotic cell include the circular DNA of the nucleoid, the lack of membrane-bound organelles, the cell wall of peptidoglycan, and flagella.
::将细菌细胞与尤卡利细胞区分开来的特点包括核素的圆形DNA、缺乏受膜环绕的有机物、小动物的细胞墙和旗状动物。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the following questions.
::利用以下资源回答下列问题。Explore More I
::探索更多-
Prokaryotic Cells
at
(2:23)
::2:23时的蛋白质细胞
-
What does the word prokaryote mean?
::普罗卡利奥特这个词是什么意思? -
How does bacterial DNA differ from the DNA in eukaryotic cells? What is one explanation for this difference?
::细菌DNA与表情细胞中的DNA有何不同?这种差异的一个解释是什么? -
What is the bacterial capsule? Are all bacterial capsules made of the same material?
::细菌胶囊是什么?所有细菌胶囊都是由同一材料制成的吗? -
How does the movement of bacterial flagella differ from the movement of eukaryotic flagella?
::细菌旗子的移动与表层旗子的移动有何不同?
Review
::回顾-
How are bacteria classified?
::细菌如何分类? -
How are bacterial cells like your cells?
::细菌细胞如何 像你的细胞一样? -
How are bacterial cells different from your cells?
::细菌细胞与你的细胞有什么不同? -
Describe the bacterial flagella.
::描述细菌国旗
-
Bacilli
are rod-shaped.