5.4 细菌
章节大纲
-
How can bacteria reproduce so rapidly?
::细菌怎么能这么快的繁殖呢?Bacteria can divide very rapidly. This image is of a growing colony of E. coli bacteria. In the right environment, a single E. coli can divide to form a colony of hundreds of bacteria in just a few hours.
::细菌可以快速分裂。 这张图显示,在正确的环境中,单种大肠杆菌可以在几个小时内分裂成数百种细菌的聚居区。Bacteria Reproduction
::细菌生殖Bacteria, being single-celled prokaryotic organisms , do not have a male or female version. Bacteria reproduce asexually. In asexual reproduction , the "parent" produces a genetically identical copy of itself.
::细菌是单一细胞的孕育生物,没有男性或女性的版本。细菌是性繁殖的。在性生殖中,“父母”产生基因相同的自我复制。Binary Fission
::二进制纤维Bacteria reproduce through a process called binary fission . During binary fission, the chromosome copies itself, forming two genetically identical copies. Then, the cell enlarges and divides into two new daughter cells . The two daughter cells are identical to the parent cell . Binary fission can happen very rapidly. Some species of bacteria can double their in less than ten minutes! This process makes it possible for a tremendous bacterial colony to start from a single cell.
::细菌通过一个叫做二进制裂变的过程繁殖。 在二进制裂变期间, 染色体复制了它本身, 形成两个基因相同的副本。 然后, 细胞扩大并分成两个新的女儿细胞。 两个女儿细胞与母细胞完全相同 。 二进制裂变可以很快发生。 一些细菌可以在不到10分钟内翻倍 ! 这个过程使得一个巨大的细菌细胞从一个细胞开始成为可能 。Exchanging DNA
::交换DNAAre there male and female bacteria? Of course the answer is no. So, sexual reproduction does not occur in bacteria. But not all new bacteria are clones . This is because bacteria can acquire new . This process occurs in three different ways:
::是否有男性和女性细菌?当然答案是否定的。因此,性生殖不会在细菌中发生。但并非所有新的细菌都是克隆的。这是因为细菌可以获得新的。这一过程以三种不同的方式发生:-
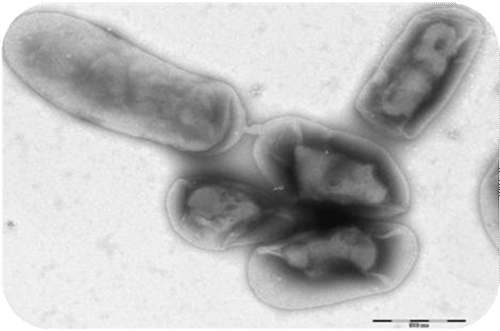
Conjugation
: In conjugation, DNA passes through an extension on the surface of one bacterium and travels to another bacterium (
Figure
). Bacteria essential exchange DNA via conjugation.
::结合:在结合过程中,DNA在一种细菌的表面通过延伸,然后到另一种细菌(图)。 -
Transformation
: In transformation, bacteria pick up pieces of DNA from their environment.
::转化:在转化中,细菌从环境中提取了DNA碎片。 -
Transduction
: In transduction,
that infect bacteria carry DNA from one bacterium to another.
::转导:在转导中,感染细菌的细菌将DNA从一个细菌传到另一个细菌。
Bacteria can exchange small segments of DNA through conjugation. Notice two bacterial cells are attached by a short extension. DNA can be exchanged through this extension.
::细菌可以通过交配交换少量的DNA。注意两个细菌细胞通过短暂的延伸附着。DNA可以通过这一延伸交换。Summary
::摘要-
Bacteria reproduce by binary fission, resulting in two daughter cells identical to the parent cell.
::细菌通过二进制裂变繁殖,产生两个与母细胞相同的女儿细胞。 -
Bacteria can exchange DNA through the processes of conjugation, transformation, or transduction.
::细菌可以通过交融、转化或移植过程交换DNA。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
Asexual Reproduction
at
(1:03)
::性生殖(1:03)
-
There are approximately 7 billion humans on the planet. How long would it take some bacteria to make 7 billion copies of themselves?
::地球上大约有70亿人。 需要多久,一些细菌才能制造出70亿的复制品?
Review
::回顾-
Describe how bacteria reproduce?
::描述细菌是如何繁殖的? -
How do bacteria exchange DNA?
::细菌如何交换DNA? -
What is binary fission?
::二进制裂变是什么? -
What is transformation involving bacteria?
::什么是涉及细菌的转变?
-
Conjugation
: In conjugation, DNA passes through an extension on the surface of one bacterium and travels to another bacterium (
Figure
). Bacteria essential exchange DNA via conjugation.