7.2 工厂演变
章节大纲
-
Where did plants come from?
::植物从哪里来?Plants have not always been around on land. For a long time, life was confined to water. The first plants evolved from green that looked somewhat like the Chara pictured above.
::植物并非总是在陆地上生长。 长期以来,生命被局限在水中。 第一批植物从绿色演变而来,看起来有点像上面所描绘的夏拉。Plants' Adaptations for Life on Land
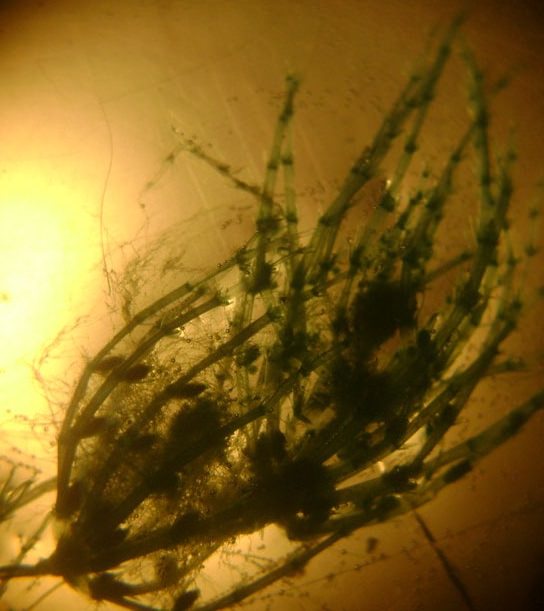
::植物适应陆上生命The first photosynthetic organisms were bacteria that lived in the water. So, where did plants come from? Evidence shows that plants evolved from freshwater green algae, a protist ( Figure ). The similarities between green algae and plants is one piece of evidence. They both have cellulose in their cell walls , and they share many of the same chemicals that give them color. So what separates green algae from green plants?
::第一种光合生物是生活在水中的细菌。 所以, 植物从哪里来? 证据表明, 植物从淡水绿藻演变而来, 一种原生植物( Figure ) 。 绿藻和植物之间的相似性是一种证据。 它们都有细胞壁上的纤维素, 并分享许多给它们颜色的化学物质。 那么, 绿色藻和绿色植物有什么区别呢?The ancestor of plants is green algae. This picture shows a close up of algae on the beach.
::植物的祖先是绿藻类,这张照片显示海滩上有近距离的藻类。There are four main ways that plants adapted to life on land and, as a result, became different from algae:
::植物有四种主要方式适应陆地上的生活,因此与藻类不同:-
In plants, the
embryo
develops inside of the female plant after
. Algae do not keep the embryo inside of themselves but release it into water. This was the first feature to evolve that separated plants from green algae. This is also the only
adaptation
shared by all plants.
::在植物中,胚胎在女性植物中发育。藻类不会将胚胎放在体内,而是放入水中。这是将植物从绿藻中分离出来的第一个进化特征。这也是所有植物共有的唯一适应性。 -
Over time, plants had to evolve from living in water to living on land. In early plants, a waxy layer called a
cuticle
evolved to help seal water in the plant and prevent water loss. However, the cuticle also prevents gases from entering and leaving the plant easily. Recall that the exchange of gasses—taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen—occurs during
.
::随着时间的推移,植物必须从生活在水中演变为在陆地上生活。在早期的植物中,一个被称为“切片”的蜡层演变为“切片”,以帮助封闭工厂的水,防止水流失。然而,切割器也防止气体轻易进入和离开工厂。 -
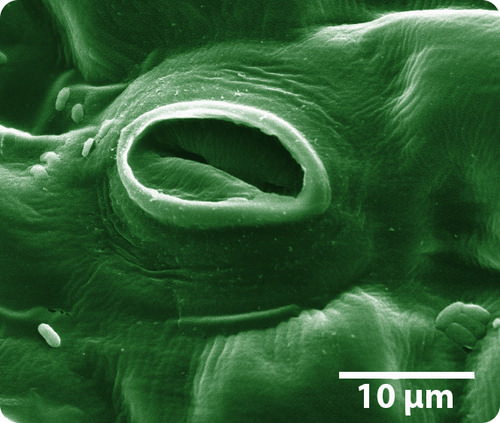
To allow the plant to retain water and exchange gases, small pores (holes) in the leaves called
stomata
also evolved (
Figure
). The stomata can open and close depending on weather conditions. When it's hot and dry, the stomata close to keep water inside of the plant. When the weather cools down, the stomata can open again to let carbon dioxide in and oxygen out.
::为了让植物保留水和交换气体, 树叶上的小孔( 孔) 也进化了( 图表 ) 。 石塔可以根据天气条件打开并关闭。 当温度和干燥时, 石塔可以让水留在植物内。 当天气变冷时, 石塔可以再次打开, 让二氧化碳进入并释放氧气 。 -
A later adaption for life on land was the evolution of
vascular tissue
.
Vascular tissue
is specialized
tissue
that transports water,
nutrients
, and food in plants. In algae, vascular tissue is not necessary since the entire body is in contact with the water, and the water simply enters the algae. But on land, water may only be found deep in the ground. Vascular tissues take water and nutrients from the ground up into the plant, while also taking food down from the leaves into the rest of the plant. The two vascular tissues are
xylem
and
phloem
.
Xylem
is responsible for the transport of water and nutrients from the
roots
to the rest of the plant.
Phloem
carries the sugars made in the leaves to the parts of the plant where they are needed.
::在藻类中,血管组织没有必要,因为整个身体与水接触,而水只是进入藻类。但是在陆地上,水只能在地下深处找到。血管组织将水和养分从地面带入植物,同时将食物从叶子带入植物的其他地方。两个血管组织是Xylm和phloem。Xyem负责将水和养分从根部转移到植物的其他地方。
Stomata are pores in leaves that allow gasses to pass through, but they can be closed to conserve water.
::斯托马塔是叶子中的孔 允许气体通过, 但它们可以关闭 保护水。Summary
::摘要-
Plants evolved from freshwater green algae.
::植物从淡水绿藻演变而来。 -
Plants have evolved several adaptations to life on land, including embryo retention, a cuticle, stomata, and vascular tissue.
::植物对陆地上的生命进行了若干次适应,包括胚胎保留、切片、斯托马塔和血管组织。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
Xylem and Phloem - Transport in Plants
at
(2:27)
::Xylem和Phloem -- -- 设备运输(2:27)
-
Xylem and Phloem - Part 2 - Transpiration - Transport in Plants
at
(3:
55
)
::Xylem和Phloem-第2部分-Tranship-在3:55时的工厂运输(3:55)
-
In what groups of plants do you find xylem and phloem? (Refer to the Plant Classification concept if necessary.)
::您在哪种植物组中发现了xylem和phloem? (必要时参考植物分类概念。 ) -
What does xylem and phloem each transport? In what direction do xylem and phloem transport these substances?
::Xylem 和 phloem 每次运输什么? xyem 和 phloem 运输这些物质的方向是什么 ? -
What is transpirational pull? How is it key to the functioning of xylem?
::什么是反光拉力?它是如何使xyum发挥功能的关键?
Review
::回顾-
How are plants different from green algae? How are they the same?
::植物和绿藻有什么不同? -
What is the purpose of vascular tissue?
::血管组织的目的是什么? -
How do plants prevent excess water loss?
::植物如何防止水的过度流失? -
Compare xylem to phloem.
::将xylem与phloem作比较。 -
What is the role of stomata?
::斯托马塔的作用是什么?
-
In plants, the
embryo
develops inside of the female plant after
. Algae do not keep the embryo inside of themselves but release it into water. This was the first feature to evolve that separated plants from green algae. This is also the only
adaptation
shared by all plants.