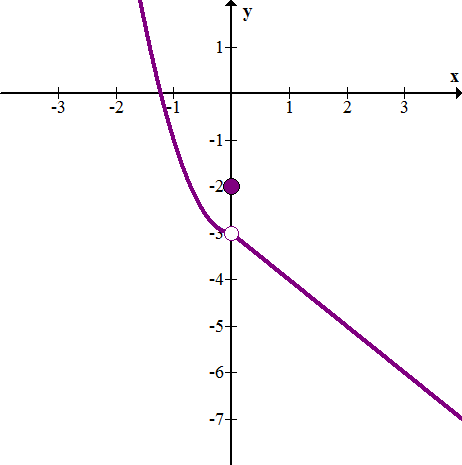14.6 1个确定界限和连续性
章节大纲
-
A one sided limit is exactly what you might expect; the limit of a function as it approaches a specific value from either the right side or the left side. One sided limits help to deal with the issue of a jump discontinuity and the two sides not matching.
::一个侧边限制正是你可能期望的;一个函数在从右侧或左侧接近特定的 x 值时的极限。一个侧边限制有助于处理跳跃不连续和两侧不匹配的问题。Is the following piecewise function continuous?
::以下的片段函数持续吗 ?
:xx) x-2x < 1 - 3 x=1x2 - 4 1 <x
Evaluating One Sided Limits and Continuity
::评价一个可靠限度和连续性A one sided limit can be evaluated either from the left or from the right. Since left and right are not absolute directions, a more precise way of thinking about direction is “from the negative side” or “from the positive side”. The notation for these one sided limits is:
::一个侧边的界限可以从左侧或从右侧评价。由于左右不是绝对方向,对方向的更精确的思考方式是“从负面”或“从正面”。
::limxa-f(x)、limxa+f(x)The negative in the superscript of is not an exponent. Instead it indicates from the negative side . Likewise the positive superscript is not an exponent, it just means from the positive side . When evaluating one sided limits, it does not matter what the function is doing at the actual point or what the function is doing on the other side of the number. Your job is to determine what the height of the function should be using only evidence on one side.
::上标的负值不是一个引号。 它从负面表示。 同样, 正上标不是引号, 它只是从正面表示。 在评价一边的限制时, 函数在实际点做什么 或函数在数字另一边做什么 都无关紧要。 您的工作是确定函数的高度应该只使用一边的证据 。Take the graph below. What are the one sided limits at -5, -1, 3 and 5?
::下图请看下图。5、1、3和5的侧边界限是多少?Each point should have two limits, one from the left and one from the right.
::每点应有两个限制,一个从左边,一个从右边。
::limx=5 - f(x)=1 limx=5+f(x)=2
::limx% 1 - f( x) = 2 limx% 1+f( x) = 3
::立方公尺xx3- f(x)=3 立方公尺x3+f(x)____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
::立方公尺=DNEYou have defined continuity in the past as the ability to draw a function completely without lifting your pencil off of the paper. You can now define a more rigorous definition of continuity.
::过去,你将连续性定义为在不将铅笔从纸上拔下来的情况下完全绘制函数的能力。现在,你可以定义一个更严格的连续性定义。Continuity at a point exists when the left and right sided limits match the function evaluated at that point. In other words, a function is continuous at if:
::当左侧和右侧的极限与当时评价的函数匹配时,一个点的连续性即存在。换句话说,如果:
::limbx_a-f(x)=f(a)=limx_a+f(x)For an entire function to be continuous, the function must be continuous at every single point in an unbroken domain.
::要使整个职能具有连续性,该职能必须在一个不间断的域的每一个点上具有连续性。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked how to confirm the function
is continuous. In order to confirm or deny that the function is continuous, graphical tools are not accurate enough. Sometimes jump discontinuities can be off by such a small amount that the pixels on the display of your calculator will not display a difference. Your calculator will certainly not display removable discontinuities.
::之前曾询问您如何确认 f( x) x- 2x < 1 - 3 x=1x2- 4 > 1 <xis continuation。 为了确认或否认函数是连续的, 图形工具不够准确。 有时跳动不连续会因小量而断开, 以至于您计算器显示的像素不会显示差异 。 您的计算器肯定不会显示可移动的不连续性 。You should note that on the graph, everything to the left of 1 is continuous because it is just a line. Next you should note that everything to the right of 1 is also continuous for the same reason. The only point to check is at . To check continuity, explicitly use the definition and evaluate all three parts to see if they are equal.
::您应该注意, 在图表中, 1 左侧的所有部分都是连续的, 因为它只是一条线。 接下来您应该注意到, 1 右侧的所有部分都是连续的, 出于同样的原因。 唯一要检查的点是 x=1 。 要检查连续性, 请明确使用定义, 并评估所有三个部分, 看看它们是否相等 。-
::立方公尺 -
::f(1) 3 -
::立方公尺x1+f(x)=12-43
Therefore, and the function is continuous at and everywhere else.
::因此, limx%1- f(x) = f(1) =limx%1+f(x) , 函数在 x=1 和其他地方是连续的 。Example 2
::例2Evaluate the one sided limit at 4 from the negative direction numerically .
::从负向数字上对一个侧向限制进行四次评价。
:xx) =x2-7x+12x-4
Remember that evaluating numerically means that you should use a table. When creating the table, only use values that are smaller than 4.
::记住,从数字角度进行评估意味着您应该使用表格。在创建表格时,只使用小于4的数值。3.9 3.99 3.999 0.9 0.99 0.999
::limx%4-(x2-7x+12x-4)=1Example 3
::例3Evaluate the following limits.
::评估以下限度。-
::立方厘米3-( 4x-3) -
::limx%2+(1x-2) -
::limx%1+(x2+2x-3x-1)
Most of the time one sided limits are the same as the corresponding two sided limit. The exceptions are when there are jump discontinuities, which normally only happen with piecewise functions, and infinite discontinuities, which normally only happen with rational functions.
::一个侧边限制的大部分时间与相应的两个侧边限制相同。 例外的情况是跳跃不连续, 通常只有片段函数和无限不连续, 通常只有理性函数发生。-
::立方厘米x3-(4x-3)=43-3-3=12-3=9 -
or
::立方公尺x%2+(1x-2)=DNE或_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The reason why is preferable in this case is because the two sides of the limit disagree. One side goes to negative infinity and the other side goes to positive infinity (see the graph below). If you just indicate DNE then you are losing some perfectly good information about the nature of the function.
::为何此例中偏好于此? 原因是限制的两面意见不一。 一方为负无穷,另一方为正无穷( 见下文图表)。 如果您只是表示 DNE, 那么您就会失去一些关于函数性质的非常好的信息 。-
::立方公尺xx1+(x2+2x-3x- 1) = 立方尺1+(x-1)(x+3)(x-1) = 立方尺1+(x+3) +(x+3)=1+3=4
Example 4
::例4Evaluate the following limits.
::评估以下限度。-
-
::立方公尺x%1-( 2x-1) = 21 - 1= 2_1= 2_1=1
::立方公尺x1 - (2x-1) 立方公尺x1 - (2x-1) 立方公尺x1 - (2x-1) = 21 - 1=2 - 1=1 -
-
-
::3+(2x+2)=2-3+2=2-1=2-1
::3+(2x+2),3+(2x+2),3+(2x+2),=2-3+2=2-2-1 -
-
::limx%2+(x3-8x-2)
Example 5
::例5Is the following function continuous?
::下列功能是否连续?
::f( x) x2 - 1 x13 x1 - x+3 - 1 < xUse the definition of continuity.
::使用连续性的定义。-
::立方公尺x_1- f(x) = (- 1) 2 - 1= 1 - 1= 1=0 -
::f(-1)=3 -
::limx% 1+f( x) @% 1+3=2
so this function is discontinuous at . It is continuous everywhere else.
::limxa-f(x)f(a) limxa+f(x) ,因此此函数在 x1 时不连续。 它在其他任何地方都是连续的 。Summary -
A
one-sided limit
is the limit of a function as it approaches a specific value from either the right side or the left side, helping to deal with jump discontinuities.
::单方限制是函数的限度,因为函数从右侧或左侧接近特定值,有助于处理跳跃不连续问题。 -
One-sided limits can be evaluated from the negative side (notated as
) or from the positive side (notated as
).
::单方限制可从负面(称为limxa-f(x))或正面(称为limxa+f(x))进行评估。 -
Continuity
at a point exists when the left and right-sided limits match the function evaluated at that point, meaning a function is continuous at a if
::当左侧和右侧限制与当时评价的函数相匹配时,就存在连续性,这意味着如果 limxa-a-f(x)=f(a)=limxa+f(x),则函数是连续的。 -
For an entire function to be continuous, the function must be continuous at every single point in an unbroken domain.
::要使整个职能具有连续性,该职能必须在一个不间断的域的每一个点上具有连续性。
Review
::回顾Evaluate the following limits.
::评估以下限度。1.
::1. limx6-6-(3x2-4)2.
::2. limx=0-3x-1x3.
::3. limx=0+3x-1x4.
::4. 立方公尺0+xxxx5.
::5. 立方公尺0-xxxx6.
::6. limx=0+x1+x-1Consider
::考虑 f( x)\%% 2x2 - 1x < 1x 1x=1- x+21 < x7. What is ?
::7. 什么是石灰1-f(x)?8. What is ?
::8. 什么是limx1+f(x)?9. Is continuous at ?
::9. f(x) 在x=1时连续持续吗?Consider
::考虑 g( x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\10. What is ?
::10. 什么是limx2-g(x)?11. What is ?
::11. 什么是limx2+g(x)?12. Is continuous at ?
::12. g(x) 在 x @ @% 2 时连续吗 ?Consider shown in the graph below.
::考虑下图中显示的h(x) 。13. What is ?
::13. 什么是立方公尺0-h(x)?14. What is ?
::14. 什么是limx=0+h(x)?15. Is continuous at ?
::15. h(x) 在x=0时连续持续吗?Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -