9.4 扁虫
章节大纲
-
Do worms have ?
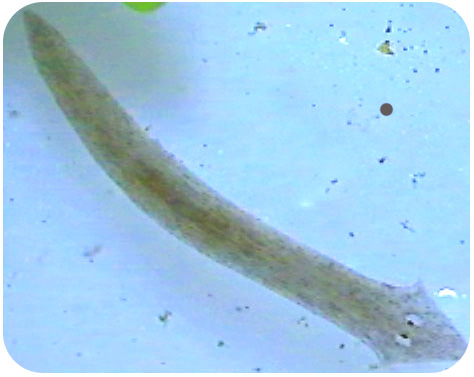
::虫子有吗?You might think that worms can't see. But some worms, such as the above Dugesia flatworm, do have eyespots. These are not exactly like your eyes, however. Eyespots can only detect light in their environment.
::你可能会认为虫子看不见。 但有些虫子,如上面的杜吉西亚扁虫,确实有眼睛水壶。 然而,它们与你的眼睛并不完全一样。 眼睛水壶只能探测到它们环境中的光亮。Flatworms
::虫类The word "worm" is not very scientific. But it is a word that informally describes animals (usually invertebrates) that have long bodies with no arms or legs. (Snakes are vertebrates , so they are not usually described as worms.) Worms are the first significant group of animals with bilateral symmetry , meaning that the right side of their bodies is a mirror of the left.
::“ 寄生虫” 一词不太科学。 但这是一个非正式地描述动物( 通常是无脊椎动物)的词, 这些动物的长身没有胳膊或腿。 (鼻涕虫是脊椎动物, 通常不被称为蠕虫 。 ) 虫是第一组具有双边对称性的重要动物, 这意味着它们身体的右侧是左边的镜像。One type of worm is the flatworm . Worms in the phylum Platyhelminthes are called flatworms because they have flattened bodies. There are more than 18,500 known species of flatworms.
::一种蠕虫是扁虫,植物中的虫子被称为扁虫,因为它们有扁平的体,已知有超过18 500种的扁虫。Features of Flatworms
::扁虫的特点The main characteristics of flatworms ( Figure ) include:
::扁虫的主要特征(图)包括:-
Flatworms have no true body cavity, but they do have bilateral symmetry. Due to the lack of a body cavity, flatworms are known as acoelomates.
::扁虫没有真正的体腔,但它们确实有双边对称性。 由于缺乏体腔,扁虫被称为阳极动物。 -
Flatworms have an incomplete
. This means that the digestive tract has only one opening.
Digestion
takes place in the
gastrovascular cavity
.
::苍蝇不完整。 这意味着消化道只有一个开口。 消化在胃血管洞中发生。 -
Flatworms do not have a
. Instead, they have pores that allow oxygen to enter through their body. Oxygen enters the pores by
.
::扁虫没有。相反,它们有孔孔,允许氧进入它们的身体。氧气进入孔。 -
There are no
in the flatworms. Their
gastrovascular cavity
helps distribute
nutrients
throughout the body.
::扁虫体内没有,它们的胃血管洞穴帮助将营养物质分布在全身。 -
Flatworms have a ladder-like
; two interconnected parallel
nerve
cords run the length of the body.
::直线虫有一个类似梯子的梯子;两条相互连接的平行神经线在身体的长度上运行。 -
Most flatworms have a distinct head region that includes nerve
cells
and sensory
organs
, such as eyespots. The development of a head region, called
cephalization
, evolved at the same time as bilateral symmetry in animals. This process does not occur in
, which evolved prior to flatworms and have
radial symmetry
.
::大多数扁虫有独特的头部区域,包括神经细胞和感官器官,如眼盆;一个头部区域的发展,称为喘气,与动物的双边对称同时演化;这一过程不会发生于在扁虫之前演化并具有射线对称的部位区域。
Marine flatworms can be brightly colored, such as this one from the class Turbellaria. These worms are mostly carnivores or scavengers.
::海洋扁虫的颜色可以亮亮,比如这个来自海龟类的。这些蠕虫大多是食肉动物或拾荒者。Flatworms in the Environment
::环境中的扁虫Flatworms live in a variety of environments. Some species of flatworms are free-living organisms that feed on small organisms and rotting matter. These types of flatworms include marine flatworms and freshwater flatworms, such as Dugesia .
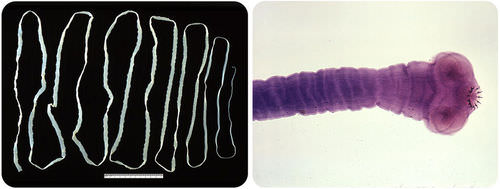
::一些种类的扁虫是自由生物,它们养活小生物体和腐烂物质,这些种类的扁虫包括海洋扁虫和淡水扁虫,如Dugesia。Other types of flatworms are parasitic. That means they live inside another organism, called a host , in order to get the food and energy they need. For example, tapeworms have a head-like area with tiny hooks and suckers (known as the scolex ) that help the worm attach to the intestines of an animal host ( Figure ). There are over 11,000 species of parasitic flatworms.
::其他种类的扁虫是寄生虫。这意味着它们生活在另一个被称作宿主的有机体中,以获得它们所需要的食物和能量。例如,虫有一个头状区域,有小钩子和吸虫(称为螺旋杆 ) , 帮助寄生虫附在动物宿主的肠子上(图 ) 。 有超过11 000种寄生虫。Tapeworms are parasitic flatworms that live in the intestines of their hosts. They can be very long ( left ). Tapeworms attach to the intestinal wall with a head region that has hooks and suckers ( right ). The majority of flatworms are parasites.
::寄生虫是寄生虫,它们生活在宿主的肠道中,可能是很长的(左侧),附在肠壁上的寄生虫,头部有钩子和吸虫(右侧),大部分寄生虫是寄生虫。Summary
::摘要-
Flatworms have no true body cavity and no blood vessels.
::扁虫没有真正的体腔 也没有血管 -
Flatworms can be free-living or parasitic. Tapeworms are parasitic flatworms.
::扁虫可以是自由生存的,也可以是寄生虫,虫是寄生虫。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
Flatworms: The First Hunter
at
(9:54)
::虫:第一猎人(9:54)
-
Why was cephalization important for flatworms? What did this allow them to do effectively?
::为什么气喘化对扁虫很重要?这使他们能有效地做些什么呢? -
How is the nervous system of flatworms different from those of most cnidarians? What does this make them better at than cnidarians?
::扁虫的神经系统与大多数童子军的神经系统有什么不同? 这使他们比童子军的神经系统更好吗? -
What do flatworm eyes sense?
::苍蝇眼睛有什么感觉? -
How do stereo senses help animals survive?
::立体感应如何帮助动物生存? -
What is internal fertilization as opposed to external fertilization? Considering that there is an energetic cost to making gametes, what advantage can internal fertilization have over external fertilization?
::内部肥化与外部肥化相比有什么不同? 考虑到制作调子需要大量成本,内部肥化与外部肥化相比有什么优势?
Review
::回顾-
What is a flatworm?
::什么是扁虫? -
What is cephalization?
::什么是气化? -
How do flatworms transport oxygen and nutrients?
::扁虫如何输送氧气和养分? -
Describe the flatworm nervous system.
::描述扁虫神经系统 -
What is one example of a flatworm?
::扁虫的一个例子是什么?
-
Flatworms have no true body cavity, but they do have bilateral symmetry. Due to the lack of a body cavity, flatworms are known as acoelomates.