2.1 限制的导言
章节大纲
-
Suppose you stand exactly 4 feet from a wall, and begin moving toward the wall by halving the distance remaining with each step. How many steps would it take to actually get to the wall? How far would you walk in the process?
::假设你站在离墙4英尺的地方,开始向墙移动,将每一步所剩距离减半。要实际到达墙要走几步才能真正到达墙上?你走多远?Limits
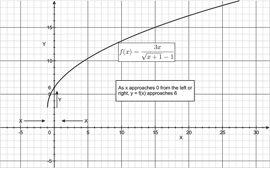
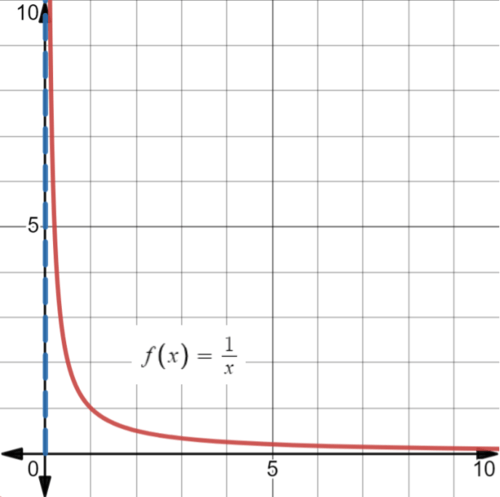
::限制限额Make a conjecture about the value of the function at .
::在 x=0 时对函数 f( x) = 3xx+1 - 1 的值进行猜测。In this problem, the function’s value is to be determined at a specific value of . But, the function is not defined at , it’s value is given by , an indeterminate form. Let’s look at the function numerically to see if we can find out what happens in the vicinity of . The table below shows samples of -values approaching 0 from the left side and from the right side. In both cases, the values of , calculated to at least 5 decimal places, get closer and closer to 6.
::在此问题上,函数的值将按x的具体值确定。 但函数 f( x) = 3xx+1-1 - 1 尚未定义为 x=0 。 函数的值由 00 表示, 一种不确定的形式。 让我们从数字上查看该函数, 看看在 x=0 附近会发生什么。 下表显示左侧和右侧接近 0 的 x 值样本。 在这两种情况下, F( x) 值计算为小数点后至少5位, 接近6位。
::x x-0.01
-0.001
-0.0001
-0.00001
0
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
:fx)
5.984962
5.9985
5.99985
5.999985
Undefined
::未定义6.000015
6.00015
6.0015
6.014963
Another way of answering the question is to graph (shown below). Notice the two horizontal arrows that show -values approaching 0 from the left side and from the right side. In both cases, the values of appear to get closer and closer to 6.
::回答问题的另一种方式是图f(x) (如下所示) 。 注意显示左侧和右侧接近 0 的 X 值的两个水平箭头。 在这两种情况下, f(x) 值似乎接近 6 。The answer to the conjecture was made numerically and graphically. Mathematically, the answer to the conjecture would be to say: the limit of as approaches 0 is 6, a specific value. This is written as .
::以数字和图形方式对猜想作了解答。从数学角度来说,猜想的解答是:F(x)的限值,作为x 接近 0,是 6,是一个特定值。这个值以 limx%03xx+1-1=6 写成。Limit Notation of a Function:
::限制函数的评分:
::limxaf(x) =LThis means that as approaches (or gets very close to) , the function gets very close to the value .
::这意味着,当 x 接近(或非常接近) a 时,函数f(x) 就会非常接近值L。is read as the limit of as approaches is .
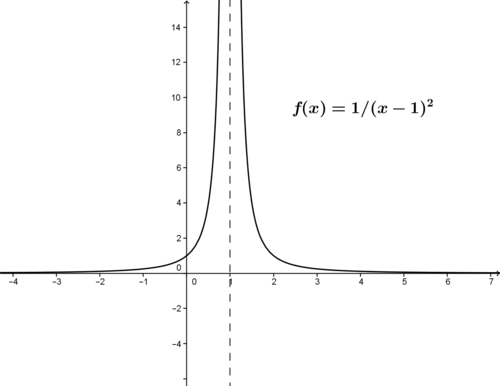
::limxaf(x)=L 被理解为 f(x) 的限值,因为 x ools a 是 L 。Consider the function . Using numerical and graphical methods, let’s determine what happens for the following conditions:
::考虑 F( x) =1( x- 1) 函数。 使用数字和图形方法,让我们确定在下列条件下会发生什么:-
approaches the value 1;
::x 接近值1; -
approaches very large
and very small values
.
::x 接近非常大 (>0) 和非常小的值(<0) 。
To find what happens as approaches the value 1, the functions value is to be determined at a specific value of . The function is not defined at : its value is given by the undefined value . Let’s look at the function numerically and graphically to see if we can find out what happens in the vicinity of . The table below shows samples of -values approaching 1 from the left side and from the right side. In both cases, the values of get increasingly larger as gets closer and closer to 1.
::要找到 x 接近值 1 时发生的情况, 函数值将按 x 的具体值确定。 函数 f( x) =1 (x- 1) 2 在 x= 1 时没有定义 : 函数 f( x) = 1 (x- 1) 的值由未定义的值给出 10 。 让我们从数字和图形角度查看函数, 看看在 x= 1 附近发生的情况 。 下表显示左侧和右侧接近 1 的 x 值样本。 在这两种情况下, f( x) 的值随着 x 越来越接近和接近 1 , f( x) 的值越来越大 。
::x x0.99
0.999
0.9999
0.99999
1.0
1.00001
1.0001
1.001
1.01
:fx)
1E04
::1,2004年1,2004年1E06
::1,2006年1,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第6号1E08
::1,081,0811E10
::1E10 1E10Undefined
::未定义1E10
::1E10 1E101E08
::1,081,0811E06
::1,2006年1,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第1,第6号,第1,第6号1E04
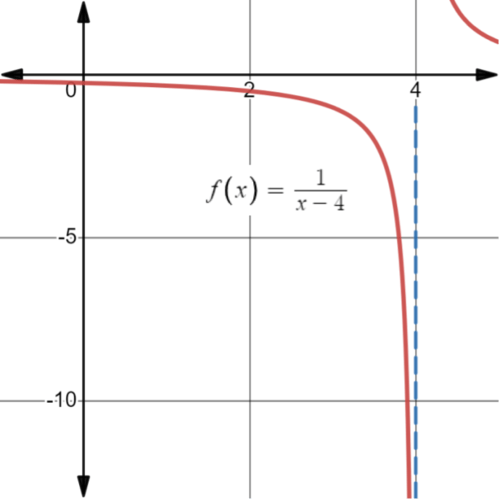
::1,2004年1,2004年The graph below also shows this trend. In fact, can be found to be arbitrarily large by the right selection of close to 1. In this case we can say that as approaches 1 from both sides, gets larger and larger, i.e. approaches positive infinity, . This condition is written in limit notation as: . The limit is not a specific value, but has an undefined value.
::下图也显示了这一趋势。 事实上, f( x) 可以通过正确选择接近 1 的 x 任意而大。 在此情况下, 我们可以说, 随着两侧的 x 接近 1 , f( x) 将变得越来越大, 即 肯定的无穷, 。 此条件以限制符号写成 : limx% 1f( x) =limx11 (x- 1) 2 。 限制不是一个特定值, 但有未定义的值 。Note that the vertical line at , is called a vertical asymptote , and represents the line that approaches from the left and right as approaches 1.
::请注意, x=1 的垂直线被称为垂直小数线,表示 f(x) 向左和向右行的直线,与 x 向1 相近。To find what happens as approaches very large , look at what happens as the values of get larger. Notice that as the values of get larger and larger, the graph gets closer and closer to the -axis. In terms of the function values, we can say that as gets larger and larger, gets closer and closer to 0, a specific value. We say that as approaches infinity, , the limit of the function is 0. This is written: .
::要找到非常大的 xpproaches (>0) 发生的情况, 请看 x 值越大会发生什么。 请注意, 随着 x 的值越大, 图形越接近x 轴。 从函数值来看, 我们可以说, 当 x 越大越接近 0 , f( x) 就会越来越接近 0 , 一个特定值。 我们说, 当 x 接近无穷度, \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ x\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Note that the line is called the horizontal asymptote of the graph, and represents the line that will never quite reach. We can also say that is asymptotic to the line .
::请注意, y=0 线被称为图的水平代表符, 表示 f( x) 将无法达到的线。 我们还可以说 f( x) 对 y=0 线是无符号的 。If we consider the behavior of the function as approaches or the value of get smaller and smaller, we see the same result as above. The limit of the function as approaches is also 0, a specific value. This is written: . Notice that the function has the same asymptote: .
::如果我们将函数的行为视为 x 方针 {} 或 x 的值变小或变小, 我们就会看到与以上相同的结果。 x 方针 {} 的函数限制也是 0, 一个特定值。 写成 : limx\\ ff( x) =limx} 1 (x- 1) 2=0. 。 注意该函数具有相同的同值 : y=0 。Because we are considering the limit of a function as approaches and , we call this being focused on the end behavior of the function .
::因为我们正在考虑一个函数的极限作为 x 接近 和\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ x \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\ \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\One-sided Limits
::片面限制Above, we looked at the value of as approached a specific value from the left and from the right. And in each example the value of the limit was the same from either direction.
::上面,我们查看了 f( x) 的值, 因为 x 从左向右接近特定值 。 在每一个例子中, 限制值从两个方向都是一样的 。A limit that is evaluated as approaches the value from one side only, left or right, is called a one-sided limit , and is represented by the following notation:
::当 x 仅从左侧或右侧接近 x=a 值时被评价的限值,称为单向限制,以下列符号表示:One-sided Limit Notation:
::片面限制符号 :
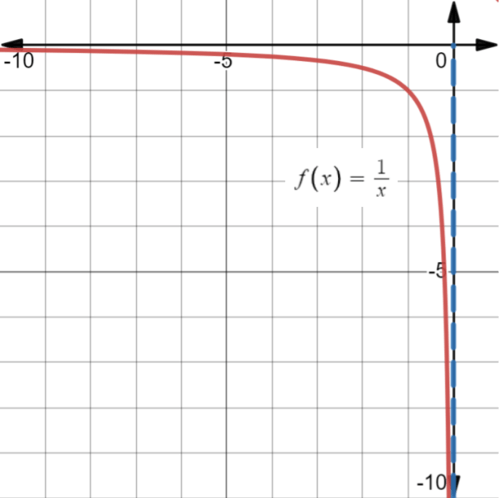
::左侧:limxa-f(x)=L-右侧:limxa+f(x)=L+Apply the definition of to identify the limit of the function as approaches 0. The function graph is shown below.
::应用定义来识别函数 f(x)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\F\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\As approaches 0 from the left, approaches -1: . On the other hand, as approaches 0 from the right, approaches 1: .
::作为左向的 x 接近 0, f(x) 方法 - 1: limx=0 x x 1. 。 另一方面, 作为 x 向右的 接近 0, f(x) 方法1: limx=1 : limx=0 xx=1 。Note that for this function, the value is not defined.
::请注意,对于此函数,没有定义f(0)值。Existence of Limits
::限制的存在The relationship between one-sided limits and the limit of a function (the two-sided limit) is whether or not a limit exists.
::片面限制与函数限制(双面限制)之间的关系是是否存在限制。In order for the limit of a function to exist, both of the one-sided limits must exist at and must have the same value.
::要使函数的限值L存在,单方的限值必须在x0时存在,并且必须具有相同的价值。Mathematically: if and only if and . T he limit is called the two-sided limit . If , we say the does not exist .
::数学学说: limxxxxx0f(x) =L, 如果且只有在 limxxxxx0- f(x) =L 和 limxxxxx0+f(x) =L 的情况下, limxxxxxxx0f(x) =L。 限制值=L 被称为双向限制。 如果 L\\\L+, 则我们说 limx=af(x) 不存在 。Note that in the problem above that asks for the limit of as approaches 0, the limit does not exist. Since the two one-sided limits are not the same, the limit of the function, the two-sided limit , does not exist.
::请注意,在要求将 f(x) xxx1x>0_1x <0作为x locess 0 的上限的上述问题中,该上限并不存在。 由于两个单向限制不同, 函数的上限, 双向限制%0xx, 不存在 。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked how many steps it will take i f you start 4 ft from a wall and halve the distance to the wall with each step. You were also asked how far you will walk before you actually touch the wall.
::早些时候,有人问到,如果你从墙上开始四英尺,每一步将距离墙的距离减半,你将走几步?有人问,你实际上触到墙之前,你将走多远?Logically, we know that there is only a total distance of 4 feet between you and the wall, so no matter how you break it up, you cannot walk more than 4 feet. However, the actual distance you cover, and the number of steps it would take, cannot truly be defined since there would always be of the remaining distance left. Technically speaking, you could continue the process forever without actually touching the wall! Of course, in practice, your ability to only move of the remaining distance is limited by your size, muscle control and measurement accuracy, so you would touch the wall before very many steps were actually taken.
::从逻辑上讲,我们知道,你与隔离墙之间只有四英尺的总距离,所以无论你如何分解,你都无法走超过四英尺。然而,你所覆盖的实际距离以及它要采取的步骤,由于剩下的距离中总是有12个,因此无法真正确定。技术上讲,你可以永远地继续这一进程,而不必实际触动墙。当然,实际上,你仅移动其余距离中的12个的能力受你的大小、肌肉控制和测量精确度的限制,所以,在采取许多步骤之前,你可以触摸墙。Mathematically: where is the number of steps, and we are looking at the end behavior.
::数学: limn( 4 - 42n) = 4, 其中 n 是步骤的数量, 我们正在查看最终的行为 。In other words: “As the remaining distance gets closer and closer to 0, the total distance approaches 4”
::换句话说:“随着剩下的距离越来越接近零,总距离接近4”For the remaining examples, describe each limit and sketch a graph of each function with the given properties. Note the graph solutions are just one example of a solution and there may be other valid answers.
::对于其余示例, 请描述每个限制并用给定属性绘制每个函数的图形。 请注意, 图形解决方案只是解决方案的一个例子, 可能还有其他有效的答案 。Example 2
::例2
::limxf(x)=2This reads: “The limit of as approaches infinity is 2 .” In other words, as gets very big, or gets infinitely close to 2.
::其内容如下:“f(x)作为x方针的无限度的限度为2。” 换言之,当x变得非常大,f(x)或y变得无限接近2时。Example 3
::例3
::limxf(x)=0This reads: “The limit of as approaches negative infinity is 0 .” In other words, as gets massively negative, or gets infinitely close to 0.
::其内容如下:“f(x)作为x接近负无限度的f(x)的限制是0。” 换句话说,当x大负时,f(x)或y无限接近0。Example 4
::例4
::立方公尺x%0+f(x){______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________This reads: “The limit of as approaches zero from the positive direction is infinite.” In other words, as approaches from the right side of the graph, and gets infinitely close to zero, or grows infinitely large.
::其内容如下:“f(x)的极限是,从正向的x接近零是无限的。” 换句话说,当x从图的右侧接近时,F(x)或y的极限无限接近零,f(x)或无限大。Example 5
::例5
::立方公尺x%4f(x) {_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________This reads: “The limit of as approaches 4 is negative infinity.” In other words, as gets infinitely close to 4, or gets infinitely negative.
::其内容如下:“f(x)作为x方针4的限制是负无限性。” 换句话说,当x无限接近4,f(x)或y变得无限负时。Review
::回顾-
Define the terms horizontal asymptote and vertical asymptote.
::定义水平单点和垂直单点。 -
Explain the difference between
and
::解释 limx6f( x) 和 limxf( x) 6 之间的区别 -
Explain what
means
::解释 limxf( x)=200 意味着什么 -
Explain what
means
::解释 limx175f( x) =175 是什么意思
For #5-8, evaluate the limits, if they exist. If a limit does not exist, explain why.
::对于# 5-8, 如果存在限制, 请对限制进行评估。 如果没有限制, 请解释原因 。-
::立方公尺3t2 - 7t- 8 -
::limt3 -
::limt( t2- t4) -
::limxx+x2+2x -
Find the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of the following function:
::查找以下函数的水平和垂直单位数 : h( g) =5g2 - 7g+9g2 - 2g- 3
For #10-11, .
::在 # 10- 11, f(x) =x2 - x-6x2 - 2x-8.-
Find the horizontal and vertical asymptotes. Determine the behavior of
near the vertical asymptotes.
::查找水平和垂直的静态。 确定在垂直静态附近 f 的行为 。 -
Find the roots,
intercept and “holes” in the graph.
::在图中找到根、截取和“洞”。
For #12-14, determine for the given values of .
::对于#12-14, 确定 n 的给定值的limt1tn。-
::n>0 -
::n<0 -
::n=0
For #15-17, let be polynomials. Find given the indicated information.
::对于#15-17, 让 G&H 成为多数值。 找到 limxG( x)H( x) , 如果有指定信息的话 。-
The degree of
is less than the degree of
::G级比H级小 -
The degree of
is greater than the degree of
::G级高于H级 -
The degree of
is the same as the degree of
::G级与H级相同 -
A pool contains 8000 L of water. An additive that contains 30 g of salt per liter of water is added to the pool at a rate of 25 L per minute.
-
Show that the concentration of salt after
minutes in grams per liter is:
::显示以每升以克计的 t 分钟后盐的浓度为: C( t) = (t) 30g=258800l+25( t)l -
What happens to the concentration as time increases to
? Physically, why does this make sense?
::随着时间的增加,浓度会怎样?从身体上看,这为什么有意义呢?
::水池含8000升水。每升水中含有30克盐的添加剂被添加到水池中,每分钟25升。显示每升水的盐浓度为:C(t)=(t)30g25800l+25(t)l。随着时间的增加,浓度会怎样?从物理角度讲,这为什么有意义? -
Show that the concentration of salt after
minutes in grams per liter is:
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
approaches the value 1;