4.5 第二次衍生试验
章节大纲
-
The derivative of a function curve at a point is the mathematical analogy to our visually determining if the function is increasing or decreasing at the point. But if you look at a function curve, you can also determine visually whether the tangent lines are getting more vertical or more horizontal over an interval. The visual recognition of this rate of change of the slope is a measure of curvature (or concavity), which in turn can tell you specifically what type of extrema are present. The mathematical representation of the rate of change of the slope is the second derivative, which is used to identify types of curvature. What is the relationship between the second derivative and the concavity ?
::函数曲线在某个点的衍生物是数学类比, 与我们直观地确定函数在点上是增加还是减少。 但是, 如果您查看函数曲线, 您也可以直观地确定正切线在一个间隔内是垂直还是水平增加。 对斜度的这一变化率的视觉识别是一种曲线度( 或凝固度) , 这反过来又可以具体地告诉你存在什么类型的外体。 斜度变化率的数学表示是第二个衍生物, 用来确定曲线的类型。 第二个衍生物和二次曲线之间的关系是什么?Concavity and the Second Derivative Test
::洞穴和第二次衍生物试验There is a property about the shape, or curvature, of a graph called concavity, which will help identify precisely the intervals where a function is either increasing or decreasing, where the maxima and minima are located, and also help to sketch the graph. Concavity is the direction in which the curve opens.
::图形的形状或曲率都有一个属性,称为“精密度”,它将有助于精确地确定函数增减的间隔、最大值和最小值的位置,并有助于绘制图形。“清晰度”是曲线打开的方向。The type of concavity on a curve is defined as follows:
::曲线上的大陆体类型定义如下:A function is said to be concave upward on contained in the domain of if is an increasing function on and concave downward on if is a decreasing function on .
::如果 f 是在[a,b] 上增加功能,而f 是在[a,b] 上下减少功能,则 f 的函数 f 上下调到[a,b] 上下调。Here is a function that illustrates these properties.
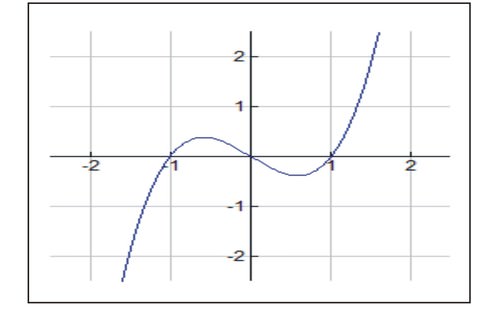
::这里有一个函数来显示这些属性 。Consider the function :
::考虑函数 f( x) =x3 - x :
Since , the function has zeros at .
::自 f( x) =x3 -x=x( x2 - 1) 后,函数在 x% 1,0 时为零 。Also, , tells us the location of extrema: a relative maximum at and a relative minimum at .
::另外,f(x)=0=3x2-1,告诉我们extrema的位置:在x33时的相对最大值和在x=33时的相对最低值。Note that the graph appears to be concave down for all intervals in and concave up for all intervals in . Where do you think the concavity of the graph changed from concave down to concave up? If you answered at you would be correct.
::请注意, 图形似乎在( , 0) 中的所有间隔中都为混凝土, 在所有间隔中( 0, ) 中为混凝土 。 您认为图的精密性从下面的混凝土到上面的混凝土在哪里? 如果您在 x=0 中回答, 您将会正确 。In general, we wish to identify not only the extrema of a function but also the points where the graph changes concavity. A point on a graph of a function where the concavity changes is called an inflection point .
::一般来说,我们不仅要确定函数的极限,还要确定图形改变洞察力的点。在函数f 的图形上,一个点,即混凝土变化被称作混凝土点。The problem above had only one inflection point. But we can easily come up with examples of functions where there are more than one points of inflection.
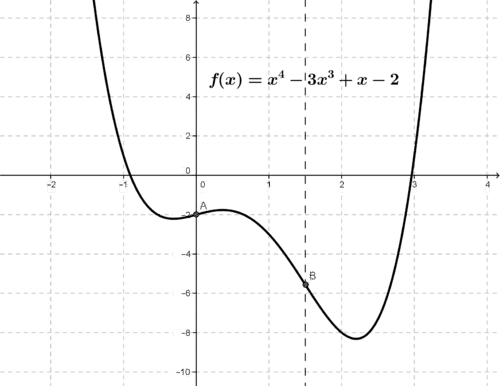
::上述问题只有一个思考点。 但我们可以很容易地提出功能的例子,其中存在不止一个思考点。Consider the function shown in the figure.
::考虑下图中显示的 F( x) =x4- 3x3+x-2 函数 。We can see that the graph has two relative minimums, one relative maximum, and two inflection points (at and ).
::我们可以看到,该图有两个相对最低点,一个相对最高点,两个反射点(A和B)。In general we can use the following test for concavity :
::一般而言,我们可以使用以下的测深标准:Suppose that is continuous on and that is some open interval in the domain of .
::假设f在[a,b]上是连续的,而我是f领域一些开放的间隔。-
If
for all
, then the graph of
is concave upward on
::如果 f( x) >0 全部 x% I, 那么 f 的图形会向上粘结到 I 上 -
If
for all
, then the graph of
is concave downward on
::如果 f( x) <0 全部 x% I, 那么 f 的图形在 I 上向下粘结
Let’s apply the concavity test to the function :
::让我们对函数 f( x) =x4- 3x3+x-2 应用精密度测试 :The second derivative is, , and the concavity is given in the table.
::第二个衍生物是, f(x) = 12x2-18x= 6x(2x-3),表中给出了混凝土。Interval or Point
::中间点或点Concavity
::混凝度[-1,0)
>0
Upward
::上上上0
=0
Change=Inflection
::更改=插入(0, 1.5)
<0
Downward
::下下下1.5
=0
Change=Inflection
::更改=插入(1.5, 3]
>0
Upward
::上上上Can you see how the concavity gives a clue to the presence of a relative maximum, or minimum, or inflection point? A consequence of the concavity test is the following test to identify where we have extrema and inflection points of .
::您能看到混凝土如何给人一个提示 相对最大或最小, 或混凝土点的存在吗? 混凝土测试的结果是 下个测试 来确定我们在哪里有 f 的 extrema 和 interf 的 extrema 和 interf 点 。The Second Derivative Test for Extrema is as follows:
::第二次极端现象衍生试验如下:Suppose that is a continuous function near and that is a critical value of Then
::假设f是接近c的连续函数,c是f的关键价值-
If
, then
has a relative maximum at
.
::如果 f(c) < 0, 那么f 在 x=c 时具有相对上限 。 -
If
, then
has a relative minimum at
.
::如果 f(c) >0, 那么f 在 x=c 时具有相对最小值 。 -
If
, then the test is inconclusive and
may be a point of inflection.
::如果 f(c) =0, 则试验没有结果, x=c 可能是反射点 。
Does the test work for our previous example of ?
::测试是否适用于 f( x) =x4- 3x3+x-2 的实例 ?We can find the critical values where , and use them to evaluate . The results are shown below.
::我们可以在 fä( x) =4x3- 9x2+1=0 处找到关键值, 并用这些值来评估 f( c) 。 结果如下:Critical Point
::关键点Conclusion
::结论 结论 结论 结论 结论
::x0.312>0
Relative Minimum
::相对最低
::x=0.364x=0.364<0
Relative Maximum
::相对最大
::x=2.198x=2.198>0
Relative Minimum
::相对最低The tests works on this function.
::测试在这个函数上起作用。Remember, however, that the Second Derivative Test cautions us that if , the test is inconclusive, because may be an inflection point. Recall that this was the case for .
::但是,请记住,第二次衍生试验告诫我们,如果f(c)=0,该试验是没有结果的,因为c可能是一个反射点。回顾f(x)=x3的情况就是这样。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked what relationship between the curvature of a function and the second derivative is. The curvature of a function graph can be described by its concavity (up or down), which in turn can be determined at each point by the second derivative (if it is defined). Because critical points can determine the locations of relative maxima or minima without identifying which, knowing the type of curvature from the second derivative can identify specifically whether we have a minimum or a maximum, or neither.
::早些时候,有人问您函数的曲线与第二个衍生物之间的关系是什么。函数图的曲线可以用其精密度(上下)来描述,而第二个衍生物(如果定义了的话)在每个点都可以确定。 因为临界点可以确定相对最大值或微型值的位置,而不知道第二个衍生物的曲线类型可以具体确定我们是否有最小值或最大值,或者两者都没有。Example 2
::例2Consider the function . Find the critical points, and determine whether they are relative maximums or relative minimums by using the Second Derivative Test.
::考虑函数 f( x) =x+4x。 查找关键点, 并通过使用第二次衍生测试确定它们是否为相对最大值或相对最低值。The first thing to notice is that the function is not defined at .
::首先要注意的是,该函数在 x=0 时没有定义。To find the critical points we look for points where .
::为了找到关键点,我们寻找的点c, 其中f'(c)=0。means there are critical points at , and .
::f_(x) = 1- 4x2= 0 表示 x_ 2 和 x= 2 有临界点 。Since and the curve is concave downward with a relative maximum; , and the curve is concave upward with a relative minimum.
::自 f(x) = 8x3:f(-2) 1 和曲线下向,以相对最大值; f(2) =1 和曲线上向,以相对最低值。The function graph is as shown.
::函数图显示如下 。Review
::回顾-
Find all extrema using the Second Derivative Test:
.
::使用第二次衍生测试查找全部extrema: f(x)=x24+4x。 -
Consider
, with
.
-
Determine
and
so that
is a critical value of the function
.
::确定 a 和 b, 使 x=1 是函数 f 的关键值 。 -
Is the point (1, 3) a maximum, a minimum or neither?
::点(1, 3)是最高、 最低还是两者兼而有之?
::考虑 f( x) =x2+ax+b, 加上 f(1)=3. 确定 a 和 b, 使 x=1 是函数的临界值 f。 点(1, 3) 是最大值, 最低值还是两者都不是? -
Determine
and
so that
is a critical value of the function
.
For #3-6, find all extrema and inflection points. Sketch the graph.
::为#3-6, 找到所有 extrema 和 穿透点。 绘制图表 。-
:xx)=x3+x2
-
:xx)=x2+3x
-
:xx) =x3 - 12x
-
:x)\\\\\}14x4+2x2
-
Use your graphing calculator to examine the graph of
(Hint: you will need to change the
range in the viewing window)
-
Discuss the concavity of the graph in the interval
.
::以间隔( 0, 12) 讨论图的精密度( 0, 12) 。 -
Use your calculator to find the minimum value of the function in the interval.
::使用您的计算器在间隔中找到函数的最小值。
::使用您的图形计算器检查 f( x) =x( x- 1) 3 的图形( 提示 : 您需要改变查看窗口中的 y 范围) 讨论间隔( 0, 12) 中的图形的精密性 。 使用您的计算器在间隔中找到函数的最小值 。 -
Discuss the concavity of the graph in the interval
.
-
True or False:
has a relative minimum at
and a relative maximum at
?
::真实或假 : f( x) =x4+4x3 的相对最小值为 x% 2 , 相对最大值为 x=0 ? -
If possible, provide an example of a non-polynomial function that has exactly one relative minimum.
::如果可能的话,请举例说明一种非政体功能,该功能的相对最小值完全相同。 -
If possible, provide an example of a non-polynomial function that is concave downward everywhere in its domain.
::如果可能的话,请提供一个例子,说明在其领域向下倾斜的非政体功能。 -
Let
be a continuous function and let
be a closed interval over which
is defined. If we know that
is positive over the interval
, does this tell us anything about the concavity of
over
?
::Letf(x) 是一个连续函数, 让 [a, b] 成为定义f(x) 的封闭间隔。 如果我们知道 f(x) 是正值, 在间隔 [a, b] 中, 这是否告诉我们f(x) 相对于 [a, b] 的默认度 ? -
Is the function
concave up or down over the interval [10, 11]?
::函数 f( x) =x4 是否在间隔[ 10、 11] 内上下? -
Is the function
concave up or down over the interval
?
::函数 f(x) (x) 的 conccave 是在间隔[%2,3]2) 内上下吗 ? -
If the first derivative of
is
, is
concave up or down over the interval
?
::如果 f( x) 的第一个衍生物是 f}( x) = 20xsin ( x) , f (x) 的 concev 是在 [ 0, 12] 间隔内向上或向下 ? -
What is an inflection point of the function
?
::函数 f( x) =4x3+3x2+2x+1 的反射点是什么 ? -
Use the second derivative test to classify the extrema of the function
over the interval
.
::使用第二次衍生物测试来分类间隔( 12, 2) f( x) =x3+x2- 5ln( x) 的函数的extrema 。 -
Use the second derivative test to classify the extrema of the function
over the interval
.
::使用第二次衍生物测试对函数 f( x) = 5sin {( x) 间隔( 4, 3 4) 的 extrema 进行分类 。 -
Use the second derivative test to classify the extrema of the function
over the interval
::使用第二次衍生物测试对函数 f( x) = ln ( 2x+x2) 的秒数( - 2,0) 进行分类。 -
Use the second derivative test to classify the extrema of the function
over the interval (1, 5).
::使用第二次衍生物测试对函数 f(x) =x4 的外形在间隔(1, 5) 范围内进行分类。 -
Can we use the second derivative test to check if
is a maximum or a minimum of the function
?
::我们能否使用第二次衍生物测试来检查 x=0 是函数 f( x) =x10+25 的最大值还是最小值 ?
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
If
for all
, then the graph of
is concave upward on