5.8 缺陷综合体:中值理论
章节大纲
-
The definite integral can be used to determine the net area under a function curve. The Mean Value Theorem for definite integrals just says that there is always a rectangle with the same area and width, and that the top of the rectangle intersects the function. Can you give an explanation for why the height of the rectangle (the intersection with the function curve) is considered (defined to be) the average value of the definite integral?
::确定整体值可以用来确定函数曲线下的网区域。确定整体体的平均值理论只是说,总是有一个与相同区域和宽度的矩形,矩形的顶部交叉函数。您能否解释为什么矩形的高度(与函数曲线的交叉点)被认为是(被界定为)确定整体体的平均值?Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals
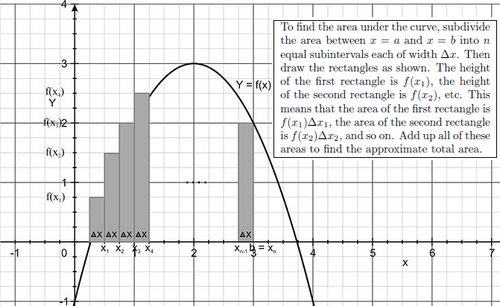
::缺药综合系统平均值理论To understand the meaning of the Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals, recall how the definite integral was defined as the area under the curve y = f ( x ) for the interval from x = a to x = b in the figure below.
::为理解 " 缺电综合体 " 中值理论的含义,回顾确定值综合体是如何定义为下图中x=a至x=b之间的曲线y=f(x)下区域。The and the definite integral were defined in this way:
::以这种方式界定了确定的整体性:A = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x = lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) △ x where △ x = b − a n .
::A=baf(x)dx=limnni=1f(xx)x where x=b-an。Replacing △ x in the summation by b − a n allows the following relationship to develop:
::以 b- an 取代 x 的相加使以下关系得以发展:lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) △ x = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 [ f ( x i ) ⋅ b − a n ] = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x ( b − a ) ⋅ lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) n = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) n = 1 b − a b ∫ a f ( x ) d x … Note that n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) n is just the average of f over lim n → ∞ n ∑ i = 1 f ( x i ) △ x = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x n samples in the interval . A v e r a g e ( f ) in [ a , b ] = 1 b − a b ∫ a f ( x ) d x
::limnn_x=1f(xxx){x=1xxxlimnnni=1[f(xxxx){b}=b*dxxx(b-a)}nni=1f(xx)n=1f(xx)n=1b-abaf(x)x...注意 ni=1f(xxx)n只是间距中f超limnnnnni=1f(xxx)x=b*ff(x)dx样本的平均值。 Average (f) in [a,b]=1b-ab=ab*af(x)dxThe above shows that the average value of a function in an interval is related to the definite integral of the function in the interval. This relationship is formalized as follows:
::上述情况表明,一个函数间隔的平均值与该间隔函数的确定组成部分有关。If f is integrable on the closed interval [ a , b ] , the average (mean) value of f on [ a , b ] is given by:
::如果 f 在封闭间隔[a,b] 上可加固,则以下给出 [a,b] 上f 的平均(平均值)值:A v e r a g e ( f ) = 1 b − a b ∫ a f ( x ) d x
::平均 (f) = 1b-ab*af(x)dxThe Mean Value Theorem of Definite Integrals is a consequence of the property of a continuous function and is stated as follows:
::独立综合体的平均值理论是连续功能财产的结果,其内容如下:If f is continuous on the closed interval [ a , b ] , then at some point c in the open interval ( a , b ) :
::如果 f 在封闭间隔[a,b]上是连续的,那么在开放间隔(a,b)的某个点上是c:b ∫ a f ( x ) d x = f ( c ) ( b − a )
:x)dx=f(c)(b)-a)
This means f ( c ) = A v e r a g e ( f ) , i.e., f ( c ) is the average value in the interval.
::这意味着 f(c) = 平均(f),即 f(c) 是间隔中的平均值。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked for an explanation for why the height of the equivalent area rectangle (that intersects the function curve) is considered (defined to be) the average value of the definite integral.
::早些时候,有人要求您解释为何将等同区域矩形的高度(横交函数曲线)视为(被界定为)确定的整体体的平均值。Try expressing the definite integral as a limit of sums and the dividing by the rectangle width. The value that you get is really the limit of the means (averages) of the function values as n , the number of function values, increases.
::尝试将确定的整体值表示为总和的限度和矩形宽度的分隔。您得到的值实际上是函数值作为 n、函数值数、函数值的增加等值的手段(平均值)的限度。Example 2
::例2Compute the average value of f ( x ) = x 3 in the interval [0, 3], and find the point c where f ( c ) equals the average value.
::在间隔 [0, 3] 中计算 f(x)=x3 的平均值,并找到 f(c) 等于平均值的点 。Using the limit definition we found that
::使用我们发现的限制定义3 ∫ 0 x 3 d x = 81 4 .
::30x3dx=814。We can now find the average value of f in the interval:
::我们现在可以在间隔中找到 f 的平均值 :f ( c ) ( b − a ) = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x … The Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals. = 3 ∫ 0 x 3 d x f ( c ) ( 3 − 0 ) = 81 4 f ( c ) = 81 4 ⋅ 1 3 f ( c ) = 27 4 … The average value of f in the interval is 6.75 .
::f(c) (b) - (a) =b) af(x)dx(x)... " 脱贫综合体的平均值理论 " 。= 3*0x3dxf(c)(3-0) = 814f(c) = 814/13f(c) = 274. 间隔中f的平均值为6.75。Because f ( c ) = c 3 = 6.75 , this means c = 3 √ 6.75 = 1.89 .
::因为f(c)=c3=6.75,这意味着c=36.75=1.89。Example 3
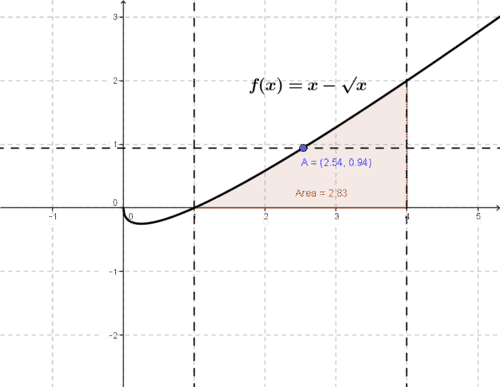
::例3Find the average value of f ( x ) = ( x − √ x ) in the interval [1, 4], and find the point c where f ( c ) equals the average value.
::在间隔 [1, 4] 中查找 f(x) = (xx) 的平均值, 并找到 f(c) 等于平均值的点 。We apply the Mean Value Theorem as follows:
::我们采用以下中值理论:f ( c ) ( b − a ) = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x … The Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals . f ( c ) ( b − a ) = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x … The Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals . f ( c ) ( 4 − 1 ) = 4 ∫ 1 ( x − √ x ) d x . f ( c ) ⋅ 3 = ( 4 ∫ 1 x d x − 4 ∫ 1 √ x d x . ) = ( x 2 2 ] 4 1 − 2 3 x 3 2 ] 4 1 ) = [ ( 8 − 1 2 ) − 2 3 ( 8 − 1 ) ] = 17 6 … The area under the curve is 2.8 ¯ 3 . f ( c ) = 17 18 … The average value of f in the interval is 0.9 ¯ 4 .
::f(c)(b)-(a) = baf(x)dx(b) = baf(x)dx(c)(b) = baf(b) = baf(x)dx(x)x(c)(1) = 41(x)x(x)x(c)3= (41xx-*4*1xxx)= (x22)41-23x32)41= [(8-12)-23(8-1)] = 176......曲线下的区域为2.8 = 3.f)= 1718... 间隔中f的平均值为 0.9 4。The area under the curve and average value are shown in the figure.
::图中显示曲线下的区域和平均值。To find the value of c requires solving the equation f ( x ) = x − √ x = 17 18 , or the equivalent equation √ c = c − 17 18 .
::要找到 c 的值,需要解析等式 f( x) =x x=1718, 或等值的等式 c = c-1718。The solution to the equation is c = 2.537 .
::方程的解决方案是C=2.537。Example 4
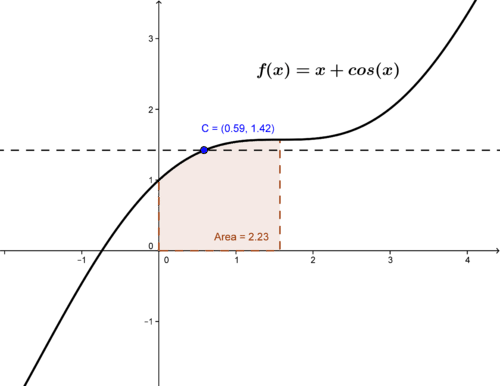
::例4Find the average value of f ( x ) = ( x + cos x ) in the interval [ 0 , π 2 ] , and find the point c where f ( c ) equals the average value.
::在间隔 [0] 2 中查找 f(x) = (x+cosx) 的平均值, 并找到 f(c) 等于平均值的点 。We apply the Mean Value Theorem as follows:
::我们采用以下中值理论:f ( c ) ( b − a ) = b ∫ a f ( x ) d x … The Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals . f ( c ) ( π 2 − 0 ) = π 2 ∫ 0 ( x + cos x ) d x . f ( c ) ( π 2 ) = π 2 ∫ 0 x d x + π 2 ∫ 0 cos x d x . = ( x 2 2 ] π 2 0 + sin x ] π 2 0 ) = [ ( π 2 8 − 0 ) + sin ( π 2 ) − sin ( 0 ) ] = [ π 2 8 + 1 ] ⋯ The area under the curve is 2.234 f ( c ) = 2 π ⋅ π 2 + 8 8 = π 2 + 8 4 π … The average value of f in the interval is 1.422.
::f(c)(b)(a) = baf(x)(x)dx(.)... 断裂综合体的平均值理论. f(c)(2-0) 20(x+cos x) dx(c)(2) 2) 20x(x) 20cos x dx.=(x22) 20+sinxxx) =[(28-0) +sin(x2)-sin(0)] =[28+1] = 曲线下的区域为 2.234f(c) = 22+88 2+84}... 间隔中f的平均值为 1.422。The area under the curve and average value are shown in the figure.
::图中显示曲线下的区域和平均值。To find the value of c requires solving the equation f ( c ) = c + cos c = π 2 + 8 4 π .
::要找到 c 的值,需要解析公式 f(c) = c+csc% 2+84。The solution to the equation is c = 0.592 r a d i a n s .
::方程的解决方案是 c=0.592 弧度。Example 5
::例5Suppose g ( x ) = x 2 + 3 x + 1 . Find a value c in the interval [1, 3] such that g ′ ( c ) equals the average rate of change of g ( x ) on the interval.
::假设 g(x) =x2+3x+1. 在间隔 [1, 3] 中查找值c, 即 g_(c) 等于间隔中 g(x) 的平均变化率 。With g ( x ) = x 2 + 3 x + 1 , then g ′ ( x ) = 2 x + 3 .
::g( x) =x2+3x+1, 然后 g_( x) =2x+3 。We apply the Mean Value Theorem as follows:
::我们采用以下中值理论:g ′ ( c ) ( b − a ) = b ∫ a g ′ ( x ) d x … The Mean Value Theorem for Definite Integrals . g ′ ( c ) ( 3 − 1 ) = 3 ∫ 1 ( 2 x + 3 ) d x . g ′ ( c ) ( 2 ) = ( x 2 + 3 x ) | 3 1 = ( 9 + 9 ) − ( 1 + 3 ) = 14 … The area under the curve is 14. g ′ ( c ) = 7 … The average value of g ′ in the interval is 7.
::g{(c)(b)-(a) = b}ag}(x) dx... 脱硫综合体的平均值理论g}(c)(3)-(1) = 31(2x+3) dx.g}(c) (2) = (x2+3x) {(31) =(9+9) -(1+3)=14... 曲线下的区域为 14.g}(c) = 7... 间隔内g}的平均值为 7。To find the value of c requires solving the equation g ′ ( c ) = 2 c + 3 = 7 .
::要找到 c 的值,需要解析公式 g(c)=2c+3=7。The solution to the equation is c = 2 .
::方程的解决方案是 c=2 。Review
::回顾For #1-3, find the average value of the function over the given interval.
::# 1-3, 找到给定间隔内函数的平均值 。-
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
4
+
2
x
2
+
4
over [-2, 1]
::f(xx)x4+2x2+4+[-2,1] -
f
(
x
)
=
4
(
2
x
+
6
)
2
over [-6, -5]
::f(xx)=4(2x+6)2 大于[-6,-5] -
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
+
2
over [-2, 2]
:xx)x+2以上[-2,2]
For #4-10, find the value c in the given interval such that the function equals its average value over the interval at c .
::对于# 4- 10, 在给定间隔中查找 c 值, 使函数等于 c 间隔中其平均值 。-
9
∫
4
(
3
√
x
)
d
x
::============================================================================================================================================== ============================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================================== -
1
∫
0
(
t
−
t
2
)
d
t
::10(t- t2)dt -
5
∫
2
(
1
√
x
+
1
√
2
)
d
x
::52(1x+12)dx -
1
∫
0
4
(
x
2
−
1
)
(
x
2
+
1
)
d
x
::104(x2- 1)(x2+1)dx -
8
∫
2
(
4
x
+
x
2
+
x
)
d
x
::82( 4x+x2+x) dx -
4
∫
2
(
e
3
x
)
d
x
::42(e3x)dx -
4
∫
1
2
x
+
3
d
x
::412x+3dx -
Find the average value of
f
(
x
)
=
√
x
over [1, 9].
::查找 [1, 9] 以上 f(x) x 的平均值。 -
If
f
is continuous and
4
∫
1
f
(
x
)
d
x
=
9
, show that
f
takes on the value 3 at least once on the interval [1, 4].
::如果 f 是连续的, 41f(x)dx=9, 则显示 f 在 [1, 4] 间距上至少拿取3 值一次 。 -
Find the value of
A
such that the average rate of change of the function
f
(
x
)
=
x
3
on the interval
[
0
,
A
]
is equal to the instantaneous rate of change of the function at
x
=
1
.
::查找 A 的值,使间隔 [ 0, A] 的函数 f(x)=x3 的平均变化速率等于 x=1 的函数的瞬时变化速率。 -
Let
g
(
x
)
=
x
3
+
2
x
. Find a value of
c
between 1 and 3 such that the average rate of change of
g
(
x
)
in [1, 3] is equal to the instantaneous rate of change of
g
(
x
)
at
x
=
c
.
::Lets(x) =x3+2x. 查找在 1 和 3 之间的 c 值,使 [1, 3] 中的 g(x) 平均变化速率等于 x= c 时g(x) 的瞬时变化速率。 -
Let
f
(
x
)
=
t
2
. Find a value
A
such that the average rate of change of
f
(
x
)
from 1 to
A
equals the instantaneous rate of change at
t
=
2
A
.
::Let f(x) = t2. 找到一个值A, 使f(x) 从 1 到 A 的平均变化率等于 t= 2A 的瞬时变化率 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
f
(
x
)
=
−
x
4
+
2
x
2
+
4
over [-2, 1]