7.9 超双曲函数
章节大纲
-
The hyperbolic functions are a set of functions with definitions and some properties that bear resemblance to the set trigonometric functions. But, the hyperbolic functions are exponential functions and, therefore, are not periodic. They are useful in describing physical phenomenon (e.g., ocean wave speed, and the drag on an object in a fluid) and for their convenience in solving differential equations. The hyperbolic functions figure prominently in Einstein’s, Special Theory of Relativity in the transformation equations relating to different frames of reference . In addition, a few of the hyperbolic functions are useful in describing the shape and characteristics of the physical form of a hanging power line, or a necklace, or the architecture of some well known structures. Do you know the name of this physical form described by ?
::双曲函数是一组带有定义的函数,有些属性与一组三角函数相似。但是,双曲函数是指数函数,因此不是周期函数。它们有助于描述物理现象(例如,海浪速度和在流体中拖动一个对象),也有利于解决差异方程。双曲函数在爱因斯坦(Einstein)中占据突出位置,在与不同参照框架有关的变异方程中具有特别相对性理论。此外,一些双曲函数有助于描述绞刑线或项链或一些已知结构的结构的物理形态和特征。你知道这种物理形态的名称吗?Hyperbolic Functions
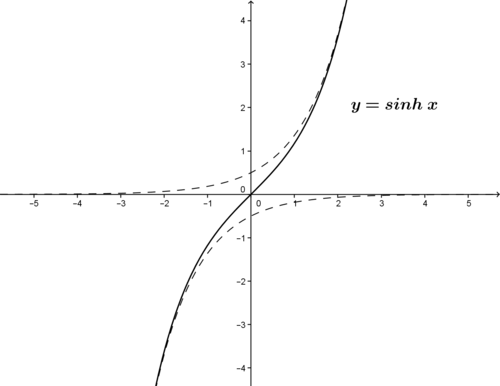
::超双曲函数As with the trigonometric functions, there is a hyperbolic sine and a hyperbolic cosine that form the basis for defining the other hyperbolic functions. The definitions of the hyperbolic sine ( sinh x , pronounced “sinch x”) and the hyperbolic cosine ( cosh x , pronounced “kosh x”), and the related hyperbolic functions are as follows:
::与三角函数一样,有一个双曲正弦和一个双曲余弦,构成定义其他双曲函数的基础。双曲正弦(辛克斯,直译为“inhxxx”)和双曲余弦(coshx,直译为“koshxx”)的定义和相关的双曲余弦函数如下:Definitions of the Hyperbolic Functions sinh x = e x − e − x 2
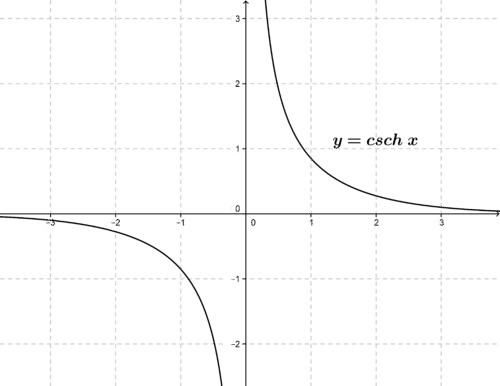
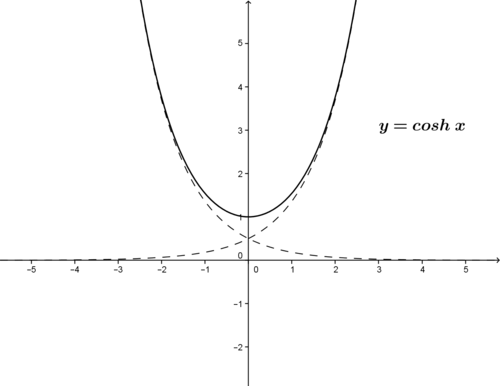
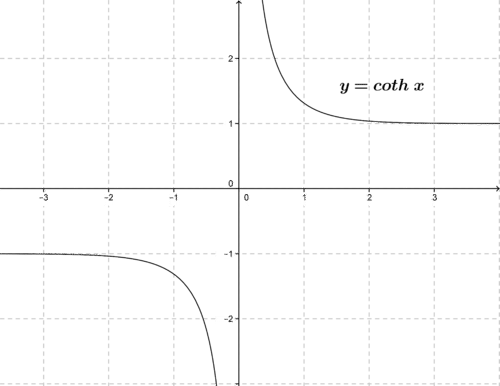
::sinhx =ex-e-x2 ex- ex-e-x2 exinhx=ex-e-x2 exinhx=ex-e-x2csch x = 1 sinh x = 2 e x − e − x cosh x = e x + e − x 2 sech x = 1 cosh x = 2 e x + e − x tanh x = sinh x cosh x = e x − e − x e x + e − x coth x = 1 tanh x = e x + e − x e x − e − x The graphs of these functions are shown in the following figures.
::这些函数的图表如下图所示。In fluid dynamics, linear wave theory predicts that the velocity v of a single ocean wave can be approximated as: v = √ g λ 2 π tanh ( 2 π d λ ) , where
::在流体动态中,线性波理论预测,单海洋波的速度与速度之比可大致如下:vg2tanh(2d),其中λ is the wavelength of the ocean wave ( distance between crests)
::是海浪的波长(海脊之间的距离)d is the depth of the ocean, and
::d 是海洋的深度,和g is the acceleration of gravity, 9.8 m/s 2 .
::g 是重力加速度,9.8 m/s2。Given the above, determine the velocity of a tsunami wave, of wavelength 20 km, traveling across an ocean of depth 4 km.
::鉴于上述情况,确定横跨4公里深海洋的波长为20公里的海啸波的速度。The tsunami wave’s velocity is given by v = √ g λ 2 π tanh ( 2 π d λ ) .
::海啸波的速度由 v2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222222We need to evaluate tanh ( 2 π d λ ) = tanh ( 2 π 4 20 ) = tanh ( 1.257 ) :
::我们需要评估Tanh( 2d) =tanh( 2420) =tanh( 1. 257):tanh 1.257 = sinh 1.257 cosh 1.257 = e 1.257 − e − 1.257 e 1.257 + e − 1.257 = 1 − e − 2 ( 1.257 ) 1 + e − 2 ( 1.257 ) = 1 − 0.0809 1 + 0.0809 tanh 1.257 = 0.85
::tanh1.257=sinh1.257osh1.257=e1.257-e-1.257e1.257+e-1-e-2(1.257)1+e-2(1.257)1+e-2(1.257)=1-0.08091+0.0809tanh1.257=0.85。So that,
::因此,v = √ g λ 2 π tanh ( 2 π d λ ) = √ 9.8 ⋅ 20000 2 π ⋅ 0.85 = 162.8 m/s.
::{\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么? {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么 {\fn黑体\fs22\bord1\shad0\3aHBE\4aH00\fscx67\fscy66\2cHFFFFFF\3cH808080}为什么?This is a tsunami wave speed of about 366 miles per hour.
::这是每小时366英里的海啸波速Hyperbolic Function Identities and Properties
::超双曲函数特性和属性The hyperbolic functions have some identities that resemble the trigonometric properties.
::双曲函数有一些类似三角属性的身份 。Recall the trigonometric property: cos 2 x + sin 2 x = 1 .
::回顾三角数属性: cos2x+sin2x=1。The corresponding hyperbolic identity is : cosh 2 x − sinh 2 x = 1 . The proof is as follows:
::相应的双曲身份是:cosh2x-sinh2x=1. 证明如下:cosh 2 x − sinh 2 x = ( cosh x − sinh x ) ( cosh x + sinh x ) … Factor for difference of squares = ( e x + e − x 2 − e x − e − x 2 ) ( e x + e − x 2 + e x − e − x 2 ) … Use definition of hyperbolic functions = ( 2 e − x 2 ) ( 2 e x 2 ) … Simplify factors = 1
::cosh2x-sinh2x=(coshx-sinhx)(coshx+sinhx)...正方形差的因子=(ex+e-x2-ex-ex-ex-ex-ex-x2)(ex+e-x2+ex-ex-e-x2). 使用双叶函数定义=(2e-x2)(2ex2)。The table below summarizes key hyperbolic identities with a comparison to trig identities.
::下表汇总了关键双曲身份,并与三角身份进行比较。Trigonometric vs Hyperbolic Identities Trigonometric
::三角数Hyperbolic
::超双曲cos 2 x + sin 2 x = 1
::CO2x+sin2x=1cosh 2 x − sinh 2 x = 1
::COsh2x- 辛h2x=11 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x
::1+tan2x=sec2x 1+tan2x=sec2x1 − tanh 2 x = sech 2 x
::1 - tanh2x=sech2x1 + cot 2 x = csc 2 x
::1+cot2x=csc2x1 − coth 2 x = − csch 2 x
::1 - coth2xcsch2 xsin ( x ± y ) = sin x cos y ± cos x sin y
:sin(xy) =sinxcosy xsiny
sin ( 2 x ) = 2 sin x cos x
::sin( 2x) = 2sinxcosxsinh ( x ± y ) = sinh x cosh y ± cosh x sinh y
::hh sin( xy) =sinhxcoshy coshsinh (xy) =sinhxxcoshy xsinhy (xy) =sinhxxxxxxsinhy =sinhsinh ( 2 x ) = 2 sinh x cosh x
::sinh sinh( 2x) = 2sinhxcoshxcos ( x ± y ) = cos x cos y ∓ sin x sin y
::COs(xy) =cosxcosysinxsinycos ( 2 x ) = cos 2 x − sin 2 x
::CO( 2x) =cos2x- 辛2xcosh ( x ± y ) = cosh x cosh y ± sinh x sinh y
::cosh( xy) = coshxcoshy sinhxsinhcosh ( 2 x ) = cosh 2 x + sinh 2 x
::cosh( 2x) = osh2x+sinh2x = osh2x+sinh2xIt should be noted that the hyperbolic identities can be written from the trigonometric identities by changing the sign of any trigonometric term that involves the product of two sines (e.g., tan 2 x involves the product sin 2 x ).
::应当指出,从三角特征中可以写出双曲特征,改变任何涉及两个正弦产物的三角术语(例如,tan2x涉及产品sin2x)的标志。Recall the two trigonometric properties involving negative arguments:
::回顾涉及否定论点的两个三角特性:-
sin
(
−
x
)
=
−
sin
x
:-x)\\sinx
-
cos
(
−
x
)
=
cos
x
::COs(- x) =cosx
For sinh x , the negative argument gives the following result:
::对于 sinhx, 否定论点得出以下结果:sinh ( − x ) = e − x − e x 2 … Use definition of hyperbolic functions = − e x + e − x 2 … Simplify = − sinh x … Use definition of hyperbolic functions
::sinh (- x) =e- x- ex2... 使用双曲函数定义@ ex+e- x2... 简单化\ sinhx... 使用双曲函数定义For cosh x , the negative argument gives the following result:
::对于coshx, 否定论点得出以下结果:cosh ( − x ) = e − x + e x 2 … Use definition of hyperbolic functions = e x + e − x 2 … Use commutative property = cosh x … Use definition of hyperbolic functions
::cosh(- x) =e- x+ex2... 使用双曲函数定义=ex+e- x2... 使用通俗属性=coshx... 使用双曲函数定义Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked for the name of the physical form that is described by a hyperbolic function.
::早些时候,有人要求您使用双曲函数描述的物理形式的名称。The form is called a catenary : the curve formed by a flexible cable of uniform density hanging from two points under its own weight. Catenaries occur naturally. The form minimizes the gravitational potential energy of the hanging, flexible rope or cable (same as minimizing the area under the rope). In addition to a hanging power line, or a hanging chain attached to two posts, the catenary shape can be seen as arches in some architecture. A catenary looks like a parabola , but that is only an approximation to the cosh x function that describes the shape of a catenary.
::窗体被称为催眠器: 由自负重量下两个点挂起的统一密度弹性电缆构成的曲线。 日记自然发生。 窗体将吊挂、 柔软绳索或电缆的引力潜能最小化( 类似将绳索下的区域最小化 ) 。 除了挂电线或挂在两个柱子上的挂链外, 催眠器形状可以被视为某种建筑中的拱门。 一种催眠器看上去像抛物线, 但这只能接近描述催眠器形状的COshx功能 。Example 2
::例2On a Mercator map, the coordinates of each point are ( X , W ) , where X is the longitude of the point on the spherical earth, and W = ln ( sec Y + tan Y ) , where Y is the latitude of the point on the spherical earth. To recover the latitude from W , a transformation is required. Using trigonometric identities, show that tan Y is related to sinh W .
::在 Mercator 地图上, 每个点的坐标是 (X, W) , X 是球状地球点的经度, W=ln(secY+tanY) 是球状地球点的纬度。 要从 W 恢复纬度, 需要一个转换。 使用三角特征, 显示 tanY 与 sinhW 有关 。Since W = ln ( sec Y + tan Y ) , we have that
::自W=ln(secY+tanY)以来,我们有了sec Y + tan Y = e W … Use definition of natural logarithm function √ 1 + tan 2 Y + tan Y = e W … Use trig identity: sec 2 x = 1 + tan 2 x √ 1 + tan 2 Y = e W − tan Y 1 + tan 2 Y = ( e W − tan Y ) 2 1 = ( e 2 W − 2 e W tan Y + tan 2 Y ) − tan 2 Y 0 = e W ( e W − 2 tan Y ) − 1 2 tan Y = e W − e − W … After dividing both sides by e W tan Y = e W − e − W 2 tan Y = sinh Y
::secY+tanY=eW... 使用自然对数函数%1+tan2Y+tan2Y+tanY=eW=y1+tan2Y=eW-tanY1+tan2Y=(eW-tanY)21=(e2W-2W-2WtanY+tan2Y)-tan2Y=e2Y0=e(eW-2tanY)-112tanY=e-e-e-W-W...在用eWtanY=e-e-W-W-W2tanY=sinY分隔两侧后使用三重识别:sec2x=1+tan2x}1+tan2Y=eW-W-W2tanY=sinYReview
::回顾For #1-5, evaluate the following hyperbolic functions without using a calculator.
::对于 # 1 5, 在不使用计算器的情况下评价以下双曲函数 。-
sinh
0
::血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 血 -
cosh
0
::COsh0 -
tanh
0
::坦h0 -
sinh
(
ln
3
)
::罪( ln3) -
cosh
(
ln
2
)
::COsh( ln2)
For #7-9, solve for the value of x (using natural logarithms):
::# 7- 9, 解析 x (使用自然对数) 的值 :-
cosh
x
=
13
5
::COshx=135 COshx=135 -
sinh
x
=
3
4
::血原=34 -
3
sinh
x
−
cosh
x
=
1
::3sinhx - oshx=1 3sinhx - oshx=1 -
If
sinh
x
=
tan
y
, show that
x
=
ln
(
sec
y
+
tan
y
)
.
::如果sinhx=tany, 请显示 x=in( secy+tany) 。
For #11-15, given the information about one hyperbolic function, evaluate the other hyperbolic function.
::对于 # 11-15, 鉴于关于一个双曲函数的信息, 请评价另一个双曲函数 。-
If
sinh
x
=
3
4
, evaluate
sech
x
.
::如果sinhx=34, 评估 sech x。 -
If
tanh
x
=
4
5
, evaluate
coth
x
.
::如果 tanhx=45, 评估 Cothx 。 -
If
sinh
x
=
−
7
24
, evaluate
cosh
x
.
::如果sinhx724, 评估 Coshx 。 -
If
cosh
x
=
2.5
, evaluate
cosh
2
x
.
::如果 cosx=2.5, 则评价 cos2x 。 -
If
coth
x
=
−
3
, evaluate
csch
x
.
::如果Cohsx*% 3, 评估 csch x 。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
sin
(
−
x
)
=
−
sin
x