9.16 Taylor和Maclaurin多面体: 系列排挤错误
章节大纲
-
One of the best ways to introduce this concept is to ask the question: How does a calculator compute functions like , , , etc.? Do you know the answer? Is there a large look-up table stored in memory that gets used? The answer is related to the use of power series . Do you know how to compute using what you have learned about power series? If so, how accurate is your result? How do you get around the problem that power series have an infinite number of terms?
::引入这个概念的最佳方法之一是问一个问题: 计算器如何强制执行 sinx、 ex、 x 等函数? 您知道答案吗 ? 在记忆中是否有一个大型的查找表被存储在可以使用的记忆中? 答案与权力序列的使用有关。 您知道如何使用您所学到的关于权力序列的知识来计算sin( 6) 吗? 如果是这样, 您的结果有多准确? 您如何绕过权力序列有无限多条件的问题?Series Truncation Error of Taylor and Maclaurin Polynomials
::Taylor和Maclaurin复合体错误A Taylor (Maclaurin) polynomial is a polynomial that results from truncating a Taylor (Maclaurin) power series to a specified degree . We can define the polynomial this way:
::A Taylor(Maclaurin)的多元性是一个多元性,它源自于将一个泰勒(Maclaurin)的电力序列缩短到一定的水平。 我们可以这样定义多元性:The th-degree Taylor polynomial of a function at is the polynomial formed by using terms of the Taylor series representation, , of the function:
::x=x0 函数 f(x) 的 nth- 度 TaylorpolynomialTn(x) 是函数 Taylor 序列表示的 T(x) 术语, 函数的 T(x) 构成的多元值 :%7D(x_0)%7D%7Bn!%7D(x-x_0)%5En">
::Tn( x) @ k@ k=0nf( k)( x0) k! (x- x0) k=f( x0) +f*( x0)( x- x0) +f* (x0) 2! (x- x0) 2+...+f( n)( x0) n! (x- x0) nThe th-degree Maclaurin polynomial of a function is the th-degree Taylor polynomial for :
::函数 f( x) 的 nth- 度 Maclaurin 多边Mn( x) 是 x0=0 的 nth- 度 Taylor 多边Monial:%7D(0)%7D%7Bn!%7Dx%5En">
::Mn(x) @k=0nf(k)(0)k!xk=f(0)+f(0)_(0)x+f}{(0)2!x2+...+f(0)n!xn
Now, let's find the first three Taylor polynomial representations of at of the function
::现在,让我们找到函数 f( x) =x36 x0=1 的 f( x) 时 f( x) =x36 的 f( x) = 1 的前三 Taylor 多边多边表示式First evaluate the function and its at :
::首先在 x0 = 1 时对函数及其值进行评估 :
::f( x) =x36f( x0=1) =16f_( x) =x22_f_( x0=1) =12f_( x) =x_f* (x0=1) =1f_( x) =1* (x) =1*f_( x) =1* (x0=1) =1Next, write the Taylor polynomials:
::写下泰勒的多面性:
::T1 (xx)\\ k=01f(k)(x0) k! (x- x0) k=16+12(x-1) T2(x) T2(x)\k=02f(k)(x0) k! (x-x0) 16+12(x-x0) k=16(x-x) x1 1) 1+(x- 1) 1+(x- 1) 222+(x-132=x36=f(x)Taylors (Maclaurin) Series Remainder and Truncation Error
::泰勒(Maclaurin)系列遗留物和排出错误The use of the th-degree Taylor (Maclaurin) polynomials to represent a function can often provide an easier method for evaluating the function. However, the question becomes how much error is associated with approximating the function using the polynomial. We would like to know how to determine the magnitude of the difference between the function and polynomial approximation at a specific value.
::使用nth-doral Taylor (Maclaurin) 多边比喻来代表函数通常可以提供一个比较容易的方法来评估函数。 但是,问题在于使用多数值函数接近函数时会发生多少错误。 我们想知道如何确定函数和多数值接近之间的差别大小 。Recall the remainder of the th-degree Taylor polynomial at is given by .
::将nn(x)=x0时的Nn(x)-Tn(x)-Tn(x)给定为n(x)=x0时的nn(x)-n(x)-n(x)。The Taylor (Maclaurin) Polynomial Remainder Estimation Theorem is as follows:
::泰勒(Maclaurin)多面残骸估计估计理论如下:If the function has derivatives for each point in the interval , and in the interval , then the th-degree Taylor (Maclaurin) polynomial has the following bound for the remainder :
::如果函数 f( x) 有 n+1 衍生物, 用于 {x_ x0}r 间隔内的每个点, 并在 {f(n+1)(x)}}} 间隔内, 函数 f( x) 具有 n+1 衍生物, 那么 nth- 度 泰勒( Maclaurin) 的多元性则为剩余 Rn( x) 受以下约束 :
::@rn(x) @m(n+1)! @x-x0_n+1 代表 *x-x0_r。The above means that given any differentiable function, we can expand it as a polynomial at a given point. If the associated truncation error is reasonably small enough, the polynomial expansion through Taylor’s series becomes a good approximation to the function.
::上述情况意味着,如果存在任何不同的功能,我们可以在某个特定点将它作为多元性扩展。 如果相关的缺勤误差相当小,那么泰勒系列的多元性扩展就会成为该函数的近似值。Let's use the formula to find the error. For the function :
::让我们使用公式来查找错误。 对于函数 f( x)=1+x , 函数 f( x)=1+x :-
What is the third-degree Maclaurin polynomial in for
?
::三度的Maclaurin 多元度是多少? -
What is the truncation error?
::缩短错误是什么?
First evaluate the function and its first 4 derivatives at :
::第一次在 x0=0 时评价函数及其前四个衍生物 :
::f( x) = 1+x*\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Next, write the Maclaurin polynomial:
::下一位写下Maclaurin 多元纪念书:
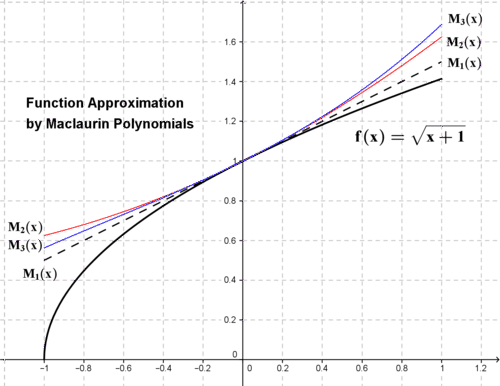
::M3 (x) k= 03f(k)(0)k! (x)k= 1+12x-18x2+116x3The figure below shows the function , and the degree 1, 2 and 3 Maclaurin polynomials. As you can see, the polynomials fit best near the center , and have more error farther away from the center.
::下图显示函数 f( x) = 1+x, 以及 1、 2 和 3 度的Maclaurin 多元动物。 正如您所看到的, 多边动物最适合在中心 x=0 附近, 并且离中心更远的错误更多 。The truncation error is for where .
::校正错误为 @Rn( x) @R3( x) @M( n+1)! @x_n+1=M4! @x%4=M4)。 @x_0.1 的补丁错误是 @f( n+1)(x) @f(4)(x)_M。The largest value of over the interval occurs when .
::f(4)(x) 15616(1+x) 72 之间的间隔值最大, 当 x0. 1 时, 值为 {x} 0.1 。
::f(4)(-0.1)1566(1-01)____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________Therefore,
::因此,R3(x)1.364!0.14=5.67×10-6This is the truncation error of approximating by the third-degree Maclaurin polynomial.
::这是三度Maclaurin多面体的 近似截断误差 。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were asked how a calculator computes functions like , , , etc. and how to compute using what you have learned about power series
::早些时候,有人问您计算计算器的计算公式如何函数如 sinx, ex, x 等, 以及如何使用您所学的电源序列来计算 sin%( 6) 。There are a number of methods that can be used in a calculator to calculate some of the functions we use all the time. One of the methods is to use a truncated power series appropriate for the function, i.e., just use a finite number of terms selected to provide high accuracy. We know, for example, that can be represented by the following power series:
::计算器中可以使用一些方法来计算我们所有时间使用的一些函数。 方法之一是使用适合函数的短断电源序列, 即只使用选定的有限数目的术语来提供高精度。 我们知道, 例如, sinx 可以用以下的电源序列来表示 :, which is valid for all .
::sinxn=0(- 1)nx2n+1( 2n+1)!=x- x33!+x55!-x77!@}, 对所有 x( Rc}) 有效 。Suppose the first three terms are used to approximate , then the estimate will be: . Since the exact answer is 0.5, the truncated power series result underestimates the correct answer by . Depending on your application, this error may be perfectly acceptable!
::假设前三个词用于大约sin( 6) , 那么估计是: sin( 6) x- x33! +x55!- x77! = 0.5236- 0.0239+0.0003=0. 4994。 由于准确答案是 0.5, 断电序列结果低估了 0. 006 的正确答案 。 根据您的应用, 这个错误可能是完全可以接受的 !Example 2
::例2Let . What is the third degree Maclaurin polynomial representations of ?
::Let f(x) =sinx. Maclaurin 的三度多元表示法 f(x) 是什么 ?First evaluate the function and its derivatives at :
::首先在 x0=0 时评价函数及其衍生物 :
::f(x)=sinxf(x0=0)=sin0=0f}(x)=cosxf}(x0=0)=cos0=1f}(x)sinxxxf}(x0=0)=0f}(x)cosxxxf}(x)0=0f}(x0=0=0)\}*1Next, write the Maclaurin polynomial:
::下一位写下Maclaurin 多元纪念书:
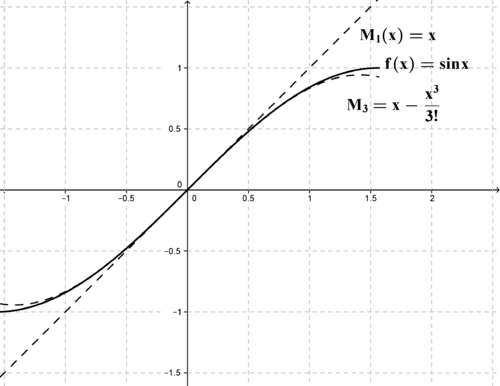
::M3(x) @k=03f(k)(0)k! (x)k=0+1x1+0x22-1x36M3(x) @k=03f(k)(0)k!(x)k=x-x36Figure below shows the function , and the degree 1 and 3 Maclaurin polynomials. As you can see, the polynomials fit best near the center , and have more error farther away from the center.
::下图显示函数 f( x) =sinx, 以及 1 和 3 度的Maclaurin 多元米亚。 正如您所看到的, 多元米亚最适合在中心 x=0 附近, 离中心更远的错误更多 。Example 3
::例3For the function :
::对于函数 f( x)=tanx :-
Find the second-degree Taylor polynomial at
;
::在 x0+4 处找到二度泰勒多面体; -
Determine the truncation error in the interval
.
::确定间距 x48 中的补缺错误 。
First evaluate the function and its first 3 derivatives at :
::首先在 x0 @% 4 处评价函数及其前三个衍生物 :
::f(x) = tanx}f(x04) = 1f}(x) = sec2x4) = 2f}(x) = 2sec2}(x04) = 4f}(x) = 4f}(x) = 4sec2 }(x) = 4sec2 xx2x2sec4} (x) = 1f}(x) = sec2}x04) = 16Next, write the Taylor polynomial:
::写下泰勒的多面性:
::T2(x) @k=02f(k) @k)(x}}k! (x}}}k=1+2(x})+4(x)+4(x)2T2(x)=1+2(x)2(x)4+2(x)4The figure below shows the function , and the degree 2 Taylor polynomial approximation. As you can see, the polynomial fits best near the center , and has more error farther away from the center.
::下图显示函数 f( x) =tanx, 以及 2 度 Taylor 多边近似值。 正如您所看到的, 多元近似值最适合于中点 x\ 4, 离中点更远的错误也更多 。The truncation error is for where .
::校正错误为 @Rn(x4) @R2(x4) @M(n+1)! @ @(x4)n+1_M3! @(x4)3}}(x4)3}}(x4)_8}(n+1)(x)(x)f(3)(x)_M。The largest value of over the interval occurs when.
::f(x) = 4sec2xtan2+2sec4x 的最大值在 x= 448 的间距内为 f(x) = 4sec2xtan2+2sec4x 的最大值 。
::-=YTET -伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=-伊甸园字幕组=- 翻译:Therefore,
::因此,#R2(x)252.453!#3_8_4}4=10.006This is the truncation error of approximating by the 2nd-degree Taylor polynomial. Note that the 2nd-degree polynomial is not a good approximation since and the polynomial error at is 1.0006.
::这是大约2度的泰勒多元度的截断错误。 请注意, 2度的多元度不是一个好近似值, 因为 tan( 38) = 2. 4 , 而 x= 38 的多度错误是 1. 0006 。Review
::回顾For #1-6, find the Taylor series of the following functions at the given with given degree .
::对于 # 1-6, 在给定 x0 找到以下泰勒函数序列, 并给定程度 n 。-
centered at
.
::f(x) =x 以x0=1,n=2为中心。 -
at
.
::f(x)=e3xxx=0,n=3。 -
at
.
::f(x) = ln4x x= 1,n=4。 -
at
.
::f(x) = 1+x+x2+x3+x4 at x1,n= 4。 -
,
at
.
::f(x) = 43x-7, x73 at x= 0,n= 5。 -
at
.
::f(x) = cos( 23x) at x @ @ @ 2, n= 5 。 -
7. Suppose that
is a function with continuous derivatives and that:
,
,
, and
.
-
What is the Taylor polynomial of degree
for
centered at
?
::以 x=5 居于 h( x) 中心的 泰勒 多等度 n=3 是什么 ? -
Use the Taylor polynomial to approximate
.
::使用Taylor多边协议约合 h( 4. 8) 。
::7. 假设 h(x) 是连续衍生物的函数, 并且 : h(5)=3, h(5) (5) 2, h(x) =7, h(x) =7, 和 h(x) 3 。 以 x=5 为中心的 h(x) 多重度 n=3 是什么? 使用 Taylor 组合度约等于 h( 4. 8 ) 。 -
What is the Taylor polynomial of degree
for
centered at
?
-
What is the truncation error of approximating
by its fourth-degree Maclaurin series in for
.
::F(x)=1+x的四度Maclaurin序列中的 f(x)=1+x 等值为 x=0.1 的截断错误是什么? -
Calculate the error
when
is estimated by the polynomial
with
.
::计算错误 Rn 时, e 由 X=1 的多数值 exn= 05xnn 估计 。 -
Find
in the Taylor polynomial estimation of
so that
is less than
in the interval
.
::在 Taylor 的多元估计值中找到 n, 这样Rn 在 x0. 5 的间隔中小于 10- 3 。 -
Find
in the Taylor polynomial estimation of
so that
is less than
in the interval
.
::在 Taylor 的多元估计值中找到 n, 这样Rn 在 x0. 5 的间隔中小于 10-6 。 -
Find
in the Taylor polynomial estimation of
so that
is less than
in the interval
.
::在 Taylor 的多元估计值中查找 n, 这样Rn 在 x2 的间隔中小于 10-6 。 -
Calculate the value of
using a 5
th
degree Taylor polynomial centered at:
- 0
-
Compare your results to calculator results; and compute the expected
.
::比较您的计算结果和计算结果;并计算预期 Rn。
::使用 第 5 度的 Taylor 聚度中心 : #% 2 0 计算 sin( 2radians) 的值, 比较您的计算结果; 计算预期 Rn 值 。 -
Find the Taylor series of
at
.
::在 x=0,n=4 时查找 f(x) =e(x5-x) 的泰勒序列。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
What is the third-degree Maclaurin polynomial in for
?