10.3 查找二次二次曲线的参数等量:
章节大纲
-
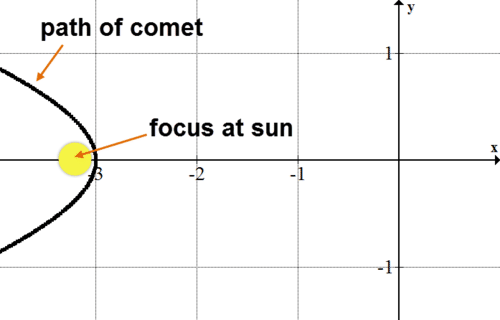
An astronomer is observing the path of a comet through the solar system. While some comets follow an elliptical orbit and return periodically, this comet follows a hyperbolic path and is not expected to pass by Earth again. The astronomer would like to model the comet’s route and use that information to predict when the comet will reach its perihelion, that is, its closest approach to the sun. She would also like to know how close the comet will pass to the sun.
::天文学家正在观察一颗彗星通过太阳系的路径。 虽然有些彗星沿椭圆轨道运行并定期返回,但这一彗星遵循双曲路径,预计不会再次经过地球。 天文学家希望模拟彗星的路线,并利用这一信息预测彗星何时会到达其近距离,即接近太阳的近距离。 她还想知道彗星会如何接近太阳。Parametric Equations of Hyperbolas
::超双氯苯醚的参数等量You may remember that an ellipse is a conic section where the sum of the distances from the two foci to any point on the ellipse is constant. A is like an ellipse turned inside out. For any point on the hyperbola, the difference between the distances to the foci is a constant. As a result, the hyperbola consists of two curved paths, each going on forever. A hyperbola has two diagonal asymptotes that cross at its center . One focus point lies inside each curved path.
::您可能记得, 椭圆是一个二次曲线段, 其间从两端到椭圆上任何一点的距离总和是恒定的。 A 就象一个椭圆翻转了。 对于超博拉的任何一点, 与方圆的距离是恒定的。 因此, 双曲线由两条弯曲的路径组成, 每个曲折的路径将永远持续。 双曲线段在中间有两个对角的单点。 每个曲线道内有一个焦点点 。Hyperbolas in Standard Form
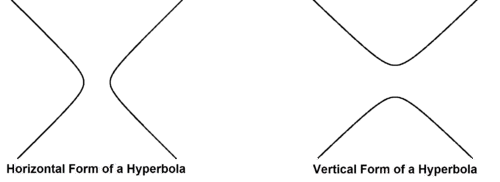
::标准表格中的超光蜡There are two forms of the standard equation for a hyperbola – the horizontal form, and the vertical form. In the horizontal form of a hyperbola with a center at (0, 0), the hyperbola is symmetrical across the y -axis. Both types of hyperbolas are shown below:
::双倍波拉的标准方程式有两种形式 — — 水平形式和垂直形式。以双倍波拉的横向形式,以0,0为中心,双倍波拉横跨y轴对称。两种双倍的双倍形式如下:The equation for a hyperbola in the horizontal form is:
::水平形式的双倍波拉方程式的方程式是:x 2 a 2 − y 2 b 2 = 1 , where y = b a x and y = − b a x are the hyperbola’s asymptotes.
::x2a2-y2b2=1,其中y=bax和ybax是超重波拉的微粒。In the vertical form of a hyperbola with a center at (0, 0), the hyperbola is symmetrical across the x -axis. A vertical hyperbola’s equation can be represented as:
::高重波拉的垂直形式是高重波拉,中心在0,0,超重波拉横跨 x 轴对称。 垂直超重波拉的方程式可以以下列方式表示:y 2 a 2 − x 2 b 2 = 1 , where x = b a y and x = − b a y are the hyperbola’s asymptotes.
::y2a2-x2b2=1,其中 x=bay 和 xbay 是超双波拉的微粒。For hyperbolas with centers that are not at the origin, the equations change slightly. For a horizontal hyperbola with a center at ( h , k ) , use the formula ( x − h ) 2 a 2 − ( y − k ) 2 b 2 = 1 with asymptotes at y − k = ± b a ( x − h ) . For a vertical hyperbola with a center at ( h , k ) use ( y − k ) 2 a 2 − ( x − h ) 2 b 2 with asymptotes at x − h = ± b a ( y − k ) .
::对于具有非原点中心的超高波拉,方程略有变化。对于在 (h,k) 上有一个中心的水平双波拉,使用公式(x-h)2a2-(y-k)2b2=1,在 y-kba(x-h) 上有小数的公式(x-h)2a2-(y-k) 2b2=1。对于在 (h,k) 上有一个中心(y-k) 2a2-(x-h)2b2,在 x-hba(y-k) 上有小数的垂直双波拉,在 (y-k) 上有一个中心(y-k) 2a2-(x-h)2b2。Hyperbolas in Parametric Form
::参数格式中的超双光蜡There are two ways to write the parametric form for a hyperbola. You can choose the form that best fits your needs.
::有两种方法可以写出超重波拉的参数表。 您可以选择最适合您需要的形式 。In the first form, a horizontal hyperbola can be described by the equation :
::首先,横向双倍波拉可以用公式来描述:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = a sec ( t ) y ( t ) = b tan ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = asec(t) y(t) y(t) = tan(t)A vertical hyperbola can be described by the equation:
::垂直双倍波拉可以用公式来描述:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = b tan ( t ) y ( t ) = a sec ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = tan(t) y(t) y(t) = asec(t)The second form of the parametric equation for a hyperbola uses two functions known as hyperbolic sine ( sinh ) and hyperbolic cosine ( cosh ) . These functions are defined as:
::超重波拉参数方程式的第二种形式使用两个函数,即双曲正弦(sinh)和双曲余弦(cosh)。这些函数的定义是:sinh ( x ) = 1 2 ( e x − e − x ) cosh ( x ) = 1 2 ( e x + e − x )
:x)=12(ex-e-x)cosh(x)=12(ex+e-x)
You can put a horizontal hyperbola into parametric form using these functions:
::您可以使用这些函数将水平超重波拉设置为参数形式:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = a cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = b sinh ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) y(t) ) x(t) = aosh(t) y(t) y(t) =bsinh(t)And
::还有x ( t ) = − a cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = b sinh ( t )
:t) _osh(t)y(t)=bsinh(t)
The first set of parameters traces the right half of the hyperbola, while the second set traces the left half. This form of the parametric equation is especially useful for describing the motion of objects that only trace one half of a hyperbola.
::第一组参数跟踪超重波拉的右半,第二组则跟踪左半。这种形式的参数方程对于描述只跟踪超重波拉一半的物体的运动特别有用。Let's find the equation in standard form and both parametric forms for a horizontal hyperbola with a center at (2, 4) and asymptotes with equations y − 4 = ± 3 4 ( x − 2 ) .
::让我们找到标准方程, 以及水平超重波拉的参数表(2, 4) 和以 y - 434( x-2) 等式的微量图的等式。First, you’ll need to find the values for a and b . The slope of the asymptotes is ± b a , so a = 4 and b = 3 . Substitute the values of a and b and the coordinates of the center of the hyperbola into the standard form equation. The standard form of the equation for this hyperbola is:
::首先,您需要找到 a 和 b 的值。 小数点的斜度是 ba, 所以 a= 4 和 b= 3 。 将 a 和 b 的值以及双倍波拉中心的坐标替换到标准方程式方程式中。 此双倍方程式的标准方程式形式是 :( x − 2 ) 2 16 − ( y − 4 ) 2 9 = 1 .
:x-2)216-(y-4)29=1。
Now, use the coordinates of the center and the values for a and b to write the parametric forms of the equation of the hyperbola:
::现在,使用中间的坐标和 a 和 b 的值来写出超重波方程式的参数形式 :F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 4 sec ( t ) + 2 y ( t ) = 3 tan ( t ) + 4
::F(t) = (x(t) ,y(t) ) x(t) = 4sec(t) +2y(t) = 3tan(t)+4This first parametric form traces the whole hyperbola as t moves from 0 to 2 π . Now, find the equations in the second form.
::第一个参数形式将整个超重波拉从 0 移动到 2 ° 。 现在, 在第二种形式中找到方程 。F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x r i g h t s i d e ( t ) = 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 y r i g h t s i d e ( t ) = 3 sinh ( t ) + 4 x l e f t s i d e ( t ) = − 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 y l e f t s i d e ( t ) = 3 sinh ( t ) + 4
::F(t) = (x(t) = 4cosh(t)+2yyrightside(t) = 3sinh(t)+4x左侧(t) @4cosh(t)+2yleftside(t)=3sinh(t)+4Once you have the equations for a hyperbola, you may find it helpful to sketch the hyperbola. This is especially important when you’re solving word problems that involve a point moving along a hyperbola. Take the hyperbola that we just found the equations for:
::一旦您有了超重波拉的方程式, 您可能会发现勾画超重波拉很有帮助。 当您正在解决涉及超重波拉移动点的单词问题时, 这一点特别重要 。 使用我们刚刚找到的超重波拉的方程式用于:( x − 2 ) 2 16 − ( y − 4 ) 2 9 = 1
:x-2)216-(y-4)29=1
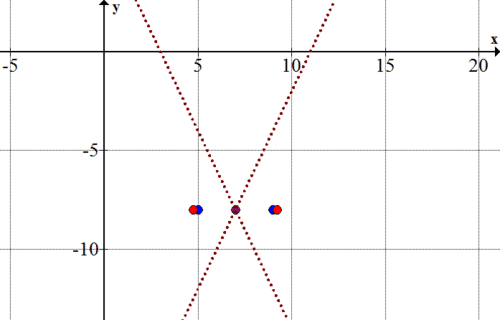
First, mark the point at the center of the hyperbola, (2, 4):
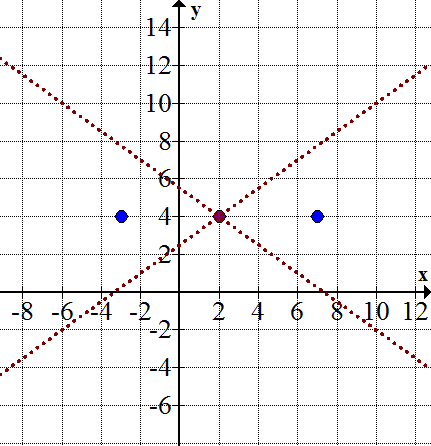
::首先,标出超光波的中心点, (2, 4) :Then, add the two asymptotes, y − 4 = ± 3 4 ( x − 2 ) :
::然后,加上两个小数,y-434(x-2):Next, find the foci for the hyperbola. You can use the formula c 2 − a 2 = b 2 to find the foci, where c is the distance that the focal point lies from the center along the main axis for the hyperbola.
::下一步, 找到超重波拉的角。 您可以使用公式 c2 - a2=b2 来找到宽波拉, 此处的 c 是连接点与超重波拉主轴的中心之间的距离 。c 2 − a 2 = b 2 c 2 − 16 = 9 c 2 = 25 c = ± 5
::c2 -a2=b2c2 -16=9c2=25c=5The foci will be 5 units to the right of the center and 5 units to the left of the center.
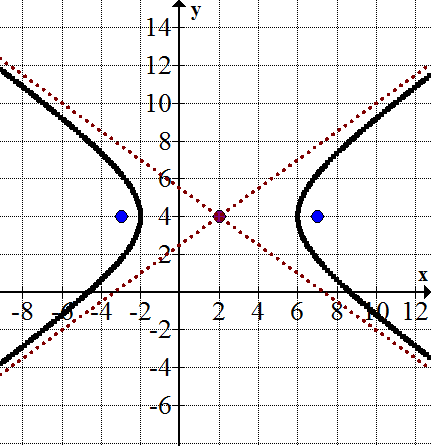
::方块在中间的右边为5个单位,在中间的左边为5个单位。Mark the foci on the graph at (7, 4) and (-3, 4):
::标记图中方块( 7, 4) 和( 3, 4) :Now, sketch the two halves of the hyperbola, using the foci and asymptotes as guides.
::现在,用光子和微粒作为向导 来绘制双倍波拉的两半草图。So, how do the two parametric forms of a hyperbola differ? Evaluate each parametric form of the hyperbola from above, ( x − 2 ) 2 16 − ( y − 4 ) 2 9 = 1 , at t = 0 , π 2 , π , 3 π 2 , 2 π . You may use a calculator and round answers to the nearest thousandth.
::因此,双倍波拉的两种参数形式有何不同?从上面评价超重波拉的每一种参数形式,(x-2)216-(y-4)29=1, t=0, 2, 3, 2, 2。您可以使用计算器和最接近千位的圆形答案。The first parametric equation was:
::第一个参数方程式是:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 4 sec ( t ) + 2 y ( t ) = 3 tan ( t ) + 4
::F(t) = (x(t) ,y(t) ) x(t) = 4sec(t) +2y(t) = 3tan(t)+4Evaluate the equation for the given values of t and organize your results into a table:
::评估 t 给定值的方程,并将结果组织成表格:t 4 sec ( t ) + 2 3 tan ( t ) + 4 ( x , y ) 0 6 4 (6, 4) π 2 undefined undefined undefined π -2 4 (-2, 4) 3 π 2 undefined undefined undefined 2 π 6 4 (6, 4) The second parametric equation was:
::第二个参数方程式是:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x r i g h t s i d e ( t ) = 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 y r i g h t s i d e ( t ) = 3 sinh ( t ) + 4 x l e f t s i d e ( t ) = − 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 y l e f t s i d e ( t ) = 3 sinh ( t ) + 4
::F(t) = (x(t) = 4cosh(t)+2yyrightside(t) = 3sinh(t)+4x左侧(t) @4cosh(t)+2yleftside(t)=3sinh(t)+4Evaluate the equation for the given values of t and organize your results into another table:
::评估 t 给定值的方程,并将结果组织成另一张表格:t 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 3 sinh ( t ) + 4 ( x , y ) − 4 cosh ( t ) + 2 3 sinh ( t ) + 4 ( x , y ) 0 6 4 (6, 4) -2 4 (-2,4) π 2 12.037 10.904 (12.037, 10.904) -8.037 10.904 (-8.037, 10.904) π 48.368 38.646 (48.368, 38.646) -44.368 38.646 (-44.368, 38.646) 3 π 2 224.654 170.963 (224.654, 170.963) -220.654 170.968 (-220.654, 168.990) 2 π 1072.987 807.235 (1072.987, 807.235) -1068.987 807.235 (-1068.987, 807.235) Notice that, while both define the same hyperbola, the equations describe different ways of moving across the hyperbola. In the first equation, as time passes, the object jumps from one curve of the hyperbola to the other. This leaves the function undefined at an infinite number of times.
::请注意,虽然两个方程式都定义了相同的超重波拉,但方程式描述的是跨超重波拉的不同移动方式。在第一个方程式中,随着时间的流逝,天体会从超重波拉的一个曲线跳到另一个曲线。这使函数在无限的时间里没有定义。In the second set of equations, an object only moves along one path at a time. These equations can be used to model continuous motion along one half of a hyperbolic path. They’re especially useful for solving problems involving gravity and motion in space.
::在第二组方程式中,一个物体只能一次沿着一条路径移动。 这些方程式可以用来模拟双曲路径的半个方向的连续运动。 它们对于解决与重力和空间运动有关的问题特别有用。Examples
::实例Example 1
::例1Earlier, you were introduced to an astronomer who wanted to model a comet's motion. She can use a parametric equation for a hyperbola to do this. First, she’ll need to write the equation that describes her comet's path in standard form.
::早些时候,你被介绍给一位天文学家,他想模拟彗星的运动。 她可以用超重波拉的参数方程来做这件事。 首先,她需要用标准格式写出描述其彗星路径的方程。After using a computer to model to find the comet’s future path based on its current trajectory, the scientist realizes that the path of the comet is a hyperbola where a = 3 A U and b = 1 A U . (An AU, or astronomical unit, is what astronomers use to measure distances within the solar system. It’s equal to the average distance between the earth and the sun.) This means that the equation for the comet’s path can be modeled by x 2 9 − y 2 1 = 1 . Since there is no coordinate plane in space, the astronomer can make the (0, 0) point on her coordinate plane the center of the hyperbola in order to simplify her calculations. The comet is only traveling along one half of the hyperbola, so the astronomer can model its path using only the left side of the hyperbola. The focus for this side will be the sun.
::科学家在使用计算机模型寻找彗星以其当前轨迹为基础的未来路径后,意识到彗星的路径是超博拉,其中一个=3AU和b=1AU。 (AAU,或天文学单位,是天文学家用来测量太阳系距离的方法。它相当于地球和太阳之间的平均距离。 )这意味着彗星路径的方程式可以用x29-y21=1. 空间没有坐标平面,因此天文学家可以将她的坐标平面上的点做为超博拉的中心,以便简化她的计算。 彗星只沿着超博拉的半个方向运行,因此天文学家只能用超博拉的左侧来模拟其路径。 这边的焦点将是太阳。Since she’s only using half of a hyperbola to model the comet’s path, the scientist should use the second form of the parametric equation for a hyperbola. Since the comet’s path is most closely modeled by the negative half, she can use the following parametric equation, where time is measured in days:
::由于她只用超重波拉的一半来模拟彗星的路径,科学家应该使用超重波拉参数方程的第二种形式。 由于彗星的路径最接近于负半,她可以使用以下参数方程,用天数衡量时间:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = − 3 cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = sinh ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t),y(t)) x(t) 3cosh(t) y(t) =sinh(t)The comet will reach its perihelion, the closest approach to the sun, when y = 0 . Right now, the comet is at x = − 100 . When will the comet reach its perihelion?
::彗星将到达它的近地点, 最接近太阳的时候, y=0。眼下, 彗星在x100. 彗星何时到达它的近地点?x ( t ) = − 3 cosh ( t ) − 100 = − 3 cosh ( t ) 100 3 = cosh ( t ) cosh − 1 100 3 = t t = ± 4.19948 y ( t ) = sinh ( t ) 0 = sinh ( t ) sinh − 1 ( 0 ) = t t = 0
::x( t) 3cosh( t) - 100_ @ 3cosh( t) 1003= osh( t) osh-11003= t4. 199448y( t) = 辛( t) 0= 辛( t) 辛( t) 辛( sinh) - 1( 0) = t=0The time difference between the comet being at x = − 100 and at y = 0 is 4.19948 days. Therefore, the comet will reach its perihelion in 4.19948 days.
::彗星在 x 100 和 y=0 之间的时间差是 4. 19948 天。 因此, 彗星将在 4. 19948 天到达它的近地点 。Example 2
::例2Write the equation for the following hyperbola in both parametric forms:
::以两种参数形式写出下列超重波拉的方程:x 2 49 − y 2 25 = 1
::x249-y225=1The standard form of a hyperbola is x 2 a 2 − y 2 b 2 = 1 . For this hyperbola, a = 7 , b = 5 .
::双重波拉的标准形式为 x2a2-y2b2=1。 对于此双重波拉, a=7,b=5。So the first form of the parametric equation would be:
::因此,第一种参数等式是:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 7 sec ( t ) y ( t ) = 5 tan ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 7sec(t) y(t) y(t) = 5tan(t)The second form has two parts, one for the right side and one for the left side.The form for the right side is:
::第二个形式有两部分,一个是右侧,一个是左侧。F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 7 cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = 5 sinh ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 7cosh(t) y(t) y(t) = 5sinh(t)The form for the left side is:
::左边的表单是:F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = − 7 cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = 5 sinh ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 5sinh(t)Example 3
::例3Write the other half of the parametric equation for the hyperbola below.
::写下下面的超重波的参数方程的另一半。F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 8 cosh ( t ) + 7 y ( t ) = 6 sinh ( t ) + 3
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 8cosh(t)+7y(t) = 6sinh(t)+3The equation given is the parametric equation for the right half of a hyperbola. The equation for the left half is of the form:
::给定的方程式是超重波拉右半的参数方程式。 左半的方程式是表单 :F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = − a cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = b sinh ( t )
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) = (t) = bsinh(t)So,
::那么,F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = − 8 cosh ( t ) + 7 y ( t ) = 6 sinh ( t ) + 3
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\(t)\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\3\\\\\\\\\\\\3\\\\\\\\\\3\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\3\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Example 4
::例4Write the standard form of the equation for the hyperbola below, then sketch the hyperbola.
::写下下面的超重波拉方程式的标准方程式, 然后绘制超重波拉的草图 。F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 2 sec ( t ) + 7 y ( t ) = tan ( t ) − 8
::F(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 2sec(t)+7y(t) = tan(t)-8First, find the values for a , b , and the center of the hyperbola. From the equation you can see that a is 2, b is 1, and the center is at (7, -8).
::首先, 找到 a, b 的值, 以及超重波拉的中心值。 您可以从公式中看到 2, b 是 1, 中心在 (7, 8) 。Substitute these values into the standard equation for the hyperbola:
::将这些值替换为超重波的标准方程:( x − 7 ) 2 4 − ( y + 8 ) 2 1 = 1
:-7)24-(y+8)21=1
Graph the center point at (7, -8):
::绘制( 7, 8) 的中心点 :Now, find the equations of the asymptotes.
::现在,找到微粒的方程。y − k = ± b a ( x − h ) y − ( − 8 ) = ± 2 1 ( x − 7 ) y + 8 = ± 2 ( x − 7 )
::y- kba(x-h)y- (-8) \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\可以\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\Graph the asymptotes:
::图形小数图 :Graph the vertices of the hyperbola at ( 7 + a , − 8 ) and ( 7 − a , − 8 ) . That is (9, -8) and (5, -8).
::图示7+a,-8)和(7+a,-8)及(7-a,-8)的超重波的顶点(9,-8)和(5,8))。Now, find the foci. The foci will be at c units to the left and right of the center. To find c , use the equation:
::现在,找到方块。 方块将位于中间的左右方块的 C 单位。 要找到 c, 请使用方程式 :c 2 − a 2 = b 2 c 2 − 4 = 1 c 2 = 5 c = √ 5
::c2-a2=b2c2-4=1c2=5c=5c=5Graph the foci at ( 7 + √ 5 , − 8 ) and ( 7 − √ 5 , − 8 ) :
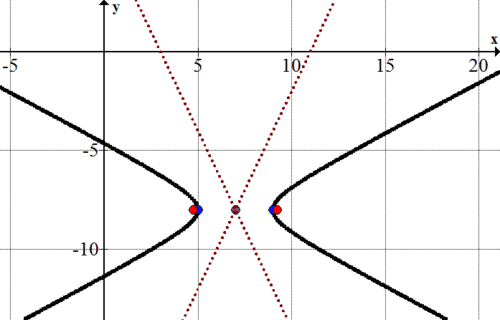
::方形图( 75, 8) 和 (75, 8) :Now sketch the hyperbola:
::现在画出双曲线:Example 5
::例5A space probe flies by Jupiter on a path that can be modeled by the positive side of the hyperbola
::由木星飞过的一个空间探测器飞过木星的一条路径上,这条路径可以由超博拉的正面模拟。x 2 16 − y 2 4 = 1
::x216-y24=1What will its coordinates be when t = 12 ?
::T=12时它的坐标是什么?First, put the equation into the parametric form for the right side of a hyperbola.
::首先,将方程式放入超重波的右侧的参数表。x 2 16 − y 2 4 = 1 F ( t ) = ( x ( t ) , y ( t ) ) x ( t ) = 4 cosh ( t ) y ( t ) = 2 sinh ( t )
::x216-y24=1F(t)=(x(t),y(t)))x(t)=4cosh(t)y(t)=2sinh(t)Now, evaluate the parametric equation for t = 12 .
::现在,评估 t=12 的参数方程。x ( t ) = 4 cosh ( t ) x ( t ) = 4 ( 1 2 ) ( e t + e − t ) x ( t ) = 2 ( e 12 + e − 12 ) x ( t ) = 325590.58 y ( t ) = 2 sinh ( t ) y ( t ) = 2 ( 1 2 ) ( e 12 − e − 12 ) y ( t ) = 162754.79 ( x , y ) = ( 325590.58 , 162754.79 )
:t)=4cosh(t)x(t)=4(12)(et+e-et)x(t)=2(e12+e-12)x(t)=325590.58y(t)=2sinh(t)y(t)y(t)=2(12)(e12-e-e-12)y(t)=162754.79(x,y)=(325590.58,162754.79)。
Review
::回顾For #1-4, write the equation for the hyperbola in both parametric forms.
::在 # 1-4 中, 以两种参数形式写出超重波拉的方程 。-
x
2
36
−
y
2
4
=
1
::x236-y24=1 -
x
2
16
−
y
2
100
=
1
::x216-y2100=1 -
(
x
−
1
)
2
25
−
(
y
+
2
)
2
64
=
1
:x-1)225-(y+2)264=1
-
(
x
+
7
)
2
100
−
(
y
−
9
)
2
81
=
1
:x+7)2100-(y-9)281=1
For #5-7, is the parametric equation shown the right half of the hyperbola or the left half of the hyperbola? Write the other half of the parametric equation for the hyperbola below.
::对于# 5-7, 参数方程是否显示超重波拉的右半或超重波拉的左半? 为下面的超重波拉写入参数方程的另一半 。-
G
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
−
3
cosh
(
t
)
+
4
y
(
t
)
=
5
sinh
(
t
)
+
6
::G(t) = (x( t) = (x( t) y( t) ) x( t) = 5sinh( t)+6 -
H
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
12
cosh
(
t
)
−
1
y
(
t
)
=
8
sinh
(
t
)
+
3
::H(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 12cosh(t)-1-y(t) = 8sinh(t)+3 -
J
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
−
cosh
(
t
)
+
1
y
(
t
)
=
8
sinh
(
t
)
+
12
::J( t) = (x( t) = (x( t) y( t) ) x( t) = * osh( t) +1y( t) = 8sinh( t) +12
For #8-12, write the standard form of the equation for the hyperbola, then sketch the hyperbola.
::对于# 8-12, 写出超重波拉方程的标准格式, 然后绘制超重波拉的草图 。-
K
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
sec
(
t
)
+
4
y
(
t
)
=
3
tan
(
t
)
+
1
:t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = sec(t)+4y(t) = 3tan(t)+1
-
L
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
12
sec
(
t
)
+
6
y
(
t
)
=
2
tan
(
t
)
−
5
::L( t) = (x( t) = (x( t) y( t) ) x( t) = 12sec( t)+6y( t) = 2tan( t) - 5 -
M
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
sec
(
t
)
−
2
y
(
t
)
=
6
tan
(
t
)
+
4
::M(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = sec(t)--2y(t) = 6tan(t)+4 -
N
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
12
sec
(
t
)
y
(
t
)
=
4
tan
(
t
)
::N(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 12sec(t) y(t) y(t) = 4tan(t) -
P
(
t
)
=
(
x
(
t
)
,
y
(
t
)
)
x
(
t
)
=
2
sec
(
t
)
−
3
y
(
t
)
=
7
tan
(
t
)
−
10
::P(t) = (x(t) y(t) ) x(t) = 2sec(t)- 3y(t) = 7tan(t)- 10 -
The path of an object can be modeled by the negative side of the hyperbola
x
2
16
−
y
2
64
=
1
::对象的路径可以由超宽系统216-y264=1的负面模拟。
What will its coordinates be when t = 10 ?
::T=10时它的坐标是什么?-
The path of an object can be modeled by the positive side of the hyperbola
x
2
25
−
y
2
121
=
1
::对象的路径可以由超宽系统225-y2121=1 的正面模拟。
What will its coordinates be when t = 4 ?
::T=4时它的坐标是什么?-
A horizontal hyperbola has a center at (1, -6) and asymptotes with slopes of
±
4
5
. Write the equation for the hyperbola in standard form and in both kinds of parametric forms.
::水平超重波拉有一个中心(1,6)和微粒,斜度为45。以标准形式和两种参数形式写出超重波拉的方程。
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
x
2
36
−
y
2
4
=
1