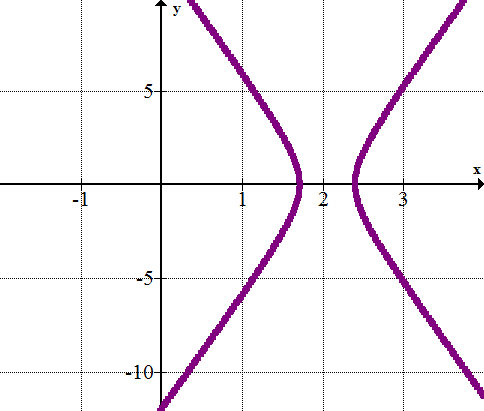10.11 二次曲线及其图示极赤道
章节大纲
-
Janet is working on a physics problem that involves multiple planets in orbit around a star. She tried to set the problem up in rectangular form , but the resulting equations were very messy. Janet needs a way to simplify her problem so that she can manipulate the equations more easily. Can you help?
::珍妮特正在研究一个物理学问题,它涉及围绕恒星的轨道上多个行星。她试图用矩形形式设置问题,但由此产生的方程式非常混乱。珍妮特需要一种简化问题的方法,以便她能够更容易地操控方程式。你能帮忙吗?Polar Equations of Conic Sections
::二次曲线区块的极平方In rectangular form, you’ve defined conic sections in terms of the variables and . Rectangular form defines a conic in relation to the origin, the -axis and the -axis .
::在矩形形式中,您用变量 x 和 y 来定义二次曲线段。矩形形式根据源、 x 轴和 y 轴来定义二次曲线段。The polar system consists of an origin and a ray called the polar axis. When you put the equations for conic sections into polar form , you define them in terms of and . To do this, you must first define conic sections in terms of a focus and a directrix. For any conic section, the distance from a point on the conic to a focal point divided by the distance from that same point to the line representing the directrix is a constant value. This value is usually symbolized with an , and it describes the eccentricity of the conic. The eccentricity of a conic will define what type of conic it is.
::极地系统由源和被称作极轴的射线组成。 当您将二次曲线部分的方程式以极形的形式设置时, 您可以用 R 和 来定义它们。 要做到这一点, 您必须首先用焦点和直线来定义二次曲线部分。 对于任何二次曲线部分, 从二次曲线的点到一个焦点的距离, 从同一点到代表直线的线之间的距离, 是一个不变值。 这个值通常用 e 符号表示, 并描述二次曲线的偏心性。 二次曲线的偏心性将决定它是什么类型的二次曲线 。Equations for conic sections will take one of the following forms:
::二次曲线的等式将采取下列形式之一:-
, where
is the eccentricity and
is the location of the directrix
::r=ed1ecos,其中e为偏心度,xd为直方向方的位置
OR
::或-
, where
is the eccentricity and
is the location of the directrix
::r=ed1esin,其中e是偏心,yd是主轴的位置
In this concept, you will focus on conic sections matching the first form given above.
::在此概念中,您将侧重于与上述第一个形式相对应的二次曲线部分。The eccentricity determines the shape of a conic section. When , the conic is an ellipse. When , the conic is a parabola, and when the shape is a hyperbola.
::偏心度决定二次曲线的形状。 当 0 < e < 1 时, 二次曲线是一个椭圆形。 当 e= 1 时, 二次曲线是一个抛物线, 当 e> 1 时, 二次曲线是一个双曲线 。When , the conic is a circle. In polar form, many graphs produce a circle including , , and .
::当 e= 0 时, 二次曲线是一个圆形。 以极形的形式, 许多图表会生成一个圆形, 包括 r= cos 、 r= 7 和 r= sin 。You can identify conic sections in polar form by putting them in the form (or ).
::您可以通过以 r=ed1+ecos (或 r=ed1esin) 的形式显示二次形的二次形的二次形区块 。What type of conic is defined by the equation ?
::公式 r= 105+5cos 定义了哪种二次曲线?To find out, first multiply by to put the denominator into the form .
::首先乘以1515 将分母放入表1+EcosThe result is . Note that in this equation , so the equation represents a parabola where .
::结果是 r= 21+cos。 请注意, 在此等式e=1中, 此等式代表了 d=2 的抛物线 。When transforming the equation for an ellipse from polar form to rectangular form, the equation of the ellipse will be:
::当将椭圆的方程从极形转换为矩形时,椭圆的方程将是x+c)2a2+y2a2-c2=1
where
::何 地
::a=ed1 - e2c=eaLet's transform the equation into rectangular form.
::让我们将正方程 r=510+3cos 转换成矩形。First put the denominator into the form so that you can determine the values of and .
::首先将分母放入表1+ecos,以便确定 d 和 e 的值。
::r=510+3cosr=510+3cos 110110r=121+310cosr=310531+310cosSo for this ellipse, and .
::所以对于这个椭圆, e=310和d=53。Now, use the equations given previously to transform the equation into rectangular form. First find and .
::现在, 使用先前给定的方程式将方程式转换成矩形。 先找到 a 和 c 。
::a=ed1-e2a=121-121(310)2=5091c=ea=1591Now substitute the values for and into to find the equation of the ellipse:
::现在将a和c的值替换为 (x+c) 2a2+y2a2-c2=1, 以找到椭圆的方程 :
:x+1591)225008281+y222758281=1
Examples
::实例Example 1
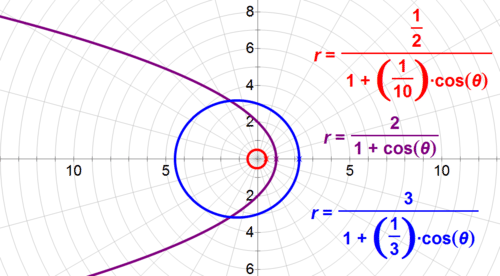
::例1Earlier, you were asked to help Janet model the paths of 2 planets and a comet around a star. By putting the equations of her orbiting objects into polar form, Janet can easily create a graph to model her problem and work with the equations in a simpler format. For instance, suppose that she’s tracking the paths of 2 planets and a comet around a star. All of these objects will have the sun as one of the focal points of their orbits, so it’s easy to represent their paths using polar equations. Assume that one planet has an orbit described by the equation , the other planet has an orbit described by the equation , while the comet’s orbit can be described by .
::早些时候,您被要求帮助珍妮特模拟两个行星和一颗彗星围绕一颗恒星的路径。 珍妮特将轨道物体的方程式以极形形式呈现出来, 就可以很容易地创建出一个图形来模拟她的问题, 并以更简单的格式处理方程式。 比如, 假设她正在跟踪两个行星和一颗彗星围绕一颗恒星的路径。 所有这些天体都将太阳作为它们轨道的焦点之一, 因此使用极式方程式来代表它们的路径很容易。 假设一个行星的轨道由方程式 r= 121+110cos 描述, 另一个行星的轨道由公式 r= 31+13cos 描述, 而彗星的轨道则可以通过 r=21+cos 来描述 。By graphing the equations on her calculator or on a site like fooplot.com, Janet can quickly see where the comet intersects the orbit of the second planet, and see that the comet will pass between the orbits of the inner planet and the outer planet on its journey past the star.
::珍妮特通过在计算器或fooplot.com等站点上绘制方程式图,可以很快地看到彗星在第二个行星的轨道之间交叉的位置,并看到彗星在穿越恒星的旅程中将穿越内行星轨道和外行星轨道。In order to see exactly where the orbits will intersect, Janet can set the equation for the planet’s orbit equal to the equation for the comet’s path, and then solve for . So:
::珍妮特可以设定地球轨道的方程 等同彗星路径的方程,然后解决 。所以:
::31+13cos21+cos3(1+cos)=2(1+13cos)3+3cos2+23cos73cos1cos37}2.014,2.#2.014Substitute back into one of the original equations to find .
::换回原来的方程式 找到r
::r=21+cos2137=247=72So, the comet will intersect the outer planet’s orbit at and .
::因此,彗星将在(72,2.014)和(72,4.269)的外行星轨道上相互交叉。Example 2
::例2When transforming the equation for a hyperbola from polar form to rectangular form, the equation of the hyperbola will be:
::当将超重波拉的方程从极形转换为矩形时,超重波拉的方程将是x-c)2a2-y2c2-a2=1
where
::何 地
::a=ede2-2-1c=eaTransform the equation into rectangular form.
::将公式 r= 41+2cos 转换成矩形。The denominator is already in the form , so you can see that and .
::分母已经在表1+ecos中, 所以您可以看到 e=2 和 d=2 。Use the equations given to transform the equation into rectangular form. First find and .
::使用给定方程式将方程式转换成矩形。首先找到 a 和 c。
::a=ede2-1=1=44-1=43c=ea=(2)(43)=83Now substitute the values for and into to find the equation of the hyperbola:
::现在将 a 和 c 的值替换为 (x-c) 2a2-y2c2-a2=1, 以找到双曲线的方程 :
:x-83)2169-y2489=1
Example 3
::例3In order to transform a parabola from polar to rectangular form, you can use the equation
::要将抛物线从极向矩形转换为矩形,您可以使用方程for polar equations of the form
::y22d(x-d2) 用于窗体 r= ed1ecos 的极方方程式or
::或for polar equations of the form
::x22d(y-d2) 窗体 r= ed1sin 的极方方程式Transform the equation into rectangular form.
::将公式 r= 41+cos 转换成矩形。First, recognize that because . Then, substitute that value into the first equation above. The equation of the parabola is .
::首先,承认 d=4 是因为 e=1. 然后将该值替换为上面的第一个方程。 抛物线的方程是 y2 8(x-2) 。For each of the following examples, identify the conic section described by the equation, transform the equation into rectangular form, and graph.
::对于以下每个示例,请标明方程式描述的二次曲线部分,将方程式转换成矩形,并绘制图表。Example 4
::例4
::r=53+cosFirst, rewrite the equation in order to determine and .
::首先,重写方程,以确定e和d。
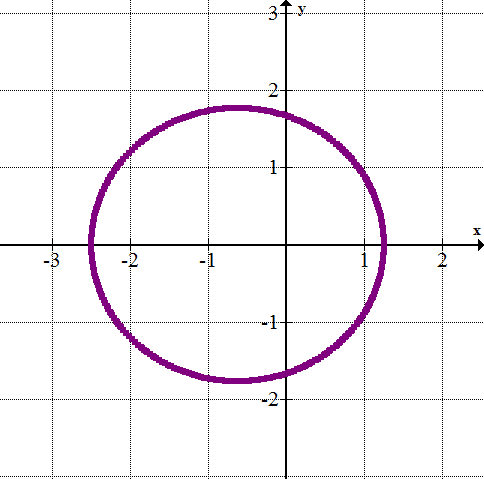
::r=53+cosr=531+13cosSo and . Since is between 0 and 1, this is an ellipse with directrix . Use the equations for transforming an ellipse to put this equation into rectangular form. First find and .
::e=13和d=5. 由于e介于0至1之间,这是直径x=5的椭圆形。使用方程式转换椭圆形,将方程式变成矩形。首先找到a和c。
::a=ed1 -e2c=eaa=ed1 -e2=531 -19=5389=158c=ea=(13)(158)=58Now substitute into .
::现在替换为 (x+c) 2a2+y2a2-c2=1。
:x+58222564+y2258=1)
Example 5
::例5
::r=121+6cosNotice that and . Since is greater than 1, this equation is for a hyperbola. Use the equations for transforming a hyperbola from polar form to rectangular form.
::注意 e= 6 和 d= 2. 由于 e 大于 1, 此方程式用于超重波拉。 使用此方程式将双重波拉从极形转换为矩形 。
::a=ede2-1=1235c=ea=7235(x-7235)21441225-y214435=1Review
::回顾For #1-5, find the value of the eccentricity . Then identify the conic section described by the equation.
::对于 # 1 5, 找到偏心值( e) 。 然后标明方程式描述的二次曲线段 。-
::r=41-cos -
::r=24+2cos -
::r=86-6cos -
::r=122+4cos -
::r=121+13cos
For #6-15, transform the equation into rectangular form and graph.
::在# 6-15中,将方程式转换成矩形形式和图形。-
::r=41-cos -
::r=24+2cos -
::r=86-6cos -
::r=122+4cos -
::r=121+13cos -
::r=121+2cos -
::r=96+3cos__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ -
::r=6 -
::r=142+2cos -
::r=323+5cos
Review (Answers)
::回顾(答复)Click to see the answer key or go to the Table of Contents and click on the Answer Key under the 'Other Versions' option.
::单击可查看答题键, 或转到目录中, 单击“ 其他版本” 选项下的答题键 。 -
, where
is the eccentricity and
is the location of the directrix