3.5 电 电
章节大纲
-
Watch out! Lightning is extremely dangerous. A single bolt of lightning can carry a billion volts of electricity. That’s enough to light a 100- watt light bulb—for three months! As impressive as it is, lightning is nothing more than a sudden flow of extremely tiny particles. What are the particles that flow in a lightning bolt? The answer is electrons.
::当心!闪电是极其危险的。 闪电一闪即能带来十亿伏的电压。 这足以在三个月的时间里点亮100瓦的灯泡。 闪电虽然令人印象深刻,但不过是极小粒子的突然流动而已。 闪电中流出的粒子是什么? 答案是电子。What Are Electrons?
::什么是电子?Electrons are one of three main types of particles that make up atoms. The other two types are and . Unlike protons and neutrons, which consist of smaller, simpler particles, electrons are that do not consist of smaller particles. They are a type of fundamental particles called leptons. All leptons have an electric charge of -1 or 0.
::电子是构成原子的三种主要粒子类型之一。其他两种类型是和。与质子和中子不同,这些质子和中子由较小、较简单的粒子组成,电子不是较小粒子组成,它们是一种称为的基本粒子,所有的电荷为-1或0。Properties of Electrons
::电子的属性Electrons are extremely small. The mass of an electron is only about 1/2000 the mass of a proton or neutron, so electrons contribute virtually nothing to the total mass of an . Electrons have an electric charge of -1, which is equal but opposite to the charge of proton, which is +1. All atoms have the same number of electrons as protons, so the positive and negative charges “cancel out,” making atoms electrically neutral.
::电子是极小的。电子的质量只有质子或中子的重量1/2000左右,所以电子对质子或中子的总质量几乎没有任何作用。 电子的电荷为-1,这与质子的电荷是相等的,但与质子的电荷是相反的,即+1。 所有原子的电量与质子的电量相同,因此正负电荷“取消”使原子在电子上保持中性。Where Are Electrons?
::电子人在哪里?Unlike protons and neutrons, which are located inside the nucleus at the center of the atom, electrons are found outside the nucleus. Because opposite electric charges attract each other, negative electrons are attracted to the positive nucleus. This force of attraction keeps electrons constantly moving through the otherwise empty space around the nucleus. The Figure shown is a common way to represent the structure of an atom. It shows the electron as a particle orbiting the nucleus, similar to the way that planets orbit the sun.
::与质子和中子不同的是,质子和中子位于原子中心的核心内,电子在核外被发现。由于对面电荷相互吸引,负电子被正核吸引。这种吸引力使电子不断在核周围的空空空空间中移动。图中显示的是代表原子结构的一种常见方式。它显示电子是围绕核运行的粒子,类似于行星绕太阳运行的方式。Orbitals
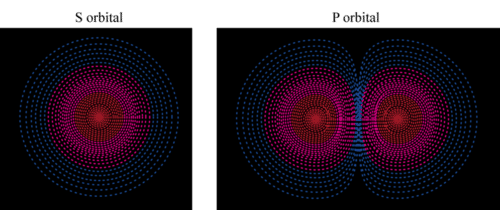
::轨道轨道The atomic model above is useful for some purposes, but it’s too simple when it comes to the location of electrons. In reality, it’s impossible to say what path an electron will follow. Instead, it’s only possible to describe the chances of finding an electron in a certain region around the nucleus. The region where an electron is most likely to be is called an orbital . Each orbital can have at most two electrons. Some orbitals, called S orbitals, are shaped like spheres, with the nucleus in the center. An S orbital is pictured in Figure . Where the dots are denser, the chance of finding an electron is greater. Also pictured in Figure is a P orbital. P orbitals are shaped like dumbbells, with the nucleus in the pinched part of the dumbbell.
::上面的原子模型在某些方面有用,但对于电子的位置来说,它太简单了。在现实中,不可能说电子会走什么道路。相反,只能描述在核心周围某个区域找到电子的可能性。电子最有可能被称作轨道。每个轨道最多可以有两种电子。有些轨道,叫做轨道,形状像球体,中间有核。图中描绘了S轨道。当点密度越大,找到电子的机会就越大。图中也描绘了P轨道。轨道的形状像哑铃,核在哑铃中。Q: How many electrons can there be in each type of orbital shown above?
::问题:上述每一类轨道可有多少电子?A: There can be a maximum of two electrons in any orbital, regardless of its shape.
::A: 任何轨道中都最多可能有两个电子,而不论其形状如何。Q: Where is the nucleus in each orbital?
::问题:每个轨道的核心在哪里?A: The nucleus is at the center of each orbital. It is in the middle of the sphere in the S orbital and in the pinched part of the P orbital.
::A: 核位于每个轨道的中心。 它位于 S 轨道的球体中间, 位于 P 轨道的紧紧部分 。What’s Your Energy Level?
::你的能源水平是多少?Electrons are located at fixed distances from the nucleus, called energy levels. You can see the first three energy levels in the Figure . The diagram also shows the maximum possible number of electrons at each .
::电子位于离核心的固定距离,即所谓的能量水平。您可以看到图中前三个能量水平。图中还显示了每个核心的最大电子数量。-
Electrons at lower energy levels, which are closer to the nucleus, have less energy. At the lowest energy level, which has the least energy, there is just one orbital, so this energy level has a maximum of two electrons.
::更接近核心的低能量水平的电能较少。 在能量最少的低能量水平,只有一个轨道,因此这种能量水平最多只能有两个电子。 -
Only when a lower energy level is full are electrons added to the next higher energy level. Electrons at higher energy levels, which are farther from the nucleus, have more energy. They also have more orbitals and greater possible numbers of electrons.
::只有当低能量水平完全达到全能水平时,电子才会被添加到下一个更高的能量水平上。 高能量水平的电离核更远,其能量也更多。 它们还有更多的轨道电子和更多的电子。 -
Electrons at the outermost energy level of an atom are called
. They determine many of the properties of an
. That’s because these electrons are involved in
with other atoms. Atoms may share or transfer valence electrons. Shared electrons bind atoms together to form chemical compounds.
::原子最外端能源水平的电被称作 。 它们决定着一个原子的许多特性。 这是因为这些电子与其他原子有关。 原子可能共享或转移价值电子。 共享电子将原子捆绑在一起形成化学化合物。
Q: If an atom has 12 electrons, how will they be distributed in energy levels?
::问题:如果原子有12个电子,它们如何在能源水平上分布?A: The atom will have two electrons at the first energy level, eight at the second energy level, and the remaining two at the third energy level.
::A:原子在第一个能源层面将有两个电子,八个在第二个能源层面,其余两个在第三个能源层面。Q: Sometimes, an electron jumps from one energy level to another. How do you think this happens?
::问题:有时,电子从一个能量水平跳到另一个能量水平。你觉得这是怎么回事?A: To change energy levels, an electron must either gain or lose energy. That’s because electrons at higher energy levels have more energy than electrons at lower energy levels.
::为了改变能源水平,电子必须获得或失去能源。 这是因为高能源水平的电子比低能源水平的电子拥有更多的能源。Summary
::摘要-
Electrons are one of three main types of particles that make up the atom. They are extremely small and have an electric charge of -1. All atoms have the same number of electrons as protons.
::电子是构成原子的三种主要粒子类型之一,它们极小,有1-1的电荷。所有原子的电子数量与质子相同。 -
Negative electrons are attracted to the positive nucleus. This force of attraction keeps electrons constantly moving around the nucleus. The region where an electron is most likely to be found is called an orbital.
::负电子被正核吸引。 这种吸引力使得电子不断在核周围移动。 最有可能发现电子的区域被称为轨道。 -
Electrons are located at fixed distances from the nucleus, called energy levels. Electrons at lower energy levels have less energy than electrons at higher energy levels
::电离核心(称为能源水平)的固定距离。 低能水平的电能比高能水平的电能低。
Review
::回顾-
What are electrons?
::什么是电子? -
Compare and contrast electrons and protons.
::比较和对比电子和质子。 -
Sketch a model of a beryllium atom, which has four protons, five neutrons, and four electrons. Your model should include the placement of electrons at the appropriate energy levels.
::绘制一个有4个质子、5个中子和4个电子的原子模型。 您的模型应该包括将电子放在适当的能量水平上。 -
What are valence electrons? Why are they so important? How many valence electrons does a beryllium atom have (see question 3)?
::物价电子是什么?它们为什么如此重要?一个原子有多少价值电子(见问题3)?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that foll ow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
Who discovered electrons? When were they discovered?
::谁发现了电子? -
Outline how electrons were discovered.
::概要说明电子是如何被发现的。 -
What was the significance of the discovery of electrons?
::发现电子的意义是什么? -
Where did Thomson think electrons were located in the atom? How does this differ from the modern view of electrons presented above?
::Thomson认为原子中存在电子在哪里?这与上述现代电子观点有何不同?
-
Electrons at lower energy levels, which are closer to the nucleus, have less energy. At the lowest energy level, which has the least energy, there is just one orbital, so this energy level has a maximum of two electrons.