4.5 象形体
章节大纲
-
What is this intricate orb? It is the greatly magnified skeleton of single-celled ocean organisms known as radiolarians. The skeleton is made of an that is extremely common on Earth. In fact, it is the second most abundant element in Earth’s crust. It is also one of the most common elements in the entire universe. What is this important element? Its name is silicon, and it belongs to a class of elements called metalloids.
::这个复杂的星体是什么? 它是一个单细胞海洋生物的巨型骨骼,叫做放射性卫星。 骨骼是由地球上极为常见的元素组成的。 事实上,它是地球地壳中第二多的元素。 它也是整个宇宙中最常见元素之一。 这个重要元素是什么? 它的名字是硅, 它属于一种叫做类类类的元素。What Are Metalloids?
::什么是代谢物?Metalloids are the smallest class of elements. (The other two classes of elements are and nonmetals). There are just six metalloids. In addition to silicon, they include boron, germanium, arsenic, antimony, and tellurium. Metalloids fall between metals and in the periodic table . They also fall between metals and nonmetals in terms of their properties.
::等离子体是最小的元素类别。 (其他两类元素为非金属)只有六种类元素。除硅外,还有、、砷、、和。等离子体介于金属和周期表之间,就其特性而言,也介于金属和非金属之间。Q: How does the position of an element in the periodic table influence its properties?
::问题:周期表中某一元素的位置如何影响其属性?A: Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their , which is the number of in their atoms. Atoms are neutral in electric charge , so they always have the same number of electrons as protons. It is the number of electrons in the outer of atoms that determines most of the properties of elements.
::A: 元素按其原子数,即原子数排列在周期表中。原子在电荷中是中性的,因此其电子数总是与质子相同。决定元素大多数特性的是原子外部的电子数。Chemical Properties of Metalloids
::代谢物的化学特性How metalloids behave in chemical interactions with other elements depends mainly on the number of electrons in the outer energy level of their atoms. Metalloids have from three to six electrons in their outer energy level. Boron, pictured in the Figure , is the only metalloid with just three electrons in its outer energy level. It tends to act like metals by giving up its electrons in . Metalloids with more than four electrons in their outer energy level (arsenic, antimony, and tellurium) tend to act like nonmetals by gaining electrons in chemical reactions. Those with exactly four electrons in their outer energy level (silicon and germanium) may act like either metals or nonmetals, depending on the other elements in the reaction.
::在与其它元素的化学互动中,甲状腺在与其它元素发生作用时如何表现主要取决于其原子外能水平中的电子数量。甲状腺在其外能水平上有3至6个电子。图中图示的甲状腺是唯一在外能水平上只有3个电子的甲状腺。它倾向于通过在外能水平中放弃其电子来表现为金属。外能水平(粗、微和)中拥有4个以上电子的甲状腺,往往通过在化学反应中获取电子而像非金属一样。外能水平中正好有4个电子的甲状腺(硅和)可能像金属或非金属,这取决于反应中的其他元素。Physical Properties of Metalloids
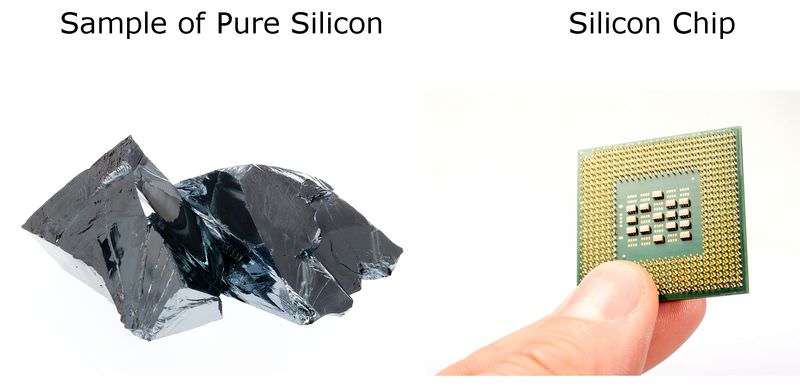
::代谢物的物理属性Most metalloids have some of metals and some physical properties of nonmetals. For example, metals are good conductors of both and electricity, whereas nonmetals generally cannot conduct heat or electricity. And metalloids? They fall between metals and nonmetals in their ability to conduct heat, and if they can conduct electricity, they usually can do so only at higher temperatures. Metalloids that can conduct electricity at higher temperatures are called semiconductors. Silicon is an example of a semiconductor . It is used to make the tiny electric in computer chips. You can see a sample of silicon and a silicon chip in the Figure .
::大多数类金属都有某些金属和非金属的物理特性,例如,金属是良好的导体和电力,而非金属一般不能进行热力或电力。和类金属?它们在其进行热力的能力中落在金属和非金属之间,如果它们能够进行电力,它们通常只能在较高的温度下进行电力。在较高温度下进行电力的类金属被称为半导体。硅是半导体的一个例子。硅被用来制造计算机芯片中的微小电。你可以在图中看到硅和硅芯样本。Metalloids tend to be shiny like metals but brittle like nonmetals. Because they are brittle, they may chip like glass or crumble to a powder if struck. Other physical properties of metalloids are more variable, including their and points, although all metalloids exist as solids at room .
::蛋白质通常像金属一样亮亮,但像非金属一样亮亮。 由于蛋白质是易碎的,它们可能像玻璃一样碎裂,或者被撞击后粉碎。 蛋白质的其他物理特性比较多变,包括其点和点,尽管所有类美素都作为固体存在于室内。Summary
::摘要-
Metalloids are the smallest class of elements, containing just six elements. They fall between metals and nonmetals in the periodic table.
::蛋白质是最小的元素类别,仅包含6个元素,在周期表中介于金属和非金属之间。 -
How metalloids behave in chemical interactions with other elements depends mainly on the number of electrons in the outer energy level of their atoms. Metalloids may act either like metals or nonmetals in chemical reactions.
::在与其他元素的化学相互作用中,甲状腺体的行为方式主要取决于其原子外能水平中的电子数量,在化学反应中,甲状腺体可能像金属或非金属一样。 -
Most metalloids have some physical properties of metals and some physical properties of nonmetals. They fall between metals and nonmetals in their ability to conduct heat and electricity. They are shiny like metals but brittle like nonmetals. All exist as solids at room temperature.
::大多数类金属具有金属的一些物理特性和非金属的一些物理特性,在进行热能和电力的能力方面,它们存在于金属和非金属之间,它们像金属一样闪亮,但像非金属一样易碎,在室温下,它们都作为固体存在。
Review
::回顾-
What are metalloids? Which elements are placed in this class of elements?
::什么是类物质? 哪些元素被放置在这个元素类别中? -
Identify physical properties of metalloids that resemble those of metals.
::查明类似于金属的类阿片的物理特性。 -
Which physical property of metalloids is like that of nonmetals?
::金属类的哪些物理属性与非金属的物理属性相似? -
Explain the variation in how metalloids react with other elements.
::解释在类固醇与其他元素反应方式上的差异。 -
Use the internet to find some examples of semiconductors being used in electronics. Summarize your findings in a poster.
::使用互联网查找电子产品中使用半导体的一些实例。 请在海报上概述您的调查结果 。
-
Metalloids are the smallest class of elements, containing just six elements. They fall between metals and nonmetals in the periodic table.