4.9 过渡金属
章节大纲
-
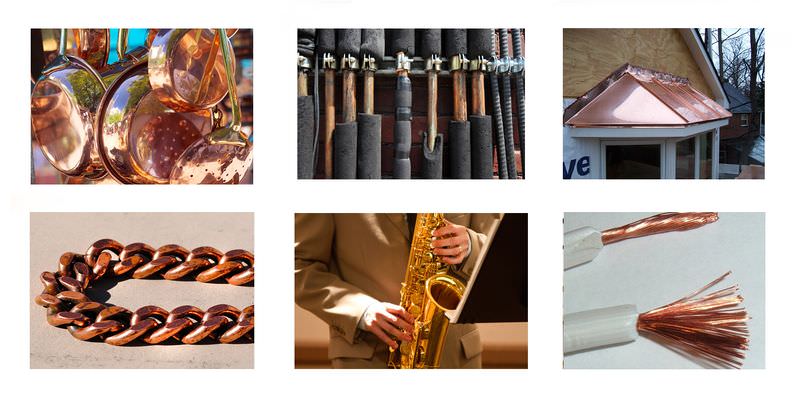
What do all of the objects pictured above have in common? All of them are made completely or primarily of copper. Copper has an amazing variety of uses, including cooking pots, plumbing pipes, roofing tiles, jewelry, , and electric wires. Copper is a good choice for these and many other objects because of its properties. It can be formed into wires and flat sheets, it’s a great conductor of and electricity, it’s hard and strong, and it doesn’t corrode easily. In all these ways, copper is a typical transition metal .
::上面所描述的所有物体有什么共同之处? 它们都是完全或主要由铜制成的。 铜有惊人的多种用途,包括烹饪锅、管道、屋顶砖、首饰和电线。 铜由于其特性,是这些和许多其他物体的好选择。 铜可以形成电线和平板,它是一个巨大的电导和电源,坚固和坚固,而且不易腐烂。 在所有这些方面,铜是一种典型的过渡金属。What Are Transition Metals?
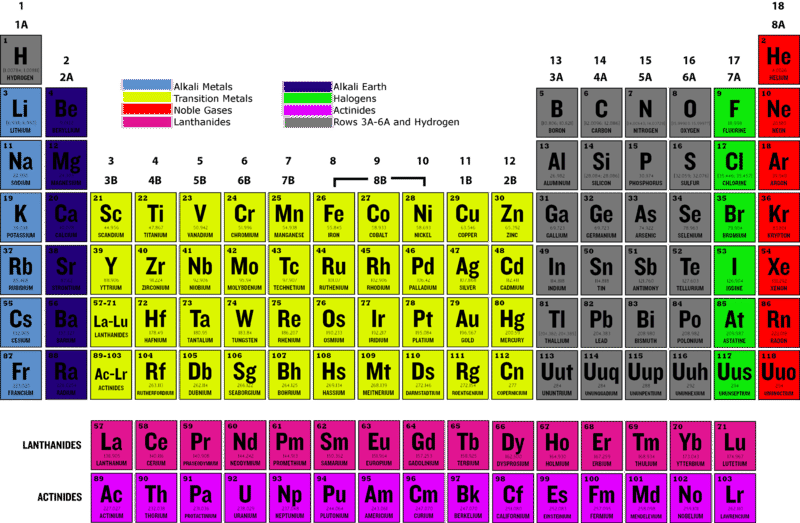
::什么是 " 过渡金属 " ?Transition metals are all the in groups 3–12 of the periodic table . In the periodic table pictured in Figure , they are the elements shaded yellow, pink, and purple. The transition metals make up about 60 percent of all known elements. In addition to copper (Cu), well known examples of transition metals include iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), silver (Ag), and gold (Au) (Copper (Cu) is pictured in its various applications in the opening image).
::过渡性金属在周期表的第3至12组中都有。 在图所示的周期表中,它们是黄色、粉色和紫色的阴影元素。 过渡性金属约占已知元素的60%。 除铜(Cu)外,众所周知的过渡性金属例子包括铁(Fe)、锌(Zn)、银(Ag)和金(Au)(Copper(Cu)在开张图像中的各种应用中都有图解 ) 。Q: Transition metals have been called the most typical of all . What do you think this means?
::问题:过渡金属被称为最典型的。你认为这意味着什么?A: Unlike some other metals, transition metals have the properties that define the metals class. They are excellent conductors of electricity, for example, and they also have luster, malleability, and ductility. You can read more about these properties of transition metals below.
::A:与其他金属不同,过渡性金属具有确定金属等级的特性。例如,它们是极好的电力导体,它们也具有光滑性、易变性和通风性。您可以阅读下面关于过渡性金属的这些特性的更多信息。Properties of Transition Metals
::过渡金属属性Transition metals are superior conductors of heat as well as electricity. They are malleable, which means they can be shaped into sheets, and ductile, which means they can be shaped into wires. They have high and points, and all are solids at room , except for mercury (Hg), which is a . Transition metals are also high in density and very hard. Most of them are white or silvery in color, and they are generally lustrous, or shiny. The compounds that transition metals form with other elements are often very colorful. You can see several examples in the Figure .
::过渡性金属既是热源,也是电力的高级导体。它们具有可移动性,意味着它们可以形成成片和衬带,这意味着它们可以形成成线。它们具有高点和点,除了汞(Hg)之外,都是在室内的固体。过渡性金属密度也很高,而且非常硬。其中多数是白色或银色的,一般是光滑的,或闪亮的。将金属与其他元素转化成的化合物往往非常多彩。你可以从图中看到几个例子。Some properties of transition metals set them apart from other metals. Compared with the alkali metals in group 1 and the in group 2, the transition metals are much less reactive. They don’t react quickly with water or oxygen, which explains why they resist corrosion.
::与第1组和第2组的碱性金属相比,过渡性金属的反应性要小得多。 它们不会对水或氧产生快速反应,这解释了它们为什么抵制腐蚀。Other properties of the transition metals are unique. They are the only elements that may use electrons in the next to highest—as well as the highest— as . Valence electrons are the electrons that form bonds with other elements in compounds and that generally determine the properties of elements. Transition metals are unusual in having very similar properties even with different numbers of valence electrons. The transition metals also include the only elements that produce a magnetic field . Three of them have this property: iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and nickel (Ni).
::过渡性金属的其他特性是独特的,它们是在最高一级和最高一级使用电子的唯一要素。Valence een 电子是与其他元素在化合物中形成联系的电子,通常决定元素的特性。过渡性金属的特性非常相似,即使价值电子的数量不同。过渡性金属还包括产生磁场的唯一元素。其中三种具有这种属性:铁(Fe)、钴(Co)和镍(Nii)。Q: How is the number of valence electrons typically related to the properties of elements?
::问题:价值电子的数量通常如何与元素的特性相关?A: The number of valence electrons usually determines how reactive elements are as well as the ways in which they react with other elements.
::A:价值电子的数目通常决定反应要素是如何反应的,以及它们与其他要素的反应方式。Those Elements Down Under
::那些下层元素Transition metals include the elements that are most often placed below the periodic table (the pink- and purple-shaded elements in the Figure ). Those that follow lanthanum (La) are called lanthanides. They are all relatively reactive for transition metals. Those that follow actinium (Ac) are called actinides. They are all radioactive. This means that they are unstable, so they decay into different, more stable elements. Many of the actinides do not occur in nature but are made in laboratories.
::过渡性金属包括经常放在周期表下面的元素(图中的粉色和紫色阴影元素),后面的元素被称为lanthanum(La),对过渡性金属来说都是相对反应性的金属。对过渡性金属来说,它们都是相对反应性的金属。在(Ac)之后的金属被称为(Ac),它们都是放射性的。这意味着它们不稳定,因此它们会变成不同的、更稳定的元素。许多不是自然的,而是在实验室中制造的。Summary
::摘要-
Transition metals are all the elements in groups 3–12 of the periodic table. More than half of all elements are transition metals.
::过渡金属是周期表第3至12组的所有元素,其中一半以上是过渡金属。 -
Transition metals are typical metals, with properties such as a superior ability to conduct electricity and heat. They also have the metallic properties of luster, malleability, and ductility. In addition, transition metals have high melting and boiling points and high density.
::过渡性金属是典型的金属,其性质如电力和热能的超强能力,还具有性欲、易腐性和导管性等金属特性,此外,过渡性金属的熔点和沸点高,密度高。 -
The lanthanides and actinides are the transition metals that are usually placed below the main part of the periodic table. Lanthanides are relatively reactive for transition metals, and actinides are radioactive.
::和是过渡性金属,通常置于周期表的主要部分之下,对过渡性金属而言,相对具有反应性,是放射性的。
Review
::回顾-
What are transition metals?
::什么是过渡金属? -
Describe properties of transition metals.
::描述过渡金属的特性。 -
How do transition metals differ from metals in groups 1 and 2? How are they different from all other elements?
::第1组和第2组中过渡金属与金属有何不同?它们与其他所有元素有何不同? -
Identify the lanthanides and actinides.
::识别和。
-
Transition metals are all the elements in groups 3–12 of the periodic table. More than half of all elements are transition metals.