5.8 极地
章节大纲
-
Like the north and south poles of a bar , Earth’s north and south magnetic poles—pictured above—are opposites in terms of their magnetic fields. Some types of and chemical compounds have “poles” similar to a bar magnet as well. But in the case of chemical bonds and compounds, the poles are opposites in terms of their electric charge . These bonds and compounds are described as polar .
::与酒吧的北极和南极一样,上面描绘的地球的北和南磁极就其磁场而言是相反的。 某些类型的化合物和化学化合物也有类似于铁磁铁的“极 ” 。 但是,就化学键和化合物而言,这些极在电荷方面是相反的。 这些联系和化合物被称为极地。Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
::极和非极共价债券are chemical bonds between atoms of that share . In some covalent bonds, electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms. These are called polar covalent bonds. The Figure shows the polar bonds in a water molecule (H 2 O). The oxygen attracts the shared electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms do because the nucleus of the oxygen atom has more positively charged . As a result, the oxygen atom becomes slightly negative in charge, and the hydrogen atoms become slightly positive in charge.
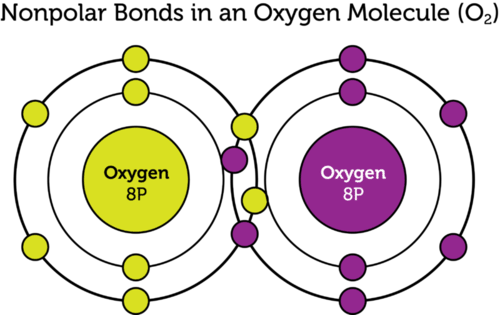
::是指该份额的原子之间的化学联系。在某些共价键中,电子不是在两个原子之间平均分享的。这称为极共价键。图中显示了水分子(H2O)中的极性联系。氧比氢原子更能吸引共享电子,因为氧原子核的电电荷增加正数。因此,氧原子在电荷中位居负数,氢原子在电荷中位居正数略为正数。In other covalent bonds, electrons are shared equally. These bonds are called nonpolar covalent bonds. Neither atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly. As a result, the atoms remain neutral in charge. The oxygen (O 2 ) molecule in the Figure has two nonpolar bonds. The two oxygen nuclei have an equal force of attraction for their four shared electrons.
::在其他共价债券中,电子被平均分享。这些债券被称为非极价共价债券。无论是原子还是原子,都无法更有力地吸引共享电子。因此,原子在电荷中仍保持中性。图中的氧(O2)分子有两个非极值债券。两个氧核对四个共享电子具有同等的吸引力。Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Compounds
::极地和无极共价化合物A covalent compound is a compound in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds. If the covalent bonds are polar, then the covalent compound as a whole may be polar. A polar covalent compound is one in which there is a slight difference in electric charge between opposite sides of the molecule. All polar compounds contain polar bonds. But having polar bonds does not necessarily result in a polar compound. It depends on how the atoms are arranged. This is illustrated in the Figure . In both molecules, the oxygen atoms attract electrons more strongly than the carbon or hydrogen atoms do, so both molecules have polar bonds. However, only formaldehyde is a polar compound. Carbon dioxide is nonpolar.
::共价化合物是原子由共价债券组合在一起的化合物。如果共价债券为极性,则共价化合物作为一个整体可以是极性。极价化合物是分子对面电荷略有差异的化合物。所有极性化合物都含有极性联结。但拥有极性联结并不一定导致极性化合物。这取决于原子是如何排列的。图中说明了这一点。在两个分子中,氧原子比碳原子或氢原子更能吸引电子,因此这两种分子都有极性联结。然而,只有甲状腺是极性的化合物。二氧化碳是非极性的。Q: Why is carbon dioxide nonpolar?
::问题:为什么二氧化碳是非极化的?A: The symmetrical arrangement of atoms in carbon dioxide results in opposites sides of the molecule having the same charge.
::A:二氧化碳中原子的对称安排导致分子的对立面产生同样的电荷。Summary
::摘要-
In polar covalent bonds, electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms, so one atom is slightly negative in charge and one is slightly positive in charge. In nonpolar covalent bonds, electrons are shared equally so the atoms remain neutral in charge.
::在极价共价债券中,电子不是在两个原子之间平均共享的,因此一个原子负责率略为负数,一个原子负责率略微正数。 在非极价共价债券中,电子平均共享,以使原子负责率保持中性。 -
Covalent compounds with polar bonds may be polar or nonpolar, depending on their arrangement of atoms.
::具有极地联结的共价化合物可能为极地或非极地,视其原子安排而定。
Review
::回顾-
What are polar covalent bonds? Give an example.
::何为极地共价债券?举个例子。 -
Why are the covalent bonds in an oxygen molecule (O
2
) nonpolar?
::为什么在氧分子(O2)的非极分子中存在共价联结? -
Carbon (C) atoms attract electrons a little more strongly than hydrogen (H) atoms do. The illustration below shows three covalent compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen atoms. Are the compounds polar or nonpolar? Explain.
::碳原子(C)吸引电子的强度比氢原子(H)吸收的强度略高。下面的插图显示了三种仅含有碳和氢原子的共价化合物。这些化合物是极性还是非极性?请解释。
Explore More
::探索更多Watch the video about polarity of molecules, and then answer the questions below.
::观看关于分子极性的视频, 然后回答下面的问题。-
When does a polar covalent bond always produce a polar covalent compound?
::何时极地共价债券总是产生极地共价化合物? -
If a covalent compound has polar bonds and more than two atoms, what determines whether the compound is polar?
::如果一种共价化合物有极地联结和两个以上原子,什么决定该化合物是否为极地? -
Is water a polar compound? Why or why not?
::水是极地化合物吗? -
Which of the following compounds are polar?
-
BF
3
::3 BF3 -
NH
3
::NH3 NH3 -
CCl
4
::CCl4 -
CHCl
3
::CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3 CHCl3
::以下哪些化合物是极性化合物? BF3 NH3 CCl4 CHCl3 -
BF
3
-
In polar covalent bonds, electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms, so one atom is slightly negative in charge and one is slightly positive in charge. In nonpolar covalent bonds, electrons are shared equally so the atoms remain neutral in charge.