2.1地球上的水
章节大纲
-
Lesson Objectives
::经验教训目标- Describe water and where it occurs on Earth.
::描述水及其在地球上的发生地点。
- Give an overview of the water cycle.
::概述水循环情况。
- Explain how the ocean is an integral part of the water cycle and is connected to all of Earth's water reservoirs via evaporation and precipitation processes.
::解释海洋如何成为水循环的一个组成部分,如何通过蒸发和降水过程与地球所有水库相连。
Lesson Vocabulary
::词汇表课程- condensation
::冷凝
- evaporation
::蒸发
- freshwater
::淡水淡水淡水
- infiltration
::渗透
- precipitation
::降水量降水量
- runoff
::径流
- transpiration
::转发
- water
::水 水
- water cycle
::水循环
Introduction
::导言Water is all around you — in pipes, in puddles, even in people. Water covers more than 70% of Earth's surface. That's a good thing, because all life on Earth depends on water. In fact, without water, life as we know it could not exist. Water is a very special substance. Do you know why?
::你们周围都是水——水管,水坑,甚至人,水覆盖了地球表面的70%以上。这是件好事,因为地球上的所有生命都依赖水。事实上,没有水,我们知道生命不可能存在。水是一种非常特殊的物质。你们知道为什么吗?What Is Water?
::水是什么东西?Water is a simple chemical compound. Each molecule of water contains two hydrogen atoms (H 2 ) and one oxygen atom (O). That's why the chemical formula for water is H 2 O.
::水是一种简单的化学化合物。每个水分子含有两个氢原子(H2)和一个氧原子(O)。这就是为什么水的化学公式是H2O。If water is so simple, why is it special? Water is one of the few substances that exists on Earth in all three states of matter. Water occurs as a gas, a liquid and a solid. You drink liquid water and use it to shower. You breathe gaseous water vapor in the air. You may go ice skating on a pond covered with solid water — ice — in the winter.
::如果水如此简单,为什么水是特别的?水是地球上所有三个物质状态中的少数物质之一;水是气体、液体和固体形式;水是液态水,用液态水淋浴;气态水蒸气在空气中呼吸;在冬天,你可以去一个水池滑冰,水池里有固体水——冰。Where Is Earth's Freshwater?
::地球的淡水在哪里?Earth is often called the “water planet.” Figure shows why. If astronauts see Earth from space, this is how it looks. Notice how blue the planet appears. That's because oceans cover much of Earth's surface. Water is also found in the clouds that rise above the planet.
::地球通常被称为“水行星 ” 。 图显示了原因。 如果宇航员从空间看到地球,那么它就会这样看。注意地球的蓝色外观。这是因为海洋覆盖了地球表面的大部分。在地球上空的云层中也发现了水。Take a look at this image. Do you think that Earth deserves the name “water planet”?
::看看这个图象。你认为地球应该称为“水行星 ” 吗?Most of Earth's water is salt water in the oceans. As Figure shows, only 3% of Earth's water is fresh. Freshwater is water that contains little or no dissolved salt. Most freshwater is frozen in ice caps and glaciers. Glaciers cover the peaks of some tall mountains. For example, the Cascade Range in North America and the Alps in Europe are capped with ice. Ice caps cover vast areas of Antarctica and Greenland. Chunks of ice frequently break off ice caps. They form icebergs that float in the oceans.
::地球的水大部分是海洋中的盐水。如图所示,地球水中只有3%是淡水。淡水是含溶盐很少或没有溶解盐的水。淡水大多被冰盖和冰川冷冻。冰川覆盖一些高山峰。例如,北美的岩礁山脉和欧洲的阿尔卑斯山脉被冰盖覆盖。冰盖覆盖了南极洲和格陵兰的广大地区。冰盖往往断裂冰盖,形成海洋中的冰山。What percentage of Earth's surface freshwater is water vapor in the air?
::空气中的水蒸气占地球地表淡水的百分比是多少?Only a tiny fraction of Earth's freshwater is in the liquid state. Most liquid freshwater is under the ground in layers of rock. Of freshwater on the surface, the majority occurs in lakes and soil. What percentage of freshwater on the surface is found in living things?
::地球淡水中只有一小部分是液态的,大部分液态淡水在地下的岩石层中,在地表淡水中,大部分在湖泊和土壤中。The Water Cycle
::水循环Did you ever wonder where the water in your glass came from or where it's been? The next time you take a drink of water, think about this. Each water molecule has probably been around for billions of years. That's because Earth's water is constantly recycled.
::你有没有想过你的玻璃杯里的水是从哪里来的,还是从何而来?下一次你喝水的时候,想想这个。每个水分子可能已经存在了数十亿年。这是因为地球的水不断被回收。How Water Is Recycled
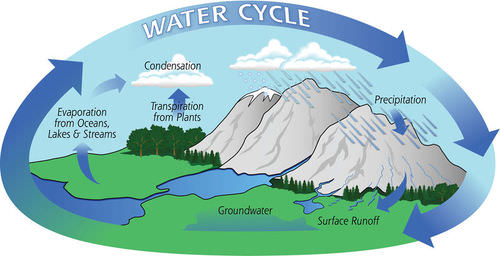
::水如何循环利用Water is recycled through the water cycle. The water cycle is the movement of water through the oceans, atmosphere, land, and living things. The water cycle is powered by energy from the Sun. Figure diagrams the water cycle.
::水循环是通过水循环回收的,水循环是水通过海洋、大气、土地和生物物质流动。水循环是由太阳的能量驱动的。图示水循环。The water cycle has no beginning or end. Water just keeps moving along.
::水循环没有开始或结束,水只是继续前进。Processes in the Water Cycle
::水循环过程Water keeps changing state as it goes through the water cycle. This means that it can be a solid, liquid, or gas. How does water change state? How does it keep moving through the cycle? As Figure shows, several processes are involved.
::当水经过水循环时,水的状态不断变化。 这意味着水可以是固体、液体或气体。 水的变化状况如何? 它是如何在循环中不断移动的? 如图所示,它涉及几个过程。- Evaporation changes liquid water to water vapor. Energy from the sun causes water to evaporate. Most evaporation is from the oceans because they cover so much area. The water vapor rises into the atmosphere.
::蒸发将液态水变成水蒸气。太阳产生的能量导致水蒸发。大部分蒸发来自海洋,因为它们覆盖了太多的区域。水蒸发进入大气。
- Transpiration is like evaporation because it changes liquid water to water vapor. In transpiration, plants release water vapor through their leaves. This water vapor rises into the atmosphere.
::蒸发就像蒸发一样,因为它将液态水变成水蒸气。在蒸发中,植物通过叶子释放出水蒸气。这种水蒸气会向大气中喷发。
- Condensation changes water vapor to liquid water. As air rises higher into the atmosphere, it cools. Cool air can hold less water vapor than warm air. So some of the water vapor condenses into water droplets. Water droplets may form clouds.
::凝聚会将水蒸气变成液态水。 当空气升到大气中时, 空气会冷却。 冷空气会比暖气少吸收水蒸气。 因此有些水蒸气会凝聚到水滴中。 水滴可能会形成云。
- Precipitation is water that falls from clouds to Earth's surface. Water droplets in clouds fall to Earth when they become too large to stay aloft. The water falls as rain if the air is warm. If the air is cold, the water may freeze and fall as snow, sleet, or hail. Most precipitation falls into the oceans. Some falls on land.
::降水是从云层流到地球表面的水; 云层中的水滴在云体太大而不能停留在高空时落到地球; 雨水降得像雨水一样,如果空气是温暖的。 如果空气是寒冷的,水会像雪、冰水或冰雹一样冷冻和落下。 大部分降水都落在海洋中。 有些降水落在陆地上。
- Runoff is precipitation that flows over the surface of the land. This water may travel to a river, lake, or ocean. Runoff may pick up fertilizer and other pollutants and deliver them to the water body where it ends up. In this way, runoff may pollute bodies of water.
::径流是指在陆地表面流动的降水,这种水可能流向河流、湖泊或海洋,径流可能收集肥料和其他污染物,并将它们送到水体中,这样,径流可能会污染水体。
- Infiltration is the process by which water soaks into the ground. Some of the water may seep deep underground. Some may stay in the soil, where plants can absorb it with their roots.
::渗入过程是水渗入地下的过程,有些水可能渗入地下深处,有些可能留在土壤中,植物可以用其根部吸收土壤。
If you look at the image above, it looks like the water cycle occurs mostly over land. That is far from the reality. In fact, the oceans are a critical part of the water cycle. Can you think why that may be?
::如果你看看上面的图象, 水循环似乎主要发生在陆地上。 这与现实相去甚远。 事实上,海洋是水循环的关键部分。 你能想到为什么吗?The oceans are an essential part of Earth's water cycle for one simple reason. Oceans cover about 2/3 of the Earth's surface. As a result, most comes from oceans. Most also occurs over the oceans.
::海洋是地球水循环的一个基本部分,原因很简单。海洋覆盖地球表面的2/3。因此,大部分来自海洋,大部分也发生在海洋上。In all these ways, water keeps cycling. The water cycle repeats over and over again. Who knows? Maybe a water molecule that you drink today once quenched the thirst of a dinosaur.
::在所有这些方面,水都是循环的。水循环反复重复。谁知道呢?也许今天你喝的水分子 曾经解开了恐龙的渴求。Lesson Summary
::经验教训摘要- Water is a simple chemical compound. It exists on Earth in all three states of matter: liquid, gas, and solid. As a gas, water is called water vapor. As a solid, water is called ice.
::水是一种简单的化学化合物。它存在于地球上所有三个物质状态:液体、气体和固体。水作为一种气体,被称为水蒸气。作为固体,水被称为冰。
- Oceans of salt water cover much of Earth's surface. Freshwater is water that contains little or no salt. Most of Earth's freshwater is frozen in ice caps and glaciers.
::淡水是含盐量很少或根本没有盐的水,地球淡水大多被冰盖和冰川冻结。
- Earth's water is constantly recycled through the water cycle. Water keeps changing state as it goes through the cycle. The water cycle includes processes such as evaporation, condensation, and precipitation.
::地球的水不断通过水循环循环循环循环循环。水在循环周期中不断变化。水循环包括蒸发、凝聚和降水等过程。
Lesson Review Questions
::经验回顾问题Recall
::回顾- What is freshwater?
::什么是淡水?
- Where is most of Earth's freshwater found?
::地球上大部分淡水在哪里?
- What process changes water from a liquid to a gas? From a gas to a liquid?
::是什么过程将水从液态改变为气体?从气体改变为液态?
- Define infiltration and runoff.
::定义渗透和径流
Apply Concepts
::应用概念- Describe the substance known as water.
::描述被称为水的物质。
- Why does most precipitation fall into the oceans?
::为什么大部分降水都掉入海洋?
Think Critically
::仔细仔细思考- Apply lesson concepts to explain how a forest fire might affect the water cycle.
::运用教训概念来解释森林火灾如何影响水循环。
- Explain why this statement is true: “The water you drink today may once have quenched the thirst of a dinosaur.”
::解释为什么这句话是真的:“今天你喝的水可能曾经消除了恐龙的口渴。”
- How does the Sun drive the water cycle? What would happen to the water cycle if the Sun decreased its intensity by half?
::太阳如何驱动水循环?如果太阳将强度降低一半,水循环会怎样?
Points to Consider
::需要考虑的要点As water moves through the water cycle, it spends some time on Earth's surface as freshwater.
::当水经过水循环时 它会花一些时间 在地表的淡水上- Where is freshwater found on Earth's surface?
::地球表面哪里有淡水?
- How do people use freshwater on Earth's surface?
::人们如何使用地球表面的淡水?
- Describe water and where it occurs on Earth.