2.31 单元司
章节大纲
-
What you will learn
::你会学到什么-
What is cell division
::什么是单元格分区 -
Cell division process in
and
eukaryotes
::细胞分裂过程和eukaryotes
Where do cells come from?
::细胞从哪里来?No matter what the , all cells come from preexisting cells through the process of cell division. The cell may be the simplest , or a complex muscle, , or cell. The cell may comprise the whole organism , or be just one cell of trillions.
::无论细胞是什么,所有细胞都是通过细胞分裂过程从原有的细胞中产生的。细胞可能是最简单的,或者一个复杂的肌肉,或者一个细胞。细胞可以是整个有机体,或者只是一个数万亿的细胞。Cell Division
::单元司You consist of a great many cells, but like all other organisms, you started life as a single cell. How did you develop from a single cell into an organism with trillions of cells? The answer is cell division. After cells grow to their maximum size, they divide into two new cells. These new cells are small at first, but they grow quickly and eventually divide and produce more new cells. This process keeps repeating in a continuous cycle.
::您是由众多的细胞组成, 但和所有其他生物一样, 您开始作为一个单一的细胞生活。 您是如何从一个单细胞发展成一个拥有数万亿个细胞的有机体的? 答案是细胞分裂。 当细胞成长到最大尺寸后, 它们会分成两个新的细胞。 这些新的细胞最初很小, 但是它们会迅速成长, 最终会分裂并产生更多的新的细胞。 这个过程会连续循环重复 。Cell division is the process in which one cell, called the parent cell , divides to form two new cells, referred to as daughter cells . How this happens depends on whether the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
::细胞分裂是一个名为父细胞的细胞分裂成两个新细胞的过程,称为女儿细胞。这取决于该细胞是prokarytology还是 eukaryatic。Cell division is simpler in prokaryotes than eukaryotes because prokaryotic cells themselves are simpler. Prokaryotic cells have a single circular , no , and few other cell structures . Eukaryotic cells , in contrast, have multiple chromosomes contained within a nucleus, and many other . All of these cell parts must be duplicated and then separated when the cell divides. A chromosome is a coiled structure made of and , and will be the focus of a subsequent concept.
::在prokaryotes中,细胞分裂比eukaryotes更简单,因为蛋白质细胞本身比较简单。Prokaryote细胞有一个单环,没有,其他细胞结构也很少。相反,Eukaryote细胞在核中含有多个染色体,而其他细胞结构则很多。所有这些细胞部分必须重复,然后在细胞分裂时分离。染色体是一个循环结构,由(或)组成,并且将成为下一个概念的焦点。Cell Division in Prokaryotes
::Prokaryotes 的单元格分区Most prokaryotic cells divide by the process of binary fission .
::大部分蛋白质细胞 被二进制裂变过程分割开来Steps of Binary Fission. Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission. This is also how many single-celled organisms reproduce. Binary fission can be described as a series of steps, although it is actually a continuous process. The steps are described below and also illustrated in the Figure . They include DNA replication , chromosome segregation, and finally the separation into two daughter cells.
::二进制裂变可以描述为一系列步骤,尽管它实际上是一个持续的过程,下文将描述这些步骤,图中也说明了这些步骤。这些步骤包括DNA复制、染色体隔离以及最后将两个女儿细胞分离。-
Step 1: DNA Replication. Just before the cell divides, its DNA is copied in a process called DNA replication. This results in two identical chromosomes instead of just one. This step is necessary so that when the cell divides, each daughter cell will have its own chromosome.
::第一步 : DNA复制。 就在细胞分裂之前, 它的DNA被复制到一个叫做DNA复制的过程。 这导致两个相同的染色体, 而不是一个。 这个步骤是必要的, 这样当细胞分裂的时候, 每个女儿的细胞都会有自己的染色体 。 -
Step 2: Chromosome Segregation. The two chromosomes segregate, or separate, and move to opposite ends (known as "poles") of the cell. This occurs as each copy of DNA attaches to different parts of the
.
::第2步:染色体隔离。两种染色体分离或分离,并移动到细胞的对面(称为“极”)。当每一份DNA副本附着在细胞的不同部分时,就会发生这种情况。 -
Step 3: Separation. A new plasma membrane starts growing into the center of the cell, and the
cytoplasm
splits apart, forming two daughter cells. As the cell begins to pull apart, the new and the original chromosomes are separated. The two daughter cells that result are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. New
cell wall
must also form around the two cells.
::步骤 3 : 分离。 一个新的等离子膜开始生长到细胞中心, 细胞顶板裂开, 形成两个女儿细胞。 随着细胞开始分离, 新的和原有的染色体被分离。 产生结果的两个女儿细胞在基因上彼此和母细胞相同。 新的细胞墙也必须在两个细胞周围形成 。
Cell Division in Eukaryotes
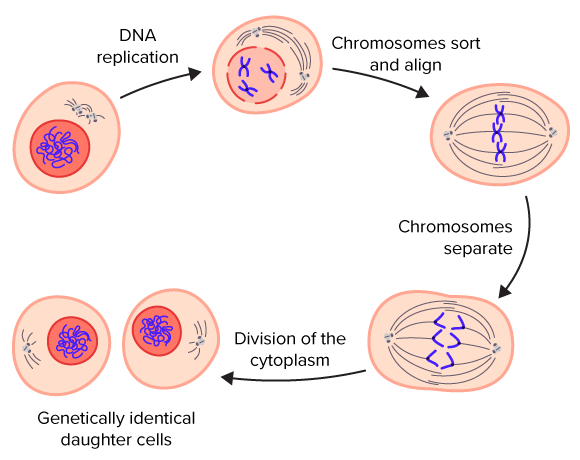
::Eukaryotes 的单元格分区Cell division is more complex in eukaryotes than prokaryotes. Prior to dividing, all the DNA in a eukaryotic cell’s multiple chromosomes is replicated. Its organelles are also duplicated. Then, when the cell divides, it occurs in two major steps:
::在 eukaryotes 中细胞分裂比 prokaryotes 更为复杂。 在分割之前, eukaryotes 中的所有DNA都会被复制。 它的有机体也会被复制。 当细胞分裂时, 它会分为两大步:-
The first step is
, a multi-phase process in which the nucleus of the cell divides. During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks down and later reforms. The chromosomes are also sorted and separated to ensure that each daughter cell receives a
diploid
number (2 sets) of chromosomes. In humans, that number of chromosomes is 46 (23 pairs). Mitosis is described in greater detail in a subsequent concept.
::第一步是一个多阶段的过程,在这个过程中细胞的核心会分裂。在分裂过程中,核膜断裂和后来的改革。染色体也进行分类和分离,以确保每个女儿的细胞得到染色体的分数(2套)。在人类中,染色体的数量为46种(23对)。随后的观念中将更详细地描述调和。 -
The second major step is
cytokinesis
. As in prokaryotic cells, the cytoplasm must divide. Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells.
::第二大步骤是细胞基质。 与蛋白质细胞一样,细胞基质必须分裂。 细胞基质是细胞基质细胞中细胞基质的划分,导致两个遗传上相同的母细胞。
Steps of cell division in eukaryotes. Science Friday : The Axolotl: A Cut Above the Rest
::科学周五:Axolotl:The axolotl is an with the incredible ability to regenerate its legs. In this video by Science Friday , Dr. Susan Bryant discusses the research on how these animals are able to accomplish this amazing feat.
::轴旋藻具有令人难以置信的再生腿的能力。在科学周五的这段视频中,苏珊·布赖恩特博士讨论了研究这些动物如何取得这一惊人成就的问题。
Summary
::摘要-
Cell division is part of the life cycle of virtually all cells. Cell division is the process in which one cell divides to form two new cells.
::细胞分裂是几乎所有细胞生命周期的一部分,细胞分裂是一个细胞分裂形成两个新细胞的过程。 -
Most prokaryotic cells divide by the process of binary fission.
::大部分蛋白质细胞 被二进制裂变过程分割开来 -
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major steps: mitosis and cytokinesis.
::在eukaryotes,细胞分裂分为两个主要步骤:肺硬化和细胞基质。
Review
::回顾-
Describe binary fission.
::描述二进制裂变 -
What is mitosis?
::什么是分裂症? -
Contrast cell division in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Why are the two types of cell division different?
::直方圆形和eukaryotes 的对等细胞分裂。 为什么两种细胞分裂不同?
-
What is cell division