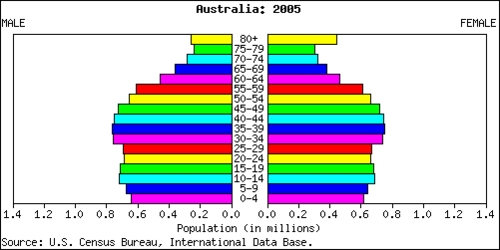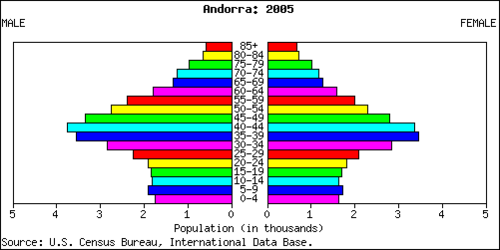2.1 人口和文化(5天)
章节大纲
-
Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Explain the
process. Understand the concept of
carrying capacity
as it relates to the planet’s
.
::解释这一过程。理解承载能力的概念,因为它与地球有关。 -
Outline the relationship between urbanization and family size. Show how the rural-to-urban shift relates to industrialization and the change in rural populations.
::概述城市化与家庭规模之间的关系,说明农村向城市的转变与工业化和农村人口变化的关系。 -
Draw or paste a
population pyramid
from this section, and interpret and infer trends from a population pyramid.
::从这一部分绘制或粘贴人口金字塔,解释和推断人口金字塔的趋势。 -
Determine if the population is increasing or declining and if the pace of growth is intensifying or slowing.
::确定人口是否在增加或下降,增长率是否在加快或放慢。 -
Explain the difference between the concepts of culture and ethnicity as
referenced
in this book.
::解释本书中提到的文化和族裔概念之间的区别。 -
Explain the difficulty in determining the number of languages and religions existing on Earth.
::解释为何难以确定地球上现有语言和宗教的数量。 -
List the main language families and the world’s major religions.
::列出主要语言系和世界主要宗教。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 02 Human Geographic Systems Chapter 2.1 Population and Culture
::TEKS 区域单位 02 人类地理系统WG.5A Analyze how the character of a place is related to its political, economic, social, and cultural elements
::WG.5A 分析一个地方的特征如何与其政治、经济、社会和文化因素相关WG.5B Interpret political, economic, social, and demographic indicators (gross domestic product per capita, life expectancy, literacy, and infant mortality) to determine the level of and standard of living in nations using the terms Human Development Index, less developed, newly industrialized, and more developed
::WG.5B 解释政治、经济、社会和人口指标(人均国内生产总值、预期寿命、识字率和婴儿死亡率),以确定使用人类发展指数、欠发达、新兴工业化和较发达等术语的国家的生活水平和生活水平WG.6B Explain the processes that have caused changes in settlement patterns, including urbanization, transportation, access to and availability of resources, and economic activities.
::WG.6B 解释导致住区模式变化的进程,包括城市化、运输、获得和获得资源以及经济活动。WG.7A Construct and analyze population pyramids and use other data, graphics, and maps to describe the population characteristics of different societies and to predict future population trends
::WG.7A 建立和分析人口金字塔,利用其他数据、图表和地图描述不同社会的人口特征,预测未来人口趋势WG.7C Describe trends in world and distribution.
::WG.7C 描述世界和分布的趋势。WG.9A Identify physical and/or human factors such as climate , vegetation, language, trade networks, political units, river systems, and religion that constitute a region
::WG.9A 查明构成区域的气候、植被、语言、贸易网络、政治单位、河流系统和宗教等有形和/或人为因素WG.13B Compare maps of voting patterns or political boundaries to make inferences about the distribution of political power.
::WG.13B 比较投票模式或政治边界地图,以推断政治权力的分配。WG.14BCompare how democracy, dictatorship, monarchy, republic, theocracy, and totalitarian systems operate in specific countries
::WG.14B 比较民主、独裁、君主制、共和国、专制和极权制度如何在特定国家运作WG.16C Explain ways various groups of people perceive the characteristics of their own and other cultures, places, and regions differently.
::WG.16C 解释不同群体对自身和其他文化、地方和区域特征的不同看法。WG.17B Describe major world religions, including Animism, Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, Islam, Judaism, Sikhism, and their spatial distribution.
::WG.17B 描述世界主要宗教,包括Animis、佛教、基督教、印度教、伊斯兰教、犹太教、锡克教及其空间分布。WG.21B Describe the rights and responsibilities of citizens and noncitizens in civic participation throughout history
::WG.21B 说明公民和非公民在整个历史上公民参与公民事务的权利和义务WG.21C Create and interpret different types of maps to answer geographic questions, infer relationships, and analyze change
::WG.21C 建立和解释不同类型的地图,以解答地理问题、推断关系和分析变化Population and Culture
::人口与文化Demographic Transition
::人口人口结构过渡Demography is the study of how human populations change over time and space. It is a branch of human geography related to population geography, which is the examination of the spatial distribution of human populations. Geographers study how populations grow and migrate, how people are distributed around the world, and how these distributions change over time. For most of human history, relatively few people lived on Earth and the world population grew slowly. Only about 500 million people lived on the entire planet in 1650 (that’s less than half of India’s population in 2000).
::人口学是人类人口随时间和空间的变化而变化的研究,它是与人口地理有关的人类地理分支,与人口地理分布有关,这是对人口空间分布的研究。 地理学家研究人口的增长和移徙情况、人口在世界各地的分布以及这些分布如何随时间的变化。 在人类历史上的多数人中,生活在地球上的人口相对较少,世界人口增长缓慢。 1650年,只有大约5亿人生活在整个地球上(2000年印度人口不到一半 ) 。Things changed dramatically during Europe’s Industrial Revolution in the late 1700s and into the 1800s when declining death rates due to improved nutrition and sanitation allowed more people to survive to and reproduce. The population of Europe grew rapidly. However, by the middle of the twentieth century, birth rates in developed countries declined, as children had become an economic liability rather than an economic asset to families. Fewer families worked in , more families lived in urban areas, and women delayed the age of marriage to pursue education, resulting in a decline in family size and a slowing of population growth. In some countries (e.g., Russia and Japan), the population is actually in decline, and the average age in developed countries has been rising for decades. The process just described is called the demographic transition .
::在1700年代末的欧洲工业革命期间,情况发生了巨大变化,到了1800年代,由于营养和卫生条件的改善,死亡率的下降使得更多的人得以生存和繁殖。 欧洲的人口迅速增长。 但是,到20世纪中叶,发达国家的出生率有所下降,因为儿童已成为家庭的经济负担而不是经济资产。 较少的家庭在城市工作,更多的家庭生活在城市地区,妇女推迟了结婚年龄以接受教育,导致家庭规模下降,人口增长放缓。 在某些国家(如俄罗斯和日本),人口实际上在下降,发达国家的平均年龄在几十年里一直在上升。 刚刚描述的过程被称为人口转型。
The Demographic Transition Model is the transition from higher birth and death rates to lower birth and death rates as a country or region develops from pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system.
::人口过渡模式是随着一个国家或地区从工业化前发展到工业化经济体系,从较高的出生和死亡率向较低的出生和死亡率的过渡。
At the beginning of the 20th century, the world’s population was about 1.6 billion. One hundred years later, there were roughly six billion people in the world, and as of 2018, the population is approximately 7.6 billion. This rapid growth occurred as the demographic transition spread from developed countries to the rest of the world. During the 20th century, death rates due to disease and malnutrition decreased in nearly every corner of the globe. In developing countries with agricultural societies, however, birth rates remained high. Low death rates and high birth rates resulted in rapid population growth.
::20世纪初,世界人口约为16亿。 一百年后,全世界人口约为60亿,到2018年,人口约为76亿。 这一快速增长随着人口从发达国家向世界其他地方的转移而出现。 在20世纪初,全球几乎每个角落的疾病和营养不良死亡率都有所下降。然而,在拥有农业社会的发展中国家,出生率仍然居高不下。低死亡率和高出生率导致人口快速增长。Meanwhile, birth rates and family size have also been declining in most developing countries as people leave agricultural professions for urban areas. This means that population growth rates—while still higher in the developing world than in the developed world—are declining. Although the exact figures are unknown, demographers expect the world’s population to stabilize by 2100 and then decline somewhat.
::与此同时,在大多数发展中国家,随着人们离开农业职业到城市地区,出生率和家庭规模也在下降,这意味着人口增长率正在下降 — — 尽管发展中世界比发达世界还要高。 尽管确切数字未知,但人口统计学家预计到2100年世界人口将稳定下来,然后略有下降。In 2010, the world’s population was growing by about 80 million people per year, a growth rate found almost exclusively in developing countries, as populations are stable or in decline in places such as Europe and North America. World population increase is more pronounced on the continent of Asia. Moreover, China and India are the most populous countries in the world, each with more than a billion people. Pakistan is an emerging population giant with a high rate of population growth. The continent of Africa has the highest fertility rates in the world, with countries such as Nigeria—Africa’s most populous and the world’s eighth most populous country—growing rapidly each year.
::2010年,世界人口每年增长约8 000万,增长率几乎完全在发展中国家,因为人口稳定或欧洲和北美等地的人口减少。 世界人口的增长在亚洲大陆更为明显。 此外,中国和印度是世界上人口最多的国家,每个人口都超过10亿。 巴基斯坦是一个新兴人口巨头,人口增长率很高。 非洲大陆的生育率是世界上最高的国家,尼日利亚等非洲人口最多的国家和世界第八大人口最多的国家每年都迅速增长。The most striking paradox within population studies is that while there has been marked decline in fertility (a declining family size) in developing countries, the world’s population will grow substantially by 2030 because of the compounding effect of a large number of people already in the world—that is, even though population growth rates are in decline in many countries, the population is still growing. A small growth rate on a large base population still results in the birth of many millions of people.
::人口研究中最引人注目的矛盾是,虽然发展中国家生育率明显下降(家庭规模下降),但到2030年世界人口将大幅增长,因为世界上已经有大量人口——尽管许多国家的人口增长率正在下降,但人口仍在增长。 大量基础人口的低增长率仍然导致数百万人的出生。Earth’s human population is growing at a rate of about 1.4 percent per year. If the current growth rate continues, the human population will double in about 50 years to more than 12 billion. The current population increase remains at about 80 million per year. A change in the growth rate will change the doubling time. Between 2010 and 2050, world population growth will be generated exclusively in developing countries.
::地球人口正在以每年约1.4 % 的增长率增长。 如果目前的增长率继续下去,人口将在50年后翻一番,达到120亿以上。 目前的人口增长率仍保持在每年8000万左右。 增长率的改变将改变翻一番的时间。 2010年至2050年间,世界人口增长将完全来自发展中国家。The three largest population clusters in the world are the regions of eastern China, South Asia, and Europe. Southeast Asia also has large population clusters. Additional large population centers exist in various countries with high urbanization. An example is the urbanized region between Boston and Washington, DC, which includes New York City, Philadelphia, Baltimore, and neighboring metropolitan areas, resulting in a region often called a megalopolis. The coastal country of Nigeria in West Africa or the island of Java in Indonesia are good examples of large population clusters centered in the tropics.
::世界上最大的三个人口集群是中国东部、南亚和欧洲地区。东南亚也有大量人口集群。在城市化程度高的不同国家,还存在更多的大型人口中心。例如波士顿和华盛顿特区之间的城市化地区,包括纽约市、费城、巴尔的摩和邻近大都会地区,导致一个经常被称为大都市的地区。 西非的尼日利亚沿海国家或印度尼西亚的爪哇岛就是以热带为中心大型人口集群的良好例子。
Jakarta, Indonesia, is located on the northwest coast of the world's most populous island of Java.
::印度尼西亚雅加达位于世界人口最多的爪哇岛西北海岸。
Social dynamics and geography will determine where the new additions to the human family will live. Providing food , energy , and materials for these additional humans will tax many countries of the world. Poverty, malnutrition, and disease are expected to increase in regions with poor sanitation, limited clean , and lack of economic resources. In 2018, more than one-third of the planet’s population live in poverty and earn less than the equivalent of two US dollars per day. The carrying capacity of the planet is not and cannot be known. How many humans can the earth sustain in an indefinite manner? There is the possibility that we have already reached the threshold of its carrying capacity.
::社会动态和地理将决定人类家庭的新增加将在哪里生存。 为这些新增人类提供食物、能源和材料将给世界许多国家带来负担。 在卫生条件差、清洁程度有限和经济资源匮乏的地区,贫困、营养不良和疾病预计会增加。 2018年,全球三分之一以上的人口生活在贫困之中,每天收入不到两美元。 地球的承载能力现在和现在都无法知晓。 地球可以无限期地维持多少人类?我们有可能已经达到其承载能力的极限。Human population will continue to grow until it either crashes due to the depletion of resources or stabilizes at a sustainable carrying capacity. Population growth exacts a toll on the earth as more people use more environmental resources. The areas most immediately affected by increased populations include forests (a fuel resource and a source of building material), fresh water supplies, and agricultural soils. These systems get overtaxed, and their depletion has serious consequences.
::人类人口将继续增长,直到资源耗竭或稳定在可持续的承载能力下。随着更多的人使用更多的环境资源,人口增长给地球造成了巨大损失。 受人口增加最直接影响的地区包括森林(燃料资源和建筑材料的来源 ) 、 淡水供应和农业土壤。 这些系统过度劳累,其耗竭产生了严重后果。Type C climates, which are moderate and , are usually the most productive and are already vulnerable to serious deforestation, , and soil erosion. Maintaining adequate food supplies will be critical to supporting a sustainable carrying capacity. The ability to transport food supplies quickly and safely is a major component of the ability to manage the of resources. Deforestation by humans using wood for cooking fuel is already a serious concern in the arid and dry type B climates.
::C型气候是中度气候,通常产量最高,已经易受严重毁林、土壤侵蚀的影响。维持足够的粮食供应对于支持可持续的承载能力至关重要。快速和安全运输粮食供应的能力是管理资源能力的重要组成部分。用木柴作为炊事燃料的人砍伐森林已经是干旱和干旱的B型气候的严重关切。Urbanization and Family Size
::城市化和家庭规模As countries move from an agricultural to an industrial economy, there is a major shift in population from rural to urban settings. The Industrial Revolution of the 19th century ushered in major technological developments and changes in labor practices, which encouraged from the farm to the city. Because of increased mechanization, fewer farm workers are needed to produce larger agricultural yields. At the same time, factories in urban areas have a great need for industrial workers. This shift continued into the information age of the late 20th century and continues in many parts of the developing world in the current century.
::随着国家从农业经济向工业经济的转变,人口从农村向城市发生了重大变化。 19世纪的工业革命带来了从农场到城市的大规模技术发展和劳工做法变化,从农场到城市都鼓励了这些变化。由于机械化程度的提高,生产更大农业产量需要的农业工人就更少了。与此同时,城市地区的工厂对工业工人的需求也很大。这一转变继续到20世纪末的信息时代,并且在本世纪发展中世界的许多地区仍在继续。A basic principle of population growth that addresses this rural-to-urban shift states that as countries industrialize and urbanize, family size typically decreases and incomes traditionally increase. Though this may not be true in all cases, it is a general principle that is consistent across cultural lines. Agricultural regions generally have a larger average family size than that of their city counterparts. The fertility rate is the average number of children a woman in a particular country has in her lifetime, whether or not they all live to adulthood.
::解决农村向城市的这一转变的人口增长基本原则指出,随着国家工业化和城市化,家庭规模通常会减少,传统上收入会增加,尽管并非所有情况都如此,但这是一项贯穿不同文化的一般原则,农业地区一般平均家庭规模大于城市对口地区,生育率是特定国家妇女一生中的平均子女数量,无论她们是否都成年。If a fertility rate for a given country is less than 2.1—the replacement level—the population of that country is in decline, unless there is significant immigration . A fertility rate greater than 2.1 indicates that the country’s population is increasing. Some children will never reach reproductive age or have children of their own, so the replacement rate has to be slightly greater than two. The concept of fertility rate is slightly different from the term family size, which indicates the number of living children raised by a parent or parents in the same household. In this textbook, family size is used to illustrate the concept of population growth and decline.
::如果一个国家的生育率低于2.1(更替水平),该国的人口将下降,除非有大量移民。生育率高于2.1表明该国的人口正在增加。有些儿童将永远不会达到生育年龄或生育自己的子女,因此更替率必须略高于2。生育率的概念与家庭规模的概念略有不同,家庭规模是指父母或父母在同一家庭中抚养的活子女数量。在教科书中,家庭规模用来说明人口增长和下降的概念。Population Demands
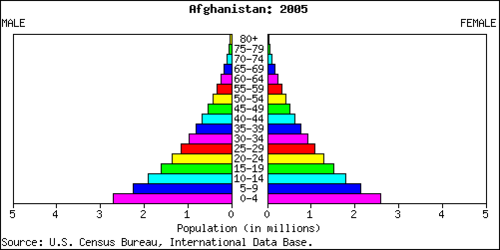
::人口需求A country’s demographic statistics can be illustrated graphically by a population pyramid. A population pyramid is essentially two bar graphs that depict male and female age cohorts either in absolute size or as a percentage of the total population. Male cohorts are typically shown on the left side of the pyramid and females are on the right side. The three pyramid types are rapid growth, slow growth, and negative growth.
::一个国家的人口统计可以用人口金字塔的图形来说明。 人口金字塔基本上是两个条形图,以绝对规模或占总人口的百分比来显示男女年龄组群。 男性组群通常出现在金字塔的左侧,女性则在右侧。 三种金字塔类型是快速增长、缓慢增长和负增长。
This population pyramid of Afghanistan is an example of rapid growth.
::阿富汗的这个人口金字塔就是快速增长的一个例子。This population pyramid of Australia is an example of slow growth.
::澳大利亚的这个人口金字塔就是缓慢增长的一个例子。This population pyramid of Andorra is an example of negative growth.
::安道尔的这个人口金字塔就是负增长的例子。
The shape of a country’s population pyramid tells a story about the history of its population growth. For example, a high-growth-rate country has a pyramid that is narrow at the top and wide at the bottom, showing that every year more children have been born than the year before. As family size decreases and women in a society have fewer children, the shape of the pyramid changes. A population pyramid for a post-industrialized country that has negative growth would be narrower at the bottom than in the middle, indicating that there are fewer children than middle-aged people. These shapes also illustrate the percentage of a population under the age of 15 or over the age of 65, which are standard indicators of population growth. Many post-industrial countries have a negative population growth rate . Their population pyramids are narrow at the bottom, indicating an urbanized population with small family sizes.
::一国人口金字塔的形状描述了其人口增长的历史。 比如,高增长率国家的金字塔在顶部和底部都非常狭窄,表明每年出生的儿童比前一年要多。随着家庭规模的减少,社会中妇女生育的子女较少,金字塔的形状也发生了变化。 后工业化国家人口金字塔的负增长在底部比中层要窄,表明儿童比中层人口少。 这些形状还显示了15岁以下或65岁以上人口的比例,这是人口增长率的标准指标。 许多后工业国家的人口增长率是负数的。 其人口金字塔在底部是狭窄的,表明人口规模小于家庭规模的城市化人口。Culture and Ethnicity
::文化与族裔The term culture is often difficult to differentiate from the term ethnicity. In this textbook, ethnicity indicates traits people are born with, including genetic backgrounds, physical features, or birthplaces. People have little choice in matters of ethnicity. The term culture indicates what people learn after they are born, including language, religion, and customs or traditions. Individuals can change matters of culture by individual choice after they are born. These two terms help us identify human patterns and understand a country’s driving forces.
::文化一词往往很难与种族一词区分。在本教科书中,种族是指人出生的特征,包括遗传背景、身体特征或出生地。人们在种族问题上没有什么选择。文化一词指人们出生后学习什么,包括语言、宗教和习俗或传统。个人出生后可以通过个人选择改变文化事务。这两个术语有助于我们识别人类模式和理解国家的驱动力。The terms culture and ethnicity might also be confused in the issue of ethnic cleansing, which refers to the forced removal of a people from their homeland by a stronger force of a different people. Ethnic cleansing might truly indicate two distinct ethnic groups: one driving the other out of their homeland and taking it over. On the other hand, ethnic cleansing might also mean cultural cleansing if both the aggressor and the group driven out are of the same ethnic stock but hold different cultural values, such as religion or language. The term ethnic cleansing has been used to describe either case.
::在种族清洗问题上,文化和族裔一词也可能被混淆。 种族清洗是指用一个不同民族的更强大力量强迫一个民族离开自己的家园。种族清洗可能真正地表明两个不同的族裔群体:一个将另一个民族赶出自己的家园并接管家园。另一方面,种族清洗还可能意味着文化清洗,如果侵略者和被赶出家园的群体都属于同一个民族,但持有不同的文化价值,例如宗教或语言。种族清洗一词被用来描述这两种情况。Languages of the World
::世界语文:世界语文Language is the mode of human culture and it represents the complete diversity of thought, literature, and the arts. All the billions of people on the planet speak at least one language. While Ethnologue , a publication pertaining to the world’s languages, estimates that there were 6,909 living languages in the world as of 2009, the exact number may never be determined. Other data sets count languages differently, but most agree that there are more than 6,000. There are communities in various parts of the world where people can communicate by whistling messages to each other or by using clicking sounds.
::语言是人类文化的一种模式,它代表着思想、文学和艺术的完全多样性。 地球上的数十亿人至少讲一种语言。 与世界语言有关的一份出版物《民族对话 》 ( Ethnologue)估计,截至2009年,世界上有6,909种活语言,确切数量可能永远无法确定。 其他数据集对语言的计算不同,但大多数都同意有超过6,000种语言。 世界各地都有社区,人们可以通过吹呼或点击声音相互沟通。
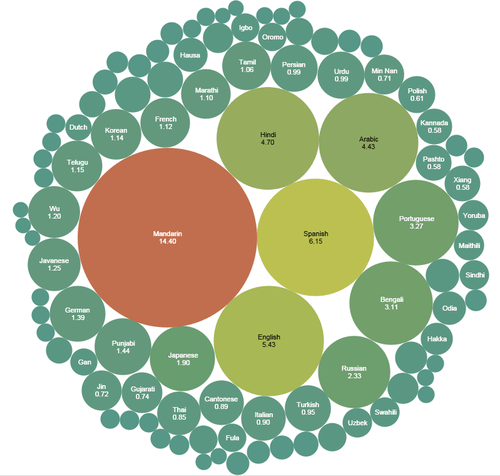
This bubble chart illustrates the languages by the proportion of native speakers worldwide from Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007).
::这个泡沫图按来自Mikael Parkvall(2007年《世界100大语言》)“Världens 100 störstta språk 2007”(2007年《世界100大语言》)的全世界本地语使用者比例来说明语言。
Of the more than 6,000 languages, about a dozen are spoken by more than 100 million people each. These are the world’s main languages used in the most populous countries. However, the vast majority of the world’s languages are spoken by a relatively small number of people. In fact, many languages have no written form and are spoken by declining numbers of people. Language experts estimate that up to half the world’s living languages could be lost by the end of the 21st century as a result of globalization. New languages form when populations live in isolation, and in the current era, as the world’s populations are increasingly interacting with each other, languages are being abandoned and their speakers are switching to more useful tongues.
::在6000多种语言中,约有十几种语言由1亿多人使用,这些是世界在人口最多国家使用的主要语言,然而,世界上绝大多数语言由相对较少的人使用,事实上,许多语言没有书面形式,而且使用的人数正在减少。 语言专家估计,到21世纪末,由于全球化,世界上有多达一半的活语言可能会丧失。 当人们与世隔绝地生活时,新语言就成为了新语言形式,在当今时代,随着世界人口日益相互交流,语言正在被抛弃,语言正在转向更有用的语言。
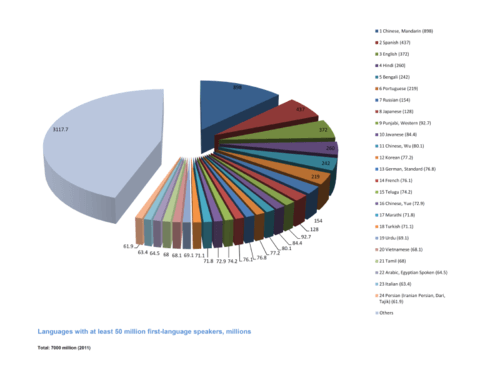
This pie chart shows the languages of the world with at least 50 million first-language speakers (in millions).
::本饼图显示世界语言,至少有5 000万第一语言使用者(百万)。
There are nine dominant language families in the world. Each of the languages within a language family shares a common ancestral language. An example of a language family is the Indo-European family, which has a number of branches of language groups that come from the same base: a language called Proto-Indo-European that was probably spoken about 6,000 years ago. As populations migrated away from the ancestral homeland, their language evolved and separated into many new languages. The three largest language groups of the Indo-European family used in Europe are the Germanic, Romance, and Slavic groups. Other Indo-European languages include Hindi (spoken in India) and Persian (spoken in Iran).
::世界上有9个主要语言家庭,一个语言家庭内的每一种语言都有一个共同的祖传语言,一个语言家庭的例子就是印度-欧洲家庭,这个家庭有许多来自同一基础的语言群体:一种叫普罗托-印多-欧洲的语言,大约在6000年前就曾使用过这种语言。随着人口从祖传家园迁移,他们的语言演变成许多新语言。欧洲印度-欧洲家庭使用的三个最大的语言群体是德意志语、罗姆语和斯拉夫语群体。其他印度-欧洲语言包括印地语(印度语)和波斯语(伊朗语 ) 。
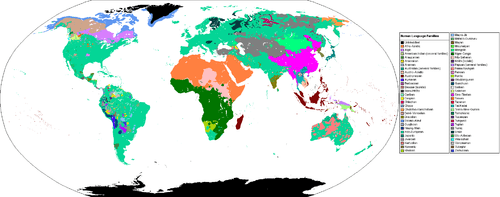
This map of the world shows the primary human languages and the locations where they are dominant.
::这张世界地图展示了主要的人类语言及其主导位置。Together, the eight countries in red contain more than 50 percent of the world's languages. The areas in blue are the most linguistically diverse in the world, and the locations of most of the world's endangered languages.
::8个红色国家合在一起拥有世界50%以上的语言。 蓝色地区是世界上语言最多样化的地区,也是世界上大多数濒危语言的所在地。Language Characteristics
::语言特点The following terms are used to describe language characteristics.
::以下术语用于描述语言特征。-
An accent is the pronunciation of words within a language that is different from that used by a different group of the same language. For example, people in Mississippi pronounce words differently from people in North Dakota, but the differences are less severe than dialects.
::口音是语言发音,语言的发音不同于不同语言群体所使用的语言。 比如,密西西比语的人的发音与北达科他人不同,但差异不如方言严重。 -
Similar to pidgin, a Creole language arises from contact between two other languages and has features of both. However, Creole is a pidgin that becomes a primary language spoken by people at home. Creole languages are often developed in colonial settings as a dialect of the colonial language (usually French or English). For example, in the former French colony of Haiti, a French-based Creole language was developed that is spoken by people at home, while French is typically used for professional purposes.
::克里奥尔语与Pidgin语相似,一种克里奥尔语来自其他两种语言的接触,具有两种语言的特点,但克里奥尔语成为人们在家里使用的一种主要语言,克里奥尔语往往在殖民环境中作为殖民语言(通常为法语或英语)的一种方言(通常为法语或英语)发展,例如,在前海地法属殖民地,开发了一种法语克里奥尔语,由人们在家里使用,而法语通常用于专业目的。 -
A dead language is one that is no longer used for local communication. For example, Latin is no longer used by local people to communicate but is still used by the Roman Catholic Church in some of its services.
::例如,当地人不再使用拉丁文进行交流,罗马天主教教会在其一些服务中仍然使用拉丁文。 -
A dialect is a regional variety of a language that uses different grammar or pronunciation. Examples include American English versus British English. Linguists suggest that there are three main dialects of the English language in the United States: a Southern dialect, a Midland dialect, and a Northern dialect. Television and public media communication have brought a focus on more uniform speech patterns that have diminished the differences between these three dialects.
::方言是使用不同语法或发音的多种区域语言,例如美国英语和英国英语。语言学家认为,美国英语有三种主要方言:南方方方言、米德兰方言和北方方言。 电视和公共媒体的传播侧重于更加统一的言论模式,从而缩小了这三种方言之间的差异。 -
An isolated language is one not connected to any other language on Earth. For example, Basque is not connected to any other language and is only spoken in the region of the Pyrenees between Spain and France.
::孤立的语言与地球上任何其他语言都没有联系,例如,巴斯克语与任何其他语言没有联系,而只在西班牙和法国之间的比利牛斯地区使用。 -
A lingua franca is a second language used for commercial purposes with others outside a language group but not used in personal lives. For example, Swahili is used by millions in Africa for doing business with people outside their own group but is not used to communicate within local communities.
::例如,非洲数百万人使用斯瓦希里语与非自己群体的人做生意,但不用于当地社区内部的交流。 -
The official language is the language that is on record by a country to be used for all its official government purposes. For example, in India, the official language is Hindi, though in many places the lingua franca is English and several local languages may be spoken.
::例如,在印度,官方语言是印地语,尽管在许多地方,通用语是英语,可以讲几种当地语言。 -
A pidgin is a simplified, created language used to communicate between two or more groups that do not have a language in common. For example, Residents of New Guinea mix English words with their own language to create a new language that can bridge speakers of different local language groups. Though the words are in English, the grammar and sentence structure is mixed up according to local vocabulary. There are many English-based pidgin languages around the world.
::Pidgin是一种简化的语言,用来在没有共同语言的两个或两个以上群体之间进行交流。例如,新几内亚居民将英语和自己的语言混为一谈,以创造新的语言,使不同地方语言群体的人能够沟通起来。虽然语言是英语,但语法和句子结构却根据当地词汇混为一谈。全世界有许多基于英语的Pidgin语言。 -
Slang is the local use of informal words or phrases that are not part of the official language. For example, a lot of musicians use slang in their lyrics.
::Slang是当地使用不属于官方语言的非正式词句或短语。 例如,许多音乐家在歌词中使用了 slan 。
Religions of the World
::世界各宗教组织Religious geography is the study of the distribution of religions and their relationship to their place of origin. Religious geographers recognize three main types of religions: universal (or universalizing), ethnic (or cultural), and tribal (or traditional) religions. Universal religions include Christianity, Islam, and various forms of Buddhism. These religions attempt to gain worldwide acceptance and appeal to all types of people, and they actively look for new members or converts. Ethnic religions appeal to a single ethnic group or culture. These religions do not actively seek out converts.
::宗教地理学承认三种主要宗教:普遍(或普及)、种族(或文化)和部落(或传统)宗教;世界宗教包括基督教、伊斯兰教和各种形式的佛教;这些宗教试图获得全世界接受和吸引所有类型的人,并积极寻找新成员或皈依者;各族裔宗教对单一族裔群体或文化有吸引力;这些宗教并不积极寻求皈依者。Broader ethnic religions include Judaism, Shintoism, Hinduism, and Chinese religions that embrace Confucianism and Taoism. Finally, traditional religions involve the belief in some form of supernatural power that people can appeal to for help, including ancestor worship and the belief in spirits that live in various aspects of nature, such as trees, mountaintops, and streams (this is often called animism). Sub-Saharan Africa is home to many traditional religions.
::更为广泛的民族宗教包括犹太教、神道教、印度教和中国信奉儒教和道教的宗教。 最后,传统宗教涉及信仰某种超自然力量,人们可以求助于这种超自然力量来寻求帮助,包括祖先的崇拜和信仰生活在各种自然方面,如树木、山顶和溪流(这通常被称为反动主义 ) 。 撒哈拉以南非洲是许多传统宗教的家园。Although the world’s primary religions are listed here, many other religions are practiced around the world, as well as many variations of the religions outlined here. The top four religions by population are Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism. Because the official doctrine of Communism was nonreligious or atheist, there are actually many more followers of Buddhism in China than demographic listings indicate. The percentage of the world’s population that follows Buddhism is probably much higher than the six percent often listed for this religion.
::尽管这里列出了世界上的主要宗教,但世界上还有许多其他宗教,以及这里概述的许多宗教。 按人口划分的四大宗教是基督教、伊斯兰教、印度教和佛教。 由于官方的共产主义教义是非宗教或无神论,中国佛教的信徒实际上比人口统计表显示的要多得多。 遵循佛教的世界人口比例可能远高于该宗教通常列出的6%。
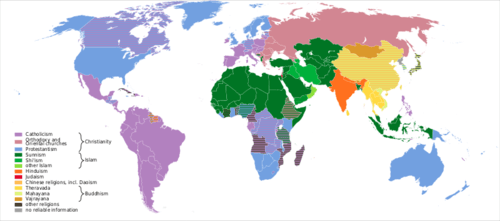
This world map is color-coded to denote the major religions found worldwide.
::这幅世界地图是用颜色编码的 来表示世界范围内发现的主要宗教
Buddhism is a religion or way of life based on the teachings and life of Siddhartha Gautama, also known as the Buddha, who lived in what is now India and Nepal around the 5th century B.C.E. There are three main branches of Buddhism: (1) southern or Theravada Buddhism; (2) eastern or Mahayana Buddhism; (3) and northern or Vajrayana Buddhism. Followers of Buddhism are called Buddhists. Buddhists follow the Eightfold Path and aspire to know and understand the Four Noble Truths.
::佛教是一种宗教或生活方式,基于Siddhartha Gautama(又称佛教徒)的教义和生活,佛教徒在公元前五世纪前后生活在现在的印度和尼泊尔,佛教有三个主要分支1) 南方或Theravada佛教;(2) 东方或Mahayana佛教;(3) 北方或Vajrayana佛教;佛教的信徒被称为佛教徒;佛教徒遵循八重道,渴望了解和理解四大真理。
Christianity originated out of Judaism in the eastern Mediterranean and the Arabian Peninsula. It is a monotheistic religion that looks to the Jewish patriarch Abraham as the founder. Christianity, based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, who lived in Palestine in the first century C.E., spread rapidly through the Roman Empire. Followers of Christianity are called Christians. The central religious text for Christians is The Bible.
::基督教起源于东地中海和阿拉伯半岛的犹太教,它是一个一神论宗教,它把犹太教家长亚伯拉罕视为创始人。 基督教基于耶稣基督的生命和教义,在公元前一世纪生活在巴勒斯坦的耶稣基督的生命和教义,在罗马帝国迅速蔓延。 基督教的追随者被称为基督徒。 基督教的中心教义是《圣经》。Hinduism, a religious tradition that originated on the Indian subcontinent, is one of the oldest major religions in the world. It may date back to as far as 2000 B.C.E. or earlier. Unlike other world religions, Hinduism has no single founder and has diverse beliefs and traditions. Followers of Hinduism are called Hindus. Hinduism has a large body of scripture, including the Vedas, the Upanishads, and epic tales such as the Mahabharata and the Ramayana.
::印度教是源于印度次大陆的宗教传统,是世界上最古老的主要宗教之一,可追溯到公元前2000年或更早。 与其他世界宗教不同,印度教没有单一的创始人,信仰和传统也各不相同。 印度教的追随者被称为印度教。 印度教拥有大量的经文,包括维达、乌帕尼沙德和史诗故事,如马哈哈拉塔和拉马亚纳。Islam also originated out of Judaism and is based on the teachings of Muhammad, a seventh-century religious and political figure who lived on the Arabian Peninsula. Islam spread rapidly across North Africa, east across southern Asia, and north to Europe in the centuries after Muhammad’s death. Followers of Islam are called Muslims. The central religious text for Muslims is the Koran.
::伊斯兰教也源于犹太教,基于穆罕默德的教义,穆罕默德是七世纪的宗教和政治人物,居住在阿拉伯半岛。 伊斯兰教迅速蔓延到北非、东亚和南亚,在穆罕默德死后几个世纪又蔓延到欧洲北部。 伊斯兰教的追随者被称为穆斯林。 穆斯林的宗教教义是《古兰经》。Judaism is the religion of the Jewish people, whose traditions and ethics are embodied in the Tanakh and the Talmud. According to Jewish tradition, Judaism began with the covenant between God and Abraham around 2000 B.C.E. The second covenant happened 450 years later when Moses led the Jews out of slavery in Egypt and gave them the 10 Commandants.
::犹太教是犹太民族的宗教,其传统和伦理体现在Tanakh和Talmud中,根据犹太传统,犹太教在公元前2000年前后从上帝和亚伯拉罕之间的盟约开始,在450年后,摩西带领犹太人走出埃及的奴隶制度,并给他们10个司令官。Human Geographic Systems Chapter 2.1
::第2.1章 人类地理系统1. Activity space : The area within which people move freely on their rounds of regular activity2. Agricultural revolution : The time when human beings first domesticated plants and and no longer relied entirely on hunting and gathering3. AIDS : A serious (often fatal) disease of the immune system transmitted through products especially by sexual contact or contaminated needles4. Arable land : land suitable for growing crops5. Arithmetic growth : population growth where population increases by the same amount over each time interval6. Arithmetic population density : The total number of people divided by the total land area7. Assimilation : the social process of absorbing one cultural group into harmony with another8. Authenticity : In the context of local cultures or customs, the accuracy with which a single stereotypical or typecast image or experience conveys an otherwise dynamic and complex local culture or its customs9. Awareness space : Knowledge of opportunity activities well beyond the normal activity space10. Carrying capacity : T he largest number of individuals of a population that an environment can support11. Commodification : Giving a price tag or value to something that was not previously perceived as having a money-related value.12. Crude birth rate : The total number of live births in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.13. Crude death rate : The number of deaths per year per 1,000 people.14. Cultural Appropriation : the process by which cultures adopt customs and knowledge from other cultures and use them for their own benefit15. Cultural Landscape : the visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape16. Custom : Practices followed by the people of a particular cultural group17. Demographic equation : The formula that calculates population change. The formula finds the increase (or decrease) in a population. The formula is found by doing births minus deaths plus (or minus) net migration. This is important because it helps to determine which stage in the demographic transition model a country is in18. Demographic momentum : this is the tendency for a growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution. This is important because once this happens a country moves to a different stage in the demographic transition model19. Demographic transition theory : Multistage model, based on Western Europe's experience, of changes in population growth exhibited by countries undergoing industrialization. High birth rates and death rates are followed by plunging death rates, producing a huge net population gain; this is followed by the convergence of birth rates and death rates at a low overall level20. demography : The scientific study of population characteristics21. routes : The spatial trajectory through which cultural traits or other phenomena spread22. distance decay : T he decline of activity or function with increasing distance from its point of origin23. Dot maps : Thematic maps that use points to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents, or births24. Doubling rate : The length of time needed to double the population25. endemic : confined to a particular country or area26. Epidemiologic transition : distinctive causes of death in each stage of the demographic transition27. Ethnic neighborhood : a neighborhood, typically situated in a larger metropolitan city and constructed by or comprised of a local culture, in which a local culture can practice its customs28. Exponential growth : Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate29. Female infanticide : the intentional killing of baby girls due to the preference for male babies and from the low value associated with the birth of females30. Folk Culture : Culture traditionally practiced by a small, homogeneous, rural group living in relative isolation from other groups31. Folk-Housing Regions : A region in which the housing stock predominantly reflects styles of building that are particular to the culture of the people who have long inhabited the area32. Geometric growth : an increase in quantity by a constant proportion each year33. Global-Local Continuum : notion that what happens at the global scale directly effects what happens at the global scale directly effects what happens at a local scale, and vice versa34. Glocalization : The process by which people in a local place mediate and alter regional, national, and global processes35. Hearth : The region from which innovative ideas originate36. Hierarchical Diffusion : A form of diffusion in which an idea or innovation spreads by passing first among the most connected places or peoples37. Infant mortality rate : The percentage of children who die before their first birthday within a particular area or country38. Life expectancy : The average number of years an individual can be expected to live, given current social, economic, and medical conditions. Life expectancy at birth is the average number of years a newborn infant can expect to live39. Local Culture : A set of common experiences or customs that shape the identity of a place and the people who live there. Local cultures are often the subjects of preservation or economic development efforts40. Material culture : the art, housing, clothing, sports, dances, foods, and other similar items constructed or created by a group of people41. Natural increase : Population growth measured as the excess of live births over deaths; does not reflect either emigrant or immigrant movements42. Neolocalism : A renewed interest in sustaining and promoting the uniqueness of a place43. Neo-Malthusians : A group who built on Malthus' theory and suggested that people wouldn't just starve for lack of food, but would have wars about food and other scarce resources44. Non-material culture : Human creations, such as values, norms, knowledge, systems of government, language, and so on, that are not embodied in physical objects45. One-child policy : A program established by the Chinese government in 1979 to slow population growth in China46. Overpopulation : The number of people in an area exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living47. Pandemic : Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population.48. Physiological population density : The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture49. Placelessness : the loss of uniqueness of place in the cultural landscape so that one place looks like the next50. Popular Culture : cultural patterns that are widespread among a society's population51. Population concentrations : Areas of the world with a large population density52. Population density : A measurement of the number of people per given unit of land53. Population explosion : a sudden increase or burst in the population in either a certain geographical area or worldwide54. Population geography : the study of spatial variations among populations and population-environment interactions55. Population pyramid : A bar graph representing the distribution of the population by age and sex56. Restrictive population policies : Government policies designed to reduce the rate of natural increase57. Reterritorialization : with respect to popular culture, when people within a place start to produce an aspect of popular culture themselves, doing so in the context of their local culture and making it their own58. Stationary population level : The level at which a national population ceases to grow59. sustainability : The use of Earth's renewable and nonrenewable natural resources in ways that do not constrain resource useKey Takeaways
::密钥外出-
The human population is moving closer to eight billion in 2018 and is increasing rapidly, mainly in developing regions of Asia and Africa.
::2018年,人类人口接近80亿,增长迅速,主要在亚洲和非洲发展中区域。 -
There is no agreement on the earth’s carrying capacity for our human population, but unless the growth rate changes, the human population will double in about 50 years.
::地球上没有关于人类承受能力的协议,但是除非增长率发生变化,否则人口将在大约50年内翻一番。 -
Since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been moving from rural areas to urban areas.
::自工业革命以来,人类从农村地区向城市地区迁移。 -
Workers were needed in the factories and fewer workers were needed on the farms because of improved technology. This trend continues in many rural areas of developing countries.
::工厂需要工人,由于技术的改进,农场需要减少工人,在发展中国家的许多农村地区这一趋势仍在继续。 -
Population pyramids are one method of illustrating demographic data for a country to show if the population is declining or increasing and at what rate.
::人口金字塔是说明人口数据的一种方法,一个国家可用以表明人口是否在下降或增加以及以何种速度增长。 -
Though often interchangeable in general terms, ethnicity is what you are born with and culture is what you learn after you are born.
::虽然通常可以互换,但种族是天生的,文化是出生后学习的。 -
There are about 6,000 languages in the world today, with about 13 of them spoken by over 100 million people or more.
::当今世界约有6 000种语言,其中约有13种语言由1亿多人或超过1亿多人使用。 -
Of the main language families, nine include at least one percent or more of the human population.
::在主要语言家庭中,9个家庭的人口至少占人口的1%或以上。 -
There are thousands of religions or variants of them in the world.
::世界上有成千上万的宗教或不同的宗教。 -
Religious geographers recognize three main types of religions: universal, ethnic, and traditional.
::宗教地理学家承认三大类宗教:普遍、族裔和传统。 -
The four main religions of the world are Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, and Islam.
::世界的四大宗教是佛教、基督教、印度教和伊斯兰教。
Interactive Notebook Activities
Applying Knowledge
::交互式笔记活动应用知识-
Describe the demographic transition process and define the concept of carrying capacity as it relates to the planet’s human population.
::描述人口结构转型过程,并界定与地球人口有关的承载能力概念。 -
Outline
the relationship between urbanization and family size. Show how the rural-to-urban shift relates to industrialization and the change in rural populations.
::概述城市化与家庭规模之间的关系,说明农村向城市的转变与工业化和农村人口变化的关系。 -
Draw or paste
a population pyramid from this section, and interpret and infer trends from it.
::从这一节中绘制或粘贴人口金字塔,并解释和推断其趋势。 -
Analyze
your population pyramid to determine whether the population is increasing or declining and if the pace of growth is intensifying or slowing.
::分析您的人口金字塔,以确定人口是增长还是下降,以及增长率是加快还是放慢。 -
Explain
the difference between the concepts of culture and ethnicity as these terms are used in this textbook.
::解释本教科书中使用的文化概念和族裔概念之间的区别。 -
Summarize
the difficulty in determining the number of languages and religions existing on Earth.
::总结确定地球上现有语言和宗教数目的困难。 -
List
the main language families and the world’s major religions.
::列出主要语言系和世界主要宗教。
Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
What is the planet’s current human population?
::地球目前的人口是多少? -
What happens when overpopulation occurs? Do we know the earth’s carrying capacity?
::当人口过多发生时会发生什么情况?我们是否知道地球的承载能力? -
Where are the earth’s three main high-density population regions?
::地球三个主要高密度人口区在哪里? -
Outline the four basic shapes of population pyramids. What do they indicate?
::概括了人口金字塔的四种基本形状。 它们表示什么 ? -
What is the difference between culture and ethnicity?
::文化和族裔之间有什么区别? -
What is ethnic cleansing? Where has ethnic cleansing occurred in the world during your lifetime?
::什么是族裔清洗?在你的一生中,世界在哪里发生了族裔清洗? -
Approximately how many languages are there in the world? Which continent has the most?
::世界上大约有多少语言?哪个大陆语言最多? -
What are the five most widely spoken languages in the world? Where would each be mainly spoken?
::世界上五种最广泛使用的语言是什么? -
What are the four major world religions by the percentage of followers?
::按信徒百分比计算,世界四大宗教是什么? -
What is the difference between an ethnic, universal, or a traditional religion? Give an example of each.
::种族、普遍或传统宗教之间有什么区别?请举例说明其中的每一种宗教。
Real-World Geography Exercise
::现实世界地理演习-
Create
a population pyramid for your state, province, or country using the population data available at
.
::为您的国家、省或国家创建人口金字塔,使用您在 .时提供的人口数据。 -
Compare
population pyramids for countries from each world region found at the
.
::比较世界每个区域各国的人口金字塔。 -
Using
, learn five common phrases in a language you do not speak.
::使用,学习五个常用的语句,使用一种不会说话的语言。
Mapping Exercise
::绘图绘制作业Mapping Our World ESRI-ARGIS Online
::在线绘制我们世界的ESRI-ARGIS地图: Students will explore the patterns of the world population in terms of total population, arithmetic density, total fertility rate, natural increase rate, and infant mortality rate. The activity uses a web-based map.
:::学生将探讨世界人口在总人口、算术密度、总生育率、自然增长率和婴儿死亡率方面的模式。活动使用网络地图。: Students will explore patterns of cultural diffusion through linguistic and religious data. The activity uses a web-based map.
::学生将通过语言和宗教数据探索文化传播模式,活动使用网络地图。Videos for Geography Enrichment
::地理丰富视频Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs , careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law .
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::是一个美国政府机构网站, 提供科学信息, 说明威胁生命、我们赖以生存的自然资源、健康与环境, 以及气候与土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。#
Answer Key
::答答键Region
::地区 地区Topic
::专题 专题 专题11
1B 2C 3C 4D 5B 6D 7B 8A
::1B 2C 3C 3C 4D 5B 6B 6D 7B 8APoland
::波兰 波兰 波兰 波兰 波兰Reading A Map
::阅读地图12
1C 2B 3D 4A 5C 6D 7C
::1C 2B 3D 4A 5C 6D 7CEurope
::欧洲 欧洲Interpreting Map Data
::解释地图数据13
1D 2B 3B 4B 5B 6A 7D
::1D 2B 3B 4B 5B 5B 6A 7DWorld
::世界世界世界Reading Line Graphs
::读取行图14
1B 2D 3D 4C 5A 6D 7A 8D 9B 10C
::1B 2D 3D 3D 4C 5C 5A 6A 6D 7A 8D 9B 10CWorld
::世界世界世界Reading Tables
::阅读表格15
1A 2A 3C 4A 5B 6A 7B 8A 9C 10D
::1A 2A 3A 3C 4A 5B 6B 6A 7B 8A 9C 10DFrance
::法国 法国 法国 法国 法国 法国Finding Routes and Distances
::寻找路线和距离 -
Explain the
process. Understand the concept of
carrying capacity
as it relates to the planet’s
.