8.2 原生体进化
章节大纲
-
What's the difference between a bacterium and a simple protist?
::细菌和单纯的先锋有什么区别?Were simple the first eukaryotic organisms to evolve? Probably. A protist is a eukaryote , so each has a . Otherwise, simple protists, like the Paramecium and amoeba , can be fairly similar to .
::简单的是第一种可以进化的蛋白质生物吗 ? 很可能。 蛋白质生物是一个eukaryote, 所以每个生物都有。 否则,简单的蛋白质生物,比如和, 可能和它相当相似 。Evolution of Protists
::原生者进化Scientists think that protists are the oldest eukaryotes. If so, they must have evolved from prokaryotic cells . How did this happen? The endosymbiotic theory provides the most widely-accepted explanation. That’s because it is well supported by evidence .
::科学家认为,原生者是古老的eukaryotes。 如果是这样,他们一定是从原生细胞进化而来的。 怎么会发生这种情况? 内生生物理论提供了最普遍接受的解释。 这是因为它得到了证据的有力支持。The First Eukaryotic Cells
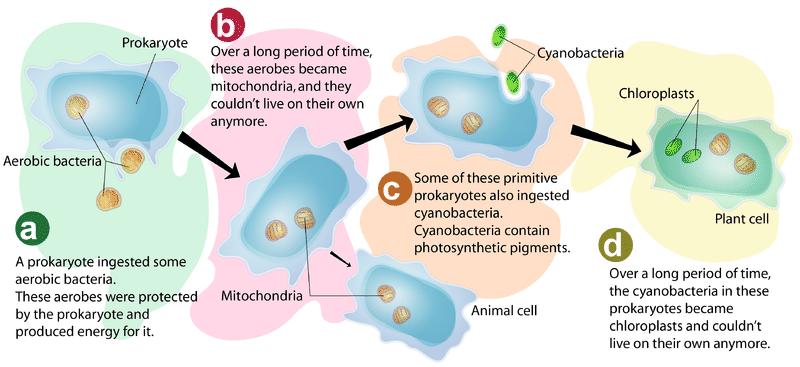
::第一批尤卡利教细胞According to the endosymbiotic theory, the first eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic relationship between two or more prokaryotic cells. Smaller prokaryotic cells were engulfed by (or invaded) larger prokaryotic cells. The small cells (now called endosymbionts ) benefited from the relationship by getting a safe home and nutrients . The large cells (now called hosts ) benefited by getting some of the organic molecules or energy released by the endosymbionts. Eventually, the endosymbionts evolved into of the host cells. After that, neither could live without the other.
::根据内分泌共生理论,第一个雌激素细胞从两个或两个以上蛋白质细胞之间的共生关系中演变而来。较小的蛋白质细胞被(或被入侵的)较大蛋白质细胞吞没。小细胞(现称为内分泌共生细胞)通过获得安全的家住和养分而从这种关系中受益。大型细胞(现称为宿主)从获得一些有机分子或由内分泌共生细胞释放的能量中受益。最终,内生共生细胞演变成宿主细胞。此后,也不能没有其他细胞而生存。As shown in Figure , some of the endosymbionts were aerobic bacteria. They were specialized to break down chemicals and release energy. They evolved into the of eukaryotic cells. Some of the small cells were cyanobacteria . They were specialized for . They evolved into the of eukaryotic cells.
::如图所示,有些内生菌是有氧细菌,它们专门用来分解化学物质和释放能量,它们演变成尿道细胞,有些小细胞是氰化物,它们专门用于.它们演变成尿道细胞。Endosymbiotic theory explains how eukaryotic cells arose.
::共生理论解释自闭细胞是如何产生的。Evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory
::内共生物理论的证据Many pieces of evidence support the endosymbiotic theory. For example:
::许多证据支持内共生理论。例如:-
Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain
that is different from the DNA found in the cell nucleus. Instead, it is similar to the circular DNA of bacteria.
::Mitochdria 和 叶绿石中含有的DNA与细胞核中发现的DNA不同,相反,它与细菌的循环DNA相似。 -
Mitochondria and chloroplasts are surrounded by their own plasma membranes, which are similar to bacterial membranes.
::Mitochondria和叶绿板周围都是他们自己的等离子膜,这些等离子膜类似于细菌膜。 -
New mitochondria and chloroplasts are produced through a process similar to
binary fission
. Bacteria also reproduce through binary fission.
::新微分数和氯板通过类似于二进制裂变的过程生产,细菌也通过二进制裂变繁殖。 -
The internal structure and
biochemistry
of chloroplasts is very similar to that of cyanobacteria.
::氯板的内部结构和生物化学与氰化物的结构非常相似。
Summary
::摘要-
Scientists think that protists are the oldest eukaryotes.
::科学家们认为 原生者是最古老的欧卡利奥特人 -
Protists most likely evolved from prokaryotic cells, as explained by the endosymbiotic theory. This theory is well-supported by evidence.
::正如内生共生理论所解释的,原生主义者最有可能从蛋白细胞中演变而来。 这一理论有充分的证据支持。
Review
::回顾-
How did the first eukaryotic cells evolve, according to endosymbiotic theory?
::根据内共生理论 第一种自闭细胞是如何进化的呢? -
Identify two pieces of evidence for endosymbiotic theory. Explain how this evidence supports the theory.
::找出两件内生理论的证据 解释这些证据如何支持这个理论 -
How are additional mitochondria produced?
::如何产生额外的中小分数?
-
Mitochondria and chloroplasts contain
that is different from the DNA found in the cell nucleus. Instead, it is similar to the circular DNA of bacteria.