8.5 藻类
章节大纲
-
Many people, if not most, believe seaweed to be a plant. Is it?
::许多人,如果不是大多数人,相信海藻是植物,是吗?Seaweed is actually a plant-like , which are also known as algae. The green color is due to what pigment? Algae, like plants, obtain their energy through .
::海藻其实是一种植物类植物,也被称为藻类。绿色颜色是由什么色素造成的?藻类和植物一样,通过植物获得能量。Plant-Like Protists: Algae
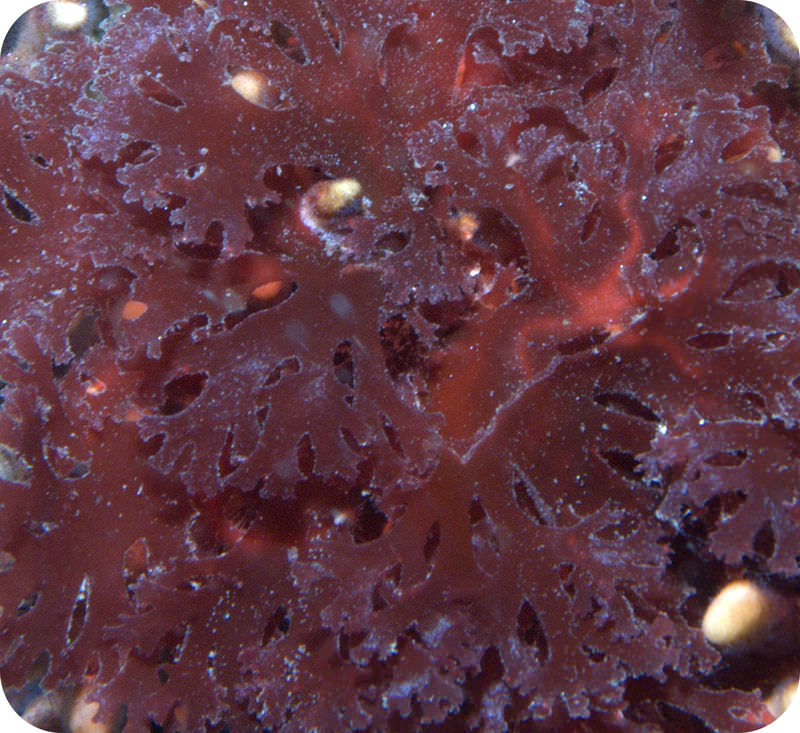
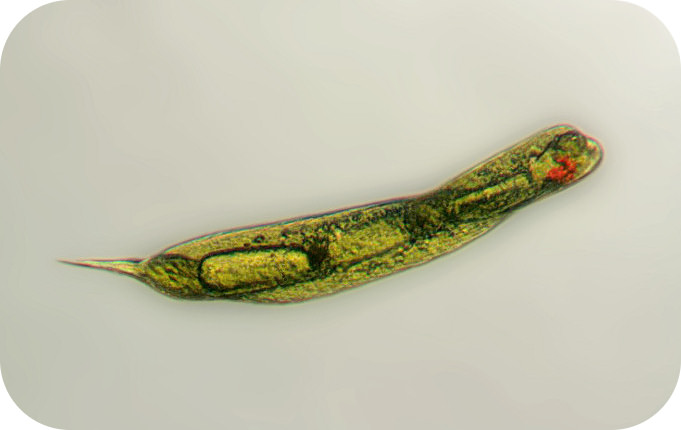
::植物类原生者:藻类Plant-like protists are called algae (singular, alga). They are a large and diverse group. Some algae, the diatoms , are single-celled. Others, such as seaweed , are multicellular (see Figure ).
::植物类原生动物被称为藻类(藻类、藻类),它们是一个大而多样的群体。有些藻类,即二亚原子,是单细胞的,而其他藻类,如海藻,则是多细胞的(见图 )。Diatoms are single-celled algae. Other forms of algae are multicellular.
::直方是单细胞藻类,其他形式的藻类是多细胞类。Why are algae considered plant-like? The main reason is that they contain and produce food through photosynthesis . However, they lack many other structures of true plants. For example, algae do not have , , or leaves. Some algae also differ from plants in being motile. They may move with pseudopods or flagella . Although not plants themselves, algae were probably the ancestors of plants.
::藻类为什么被视为植物类?主要的原因是它们通过光合作用来吸收和生产食物,但是它们缺乏许多其他真正的植物结构。例如藻类没有,或者没有叶子。有些藻类也与植物有差异,它们可能使用假花或者花旗。藻类本身虽然不是植物,但却可能是植物的祖先。Ecology of Algae
::阿尔海藻生态Algae play significant roles as in . Microscopic forms live suspended in the column. They are the main component of phytoplankton . As such, they contribute to the food base of most ecosystems.
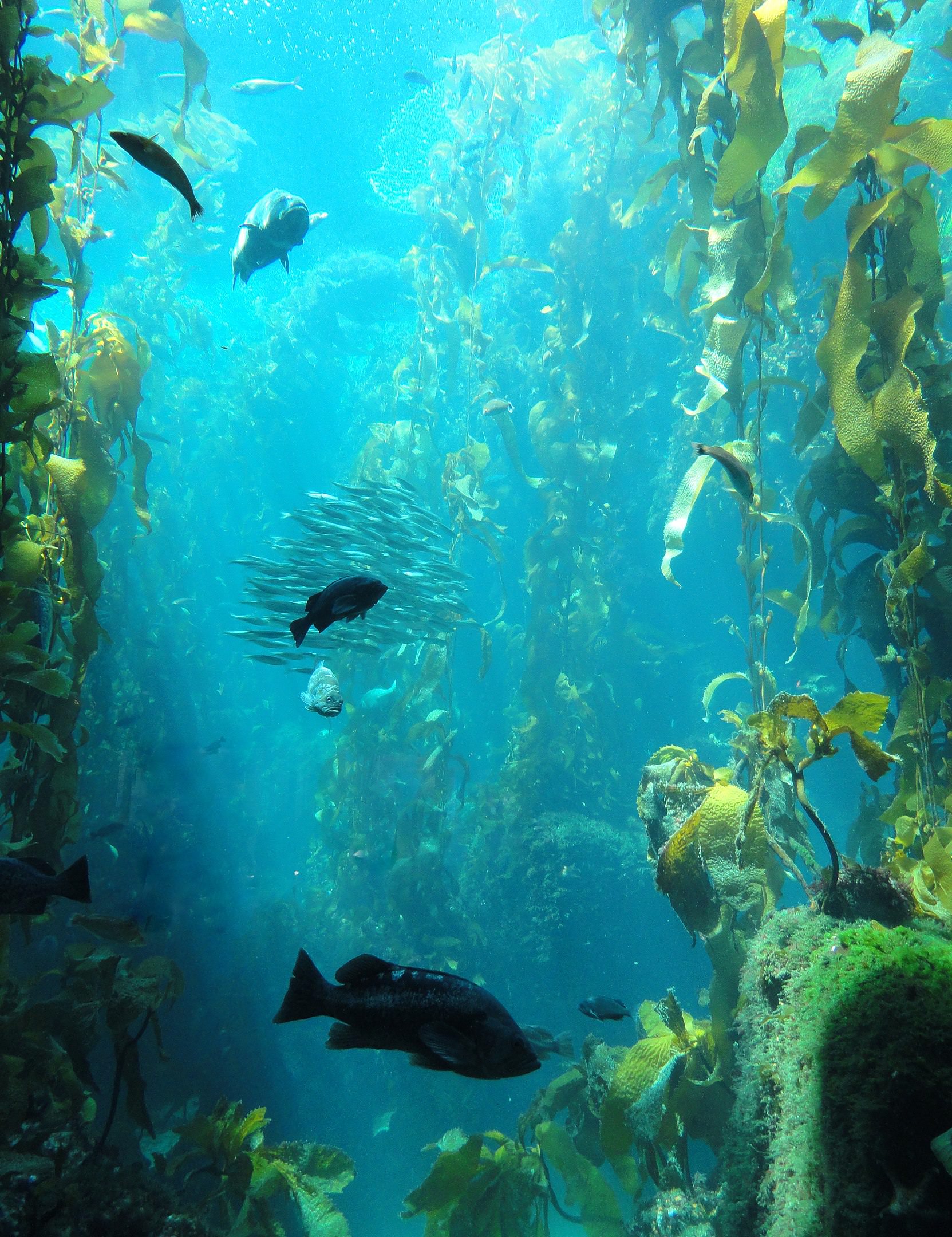
::藻类具有重要作用,如在.微粒形式在柱体中被悬浮,它们是浮游植物的主要成分,因此有助于大多数生态系统的食物基础。Multicellular seaweeds called kelp may grow as large as trees. They are the food base of ecosystems called kelp forests (see Figure ). Kelp forests are found throughout the ocean in and climates. They are highly productive ecosystems.
::称为海藻的多细胞海藻可能长得像树木一样大,它们是称为海藻森林的生态系统的粮食基础(见图 )。海藻森林在整个海洋和气候中都有,它们是生产力很高的生态系统。Kelp Forest. This kelp forest supports a large community of many other types of organisms.
::Kelp森林。这个Kelp森林支持着许多其他类型的生物群落。Classification of Algae
::藻类分类Types of algae include red and green algae, and euglenids , and dinoflagellates (see Table for examples). Scientists think that red and green algae evolved from endosymbiotic relationships with cyanobacteria . Their chloroplasts have two membranes because the of the cyanobacteria became additional plasma membranes of the chloroplasts. Scientists think that euglenids and dinoflagellates evolved later, from endosymbiotic relationships with green and red algae. This is why their chloroplasts have three membranes. Differences in the types of chlorophyll in the four types of algae also support the hypothesized evolutionary relationships.
::科学家们认为,红藻和绿藻与蓝旗藻的种类包括红藻和绿藻,以及红旗藻(见示例表)。科学家们认为,红藻和绿旗藻从与蓝菌的内生关系中演变而来。它们的绿藻和绿藻的叶板有两种膜,因为它们的黄球菌成为叶板的另外的等离子膜。科学家们认为,黄球藻和红旗藻后来从与绿藻和红藻的内生关系中演变而来。这就是它们的叶板有三种膜的原因。四类藻的叶绿素类型差异也支持了虚弱的进化关系。Type of Algae Origin of Chloroplast Type of Chloroplast Red algae
::红藻cyanobacteria two membranes, chlorophyll like the majority of cyanobacteria Green algae
::绿藻cyanobacteria two membranes, chlorophyll like a minority of cyanobacteria Euglenids
::Euglenids 欧元green algae three membranes, chlorophyll like green algae Dinoflagellates
::迪诺佛red algae three membranes, chlorophyll like red algae Reproduction of Algae
::复制藻类Algae have varied life cycles. Two examples are shown in Figure . Both cycles include phases of ( haploid , n ) and ( diploid , 2n ). Why go to so much trouble to reproduce? Asexual reproduction is fast, but it doesn’t create new . Sexual reproduction is more complicated and risky, but it creates new gene combinations. Each strategy may work better under different conditions. Rapid (asexual reproduction) is adaptive when conditions are favorable. Genetic variation (sexual reproduction) helps ensure that some organisms will survive if the environment changes.
::藻类有不同的生命周期。图中列出了两个例子。两个周期都包括阶段(藻类,n)和(浮质,2n)。为什么要繁衍如此麻烦?性生殖是快速的,但它没有创造新的。性生殖更复杂,风险更大,但创造了新的基因组合。每种战略在不同条件下都可能更好。快速(性生殖)在条件有利时是适应性的。遗传变异(性生殖)有助于确保环境改变时某些生物体的生存。Life Cycles of Algae: Zygotic Meiosis (A), Gametic Meiosis (B) and Sporic Meiosis (C). In life cycle A (left), diploid (2n) zygotes result from fertilization and then undergo meiosis to produce haploid
gametes. The gametes undergo mitosis and produce many additional copies of themselves. How are life cycles B and C different from life cycle A?
::Algae的生命周期:Zyglogic Meisis(A)、Gametic Meisis(B)和Sporic Meisis(C)。在生命周期A(左),Diploid (2n) zygotes通过施肥产生,然后进行 meicis,以产生hhanloid调子。这些调子会发生松化并产生更多的复本。生命周期B和C与生命周期A有何不同?
Summary
::摘要-
Plant-like protists are called algae. They include single-celled diatoms and multicellular seaweed.
::植物类原生动物被称为藻类,包括单细胞的对子蛋白和多细胞海藻。 -
Like plants, algae contain chlorophyll and make food by photosynthesis.
::像植物一样,藻类含有叶绿素,用光合作用做食物。 -
Types of algae include red and green algae, euglenids, and dinoflagellates.
::藻类类型包括红藻和绿藻、黄藻和二氧化花旗。
Review
::回顾-
Compare and contrast algae and plants.
::对比和对比藻类和植物。 -
State pros and cons of asexual and sexual reproduction in algae.
::藻类中的非性生殖和性生殖的利弊。 -
Explain why dinoflagellates and euglenids have chloroplasts with three membranes instead of two.
::解释为什么地诺花旗和黄花板有三毫膜而不是两毫膜的氯板。
-
Plant-like protists are called algae. They include single-celled diatoms and multicellular seaweed.