9.8 血管植物
章节大纲
-
How does water move from the roots to the top of these trees?
::水是如何从树根流到树顶的?Redwood trees found in Yosemite National Park in California. Big? Of course. How do these trees grow so tall? It has a lot to do with a very efficient system to move , sugars and other nutrients . But the first plants to have such a "vascular system" were not tall trees, but much smaller plants.
::在加利福尼亚州约塞米特国家公园发现的红木树。 大的吗? 当然,这些树怎么长得这么高? 它与一个非常高效的移动系统、糖和其他养分有许多关系。 但最早有这样的“血管系统”的植物不是高的树,而是小得多的植物。Vascular Plants
::血管植物Vascular plants are known as tracheophytes , which literally means “tube plants.” The earliest vascular plants quickly came to dominate . Why were they so successful? It was mainly because of their tube-like .
::血管植物被称为气管植物,这实际上意味着“管状植物 ” 。 最早的血管植物很快就占据了主导地位。 为什么它们如此成功?这主要是因为它们像管状的管状植物。Vascular Tissues
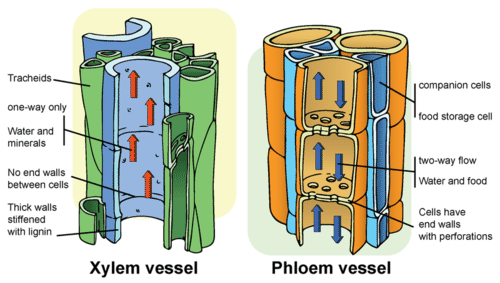
::血管组织The vascular tissues for which these plants are named are specialized to transport fluid. They consist of long, narrow arranged end-to-end, forming tubes. There are two different types of vascular tissues, called xylem and phloem . Both are shown in Figure .
::这些工厂所命名的血管组织专门用来运输液体,由长的、窄的固定端对端管组成,有两种不同的血管组织,称为Xylem和phloem。两者均在图中显示。-
Xylem
is vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved
minerals
from
to
and leaves. This type of
tissue
consists of dead cells that lack end walls between adjacent cells. The side walls are thick and reinforced with
lignin
, which makes them stiff and water proof.
::Xylem是将水和溶解的矿物输送到叶子的血管组织,这类组织由在相邻的细胞之间没有端墙的死细胞组成,侧墙厚,加固了利宁,使其僵硬和水的证明。 -
Phloem
is vascular tissue that transports
food
(sugar dissolved in water) from photosynthetic cells to other parts of the plant for growth or storage. This type of tissue consists of living cells that are separated by end walls with tiny perforations, or holes.
::Pholoem是将食物(水中溶解的糖)从光合作用细胞运到植物的其他地方以供生长或储存,这种组织包括用有细孔或孔的墙壁隔开的活细胞。
Xylem and phloem are the two types of vascular tissues in vascular plants. Evolution of Vascular Plants
::血管植物的演变The first vascular plants evolved about 420 million years ago. They probably evolved from moss-like ancestors , but they had a dominated by the diploid sporophyte generation. As they continued to evolve, early vascular plants became more plant-like in other ways as well.
::最早的血管植物大约在4.2亿年前就进化了。 它们可能从像苔丝一样的祖先进化而来,但是它们以低脂的植物代为主。 随着它们的继续进化,早期血管植物在其他方面也变得更加像植物。-
Vascular plants evolved true
roots
made of vascular tissues. Compared with
rhizoids
, roots can absorb more water and minerals from the
soil
. They also anchor plants securely in the ground, so plants can grow larger without toppling over.
::血管植物进化成由血管组织构成的真正根。 与犀牛相比,根可以从土壤中吸收更多的水和矿物质。 它们也可以安全地固定在地面上的植物,这样植物可以长大而不会翻转。 -
Vascular plants evolved
stems
made of vascular tissues and
lignin
. Because of lignin, stems are stiff, so plants can grow high above the ground where they can get more light and air. Because of their vascular tissues, stems keep even tall plants supplied with water so they don’t dry out in the air.
::血管植物的进化源由血管组织和螺旋形成。 由于螺旋和螺旋,电流是硬的,因此植物可以在地面高处生长,以获得更多的光和空气。 由于其血管组织,电源甚至保持高的植物,以备水,以免在空气中干涸。 -
Vascular plants evolved
leaves
to collect sunlight. At first, leaves were tiny and needle-like, which helped reduce water loss. Later, leaves were much larger and broader, so plants could collect more light.
::血管植物进化叶以收集阳光。 起初,叶子微小,针头相似,有助于减少水流失。 后来,叶子大得多,范围更广,植物可以收集更多的光。
With their vascular tissues and other adaptations , early vascular plants had the edge over . They could grow tall and take advantage of sunlight high up in the air. Bryophytes were the photosynthetic pioneers onto land, but early vascular plants were the photosynthetic pioneers into air.
::随着血管组织和其他适应性的变化,早期血管植物有边缘。它们可以长高,利用空气中高空的阳光。 Bryophites是地面上的光合先锋,早期血管植物则是进入空气中的光合先锋。Diversity of Seedless Vascular Plants
::多种没有种子的血管植物Surviving descendants of early vascular plants include clubmosses and . There are 1,200 of clubmoss and more than 20,000 species of fern. Both types of vascular plants are seedless and reproduce with spores. Two examples are pictured in Figures and .
::早期血管植物存活下来的后代包括夜总会和.有1 200个夜总会和20,000多种动物种类,这两种血管植物没有种子,并随螺旋而繁殖。-
Clubmosses look like
mosses
and grow low to the ground. Unlike mosses, they have roots, stems, and leaves, although the leaves are very small.
::Clubmoses 看起来像苔丝,低落到地上。 与苔丝不同,它们有根、根和叶,尽管叶子很小。 -
Ferns look more like “typical” plants. They have large leaves and may grow very tall. Some even develop into trees.
::Ferns看起来更像“典型”植物,它们有大叶子,可能长得很高,有些甚至发展成树木。
Clubmosses like these are often confused with mosses. There’s no confusing ferns with mosses. Why do these ferns look more plant-like? Summary
::摘要-
Vascular plants are known as tracheophytes.
::血管植物被称为气管植物。 -
Vascular tissues include xylem and phloem. They allow plants to grow tall in the air without drying out.
::血管组织包括xylem和phloem,它们允许植物在空气中长高而不干燥。 -
Vascular plants also have roots, stems, and leaves.
::血管植物也有根、根和叶子。
Review
::回顾-
Compare xylem to phloem.
::将xylem与phloem作比较。 -
How did vascular tissues and lignin allow vascular plants to be “photosynthetic pioneers into air”?
::血管组织和螺旋质如何允许血管植物成为“在空气中的合成先锋”? -
Why are roots more advantageous to a plant than rhizoids?
::为什么根比犀牛对植物更有利? -
What benefits do stems provide to a plant?
::植物有什么好处?
-
Xylem
is vascular tissue that transports water and dissolved
minerals
from
to
and leaves. This type of
tissue
consists of dead cells that lack end walls between adjacent cells. The side walls are thick and reinforced with
lignin
, which makes them stiff and water proof.