10.1 动物
章节大纲
-
Is an insect an animal?
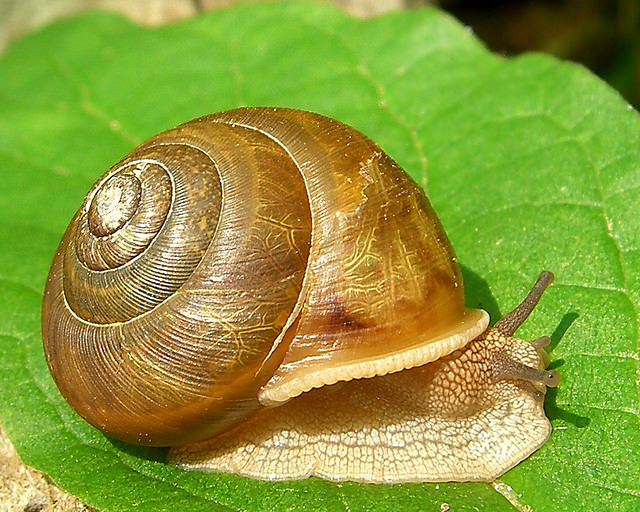
::昆虫是动物吗?Of course it is. Is a snail an insect? No, snails are . Notice the large "foot" that allows movement , and the antennas are obvious. Actually, a snail's are on the two long projections on its head, and the projections are called eyestalks. These are characteristics of this animal.
::当然是,蜗牛是一只昆虫吗?不,蜗牛是。注意允许移动的大型“脚 ” , 天线是显而易见的。事实上,蜗牛的头部有两个长长的投影,而投影被称为眼话。这些是这种动物的特征。Characteristics of Animals
::动物的特征Animals are a of multicellular eukaryotes . They cannot make their own food . Instead, they get nutrients by eating other living things. Therefore, animals are heterotrophs .
::动物是多细胞的卵巢动物,不能自己做食物。相反,它们通过吃其他生物获得营养。因此,动物是血化动物。Animal Cells
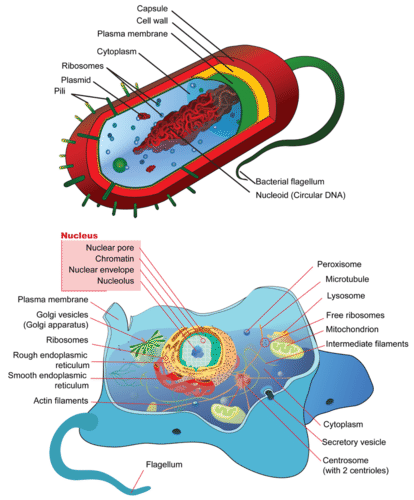
::动物细胞Like the of all eukaryotes, animal cells have a and other membrane-bound (see Figure ). Unlike the cells of plants and , animal cells lack a cell wall . This gives animal cells flexibility. It lets them take on different shapes so they can become specialized to do particular jobs. The human nerve cell shown in Figure is a good example. Its shape suits its function of transmitting over long distances. A nerve cell would be unable to take this shape if it were surrounded by a rigid cell wall.
::动物细胞与其他细胞膜不同(见图)。与植物细胞不同,动物细胞缺乏细胞墙。这给动物细胞提供了灵活性。让动物细胞有不同的形状,以便它们能够从事特殊的工作。图中显示的人类神经细胞是一个很好的例子。它的形状适合其长距离传输功能。如果被硬性细胞墙包围,神经细胞将无法形成这种形状。Animal Cell. The shape of an animal cell is not constrained by a rigid cell wall. A bacterial cell is shown above for comparison.
::动物细胞:动物细胞的形状不受硬体细胞墙的制约,细菌细胞在上文显示,以作比较。Human Nerve Cell. A human nerve cell is specialized to transmit nerve impulses. How do you think the cell’s shape helps it perform this function?
::人类神经细胞。 人类神经细胞专门用来传输神经脉冲。 你认为细胞的形状如何帮助它履行这一功能?Animal Structure and Function
::动物结构和功能Animals not only have specialized cells. Most animals also have tissues and organs . In many animals, organs form organ systems , such as a . Higher levels of organization allow animals to perform many complex functions. What can animals do that most other living things cannot? Most animals share these characteristics: sensory organs , movement , and internal digestion . All of them are illustrated in Figure .
::动物不仅有专门细胞,大多数动物也有组织和器官。在许多动物中,器官形成器官系统,例如:......组织层次越高,动物可以发挥许多复杂功能。动物能做什么,而其他大多数生物不能做什么?大多数动物都具有这些特征:感官器官、运动和内部消化。图中说明了所有这些特征。-
Animals can detect environmental
stimuli
, such as light, sound, and touch. Stimuli are detected by
sensory nerve
cells. The information is transmitted and processed by the nervous system. The nervous system, in turn, may direct the body to respond.
::动物可以检测到环境刺激,如光、声音和触碰;刺激由感官神经细胞检测到;信息由神经系统传输和处理;神经系统反过来可以引导身体做出反应。 -
All animals can move, at least during some stage of their
.
and nerves work together to allow movement. Being able to move lets animals actively search for food and mates. It also helps them escape from
predators
.
::所有动物都可以移动,至少是在它们的某个阶段,神经可以一起工作,以便可以移动。能够移动,可以让动物积极寻找食物和伴侣。这也帮助他们逃离食肉动物。 -
Virtually all animals have internal digestion of food. Animals consume other
organisms
and may use special tissues and organs to digest them. (Many other organisms absorb nutrients directly from the environment.)
::几乎所有动物都有食物内部消化,动物食用其他生物,可能使用特殊组织和器官消化。 (许多其他生物直接吸收来自环境的养分。 )
Most animals share these characteristics: sensory organs, movement, and internal digestion.
::大多数动物具有这些特征:感官器官、运动和内分泌。Animal Life Cycle and Reproduction
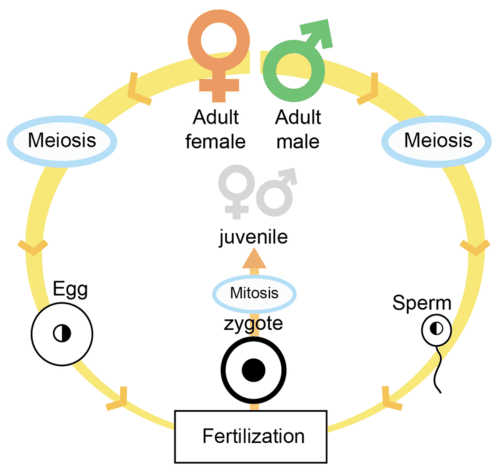
::动物生命周期和繁殖Many animals have a relatively simple life cycle. A general animal life cycle is shown in Figure . Most animals spend the majority of their life as diploid organisms. Just about all animals reproduce sexually. Diploid adults undergo to produce or eggs . occurs when a sperm and an egg fuse. The zygote that forms develops into an embryo . The embryo eventually develops into an adult.
::许多动物的生命周期相对简单,一般的动物生命周期在图中显示。大多数动物的寿命大部分是作为浸泡生物来度过的。几乎所有动物都是性繁殖的。小动物会进行生产或产卵。当精子和蛋的导体形成胚胎时,就会出现。胚胎最终会发展成成人。Animal Life Cycle. An animal life cycle that includes only sexual reproduction is shown here. Some animals also reproduce asexually. How does the animal life cycle compare with the life cycle of a plant?
::动物生命周期:这里显示只包括性生殖的动物生命周期。有些动物还性繁殖。动物生命周期与植物生命周期相比如何?Summary
::摘要-
Animals are multicellular eukaryotes that lack cell walls.
::动物是没有细胞壁的多细胞卵子。 -
All animals are heterotrophs.
::所有动物都是血化动物 -
Animals have sensory organs, the ability to move, and internal digestion. They also have sexual reproduction.
::动物有感官器官、移动能力和内部消化能力,也有性生殖。
Review
::回顾-
Identify traits that characterize all animals.
::辨别所有动物特征的特征 -
State one way that animal cells differ from the cells of plants and fungi. What is the significance of this difference?
::说明动物细胞与植物和真菌细胞不同的方式。 -
Describe animal digestion.
::描述动物消化。 -
Describe a general animal life cycle.
::描述一般动物生命周期。
-
Animals can detect environmental
stimuli
, such as light, sound, and touch. Stimuli are detected by
sensory nerve
cells. The information is transmitted and processed by the nervous system. The nervous system, in turn, may direct the body to respond.