2.1地球科学的分支
章节大纲
-
What is Earth science?
::什么是地球科学?Earth scientists seek to understand the beautiful sphere on which we live. Earth is a very large, complex set of systems. So most Earth scientists study one aspect of the planet . Researchers work together to answer complicated questions. The major branches of Earth science are described below.
::地球科学家试图了解我们所生活的美丽领域。地球是一个非常庞大、复杂的系统。因此,大多数地球科学家研究地球的一个方面。研究人员共同努力回答复杂的问题。下文将介绍地球科学的主要分支。Geology
::地质地质学Geology is the study of the solid Earth. Geologists study how and form. The way mountains rise up is part of geology. The way mountains erode away is another part. Geologists also study fossils and Earth’s history. There are many other branches of geology. There is so much to know about our home planet that most geologists become specialists in one area. For example, a mineralogist studies minerals ( Figure ).
::地质学是固体地球的研究。地质学家研究如何和形态。山区上升的方式是地质学的一部分。山区侵蚀的方式是另一部分。地质学家也研究化石和地球历史。地质学还有其他许多分支。关于我们的家园星球,还有很多东西需要了解,所以大多数地质学家都成了一个领域的专家。例如,矿学家研究矿物(图 ) 。(left) Mineralogists focus on all kinds of minerals. (right) Seismographs are used to measure earthquakes and pinpoint their origins. Some volcanologists brave molten lava to study . Seismologists monitor worldwide to help protect people and property from harm ( Figure ). Paleontologists are interested in fossils and how ancient organisms lived. Scientists who compare the geology of other planets to Earth are planetary geologists. Some geologists study the Moon. Others look for petroleum. Still others specialize in studying soil . Some geologists can tell how old rocks are and determine how different rock layers formed. There is probably an expert in almost anything you can think of related to Earth!
::一些火山学家勇敢的熔岩来研究。 地震学家监测了全球范围,以帮助保护人类和财产免受伤害(Figure)。 古生物学家对化石和古代生物的生存方式感兴趣。 将其他行星的地质学与地球进行比较的科学家是行星地质学家。 一些地质学家研究月球。 另一些地质学家研究石油。 还有一些地质学家专门研究土壤。 一些地质学家可以辨别古老的岩石是如何形成的, 并且确定不同岩层是如何形成的。 可能有一个专家, 几乎可以想到与地球有关的东西!Geologists might study rivers and lakes , the underground water found between soil and rock particles, or even water that is frozen in . Earth scientists need geographers who explore the features of Earth’s surface. They work with cartographers, who make . Studying the layers of rock beneath the surface helps us to understand the history of planet Earth ( Figure ).
::地质学家可能会研究河流和湖泊、土壤和岩石粒子之间发现的地下水,甚至冰冻的水。 地球科学家需要测量地球表面特征的地理学家。 他们与制图师一起工作,他们制造 。 研究地表下岩层有助于我们了解地球的历史(图 ) 。Geologists ask a lot of questions. They wonder what they need to know about earthquakes to be able to predict them in time to evacuate a region. They ask what will happen to shorelines as sea level rises. Some even wonder what would happen if the magnetic field reverses!
::地质学家问了很多问题。 他们想知道他们需要了解什么地震来及时预测地震,才能及时疏散一个区域。 他们问海平面升高后海岸线会发生什么。 有些人甚至想知道,如果磁场倒转,会发生什么情况!These folded rock layers have bent over time. Studying rock layers helps scientists to explain these layers and the geologic history of the area. Oceanography
::海洋学Oceanography is the study of the oceans. The word oceanology might be more accurate, since “ology” is “the study of.” “Graph” is “to write” and refers to mapmaking. But mapping the oceans is how oceanography started.
::海洋学是海洋学的研究,海洋学一词可能更准确,因为“地质学”是“研究的”。 “大地”是“写”和地图绘制。 但海洋绘图是海洋学的起源。More than 70% of Earth’s surface is covered with water. Almost all of that water is in the oceans. Scientists have visited the deepest parts of the ocean in submarines. Remote vehicles go where humans can't ( Figure ). Yet much of the ocean remains unexplored. Some people call the ocean “the last frontier.”
::地球表面的70%以上是被水覆盖的。 几乎所有的水都在海洋中。 科学家们在潜水艇中考察了海洋的最深处。 远方的飞行器去的是人类无法去的地方(图 ) 。 但海洋的大部分仍未探索。 一些人称海洋为“最后的疆界 ” 。The Alvin research vessel is specially designed to explore the seas. There are many branches of oceanography. Physical oceanography is the study of water movement, like waves and ocean currents. Physical oceanographers ask when or if a will hit a shoreline. Marine geologists look at rocks and structures in the ocean basins. These scientists ask how new ocean crust forms. Chemical oceanographers study the natural elements in ocean water. Chemical oceanographers might be concerned with where carbon dioxide goes in the oceans. Marine biologists look at marine life. There are lots of questions to ask about marine life!
::物理海洋学是研究水的移动,就像波浪和洋流。物理海洋学家问何时或是否将到达海岸线。海洋地质学家看海洋盆地的岩石和结构。这些科学家问新的海洋地壳形式如何。化学海洋学家研究海洋水中的自然元素。化学海洋学家可能关心二氧化碳在海洋中的去向。海洋生物学家们看看海洋生物。有很多关于海洋生物的问题要问!Meteorology and Climatology
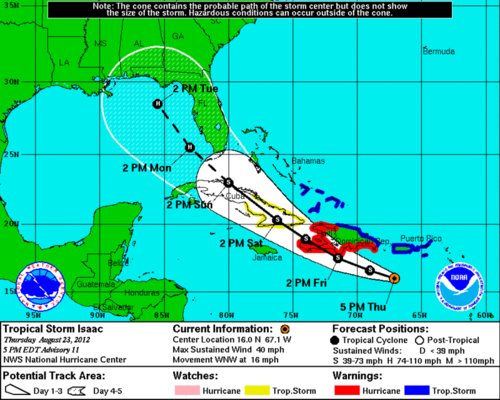
::气象和气候学Meteorologists don’t study meteors—they study the atmosphere! The atmosphere is a thin layer of gas that surrounds Earth. The word “meteor” refers to things in the air. Meteorology includes the study of patterns, , , and . Meteorology is very important. Using radars and satellites , meteorologists work to predict, or forecast, the weather ( Figure ). Meteorologists are getting better at predicting the weather all the time. Meteorologists wonder how to better predict weather. They wonder what the effects of rising water vapor in the atmosphere will be on weather.
::气象学家不研究流星 — — 他们研究大气; 大气是环绕地球的稀薄气体层。 “ 气象”一词指空气中的东西。 气象学包括模式研究、 和. 气象学非常重要。 利用雷达和卫星,气象学家工作来预测或预报天气(图 ) 。 气象学家们越来越擅长预测整个时间的天气。 气象学家们想知道如何更好地预测天气。 他们想知道大气中水蒸气上升对天气的影响。Meteorologists forecast the weather a region can expect from a tropical storm. Climatologists also study the atmosphere. These scientists work to understand the climate as it is now. They also study how climate will change in response to . There are lots of questions to ask about our changing climate.
::气候学家们也研究大气。这些科学家们努力了解气候现状。他们也研究气候如何因应气候的变化。关于气候的变化,有很多问题要问。Environmental Science
::环境科学Environmental scientists study the effects people have on their environment. This includes the landscape , atmosphere, water, and living things. These scientists ask all sorts of questions about how Earth systems are changing as a result of human actions. They try to predict what changes will come in the future.
::环境科学家研究人类对环境的影响。这包括地貌、大气、水和生物。这些科学家问了各种各样的问题,了解地球系统如何因人类行动而变化。他们试图预测未来会发生什么变化。Ecologists study lifeforms and the environments they live in ( Figure ). They try to predict the chain reactions that could occur when one part of the ecosystem is disrupted.
::生态学家研究生命形式和他们生活的环境(图 ) 。 他们试图预测当生态系统的一部分被破坏时可能发生的连锁反应 。In a marine ecosystem, coral, fish, and other sea life depend on each other for survival. We hope to find better ways of living that can help the environment.
::我们希望找到能够帮助环境的更好的生活方式。Astronomy
::天文学Astronomy is the study of outer space and the physical bodies beyond planet Earth. Astronomers use to see things far beyond what the human eye can see. Astronomers help to design spacecrafts or satellites that travel into space and send back information about faraway places ( Figure ).
::天文学是对地球以外的外层空间和物理体的研究。天文学家利用天文学家的眼光看远非人类眼目所见的东西。天文学家帮助设计航天器或卫星,这些航天器或卫星飞入太空,并发送远方地点的信息(图 ) 。The Hubble Space Telescope. Astronomers ask a wide variety of questions. How do strong bursts of energy from the , called solar flares , affect communications? How might an impact from an affect life on Earth? What are the properties of black holes ? Astronomers ask bigger questions too. How was the created? Is there life on other planets? Are there resources on other planets that people could use for space travel? Astronomers use what Earth scientists know about our planet to make comparisons with other planets.
::天文学家问了各种各样的问题。 由被称为太阳耀斑的太阳耀斑产生的强力能量暴发如何影响通信? 地球生命会受到什么影响? 黑洞的特性是什么? 天文学家也问了更大的问题。 创造出什么? 其他行星上是否有生命? 其它行星上是否有资源可供人们用于空间旅行? 天文学家利用地球科学家对地球的了解来与其他行星进行比较。Summary
::摘要- The study of Earth science includes many different fields, including geology, meteorology, oceanography, and astronomy.
::地球科学研究包括许多不同领域,包括地质学、气象学、海洋学和天文学。
- Each type of Earth scientist investigates the processes and materials of the Earth.
::每种类型的地球科学家都调查地球的工序和材料。
- Like other scientists, Earth scientists ask questions.
::与其他科学家一样,地球科学家也提出问题。
Review
::回顾- What do geologists study? Oceanographers? Meteorologists? Climatologists? Environmental scientists? Astronomers?
::地质学家研究什么? 海洋学家? 气象学家? 气候学家? 环境科学家?天文学家?
- Ask a question that is relevant to each of the fields of Earth science.
::问一个与地球科学每个领域有关的问题。
- Why is Earth science made up of all of these fields?
::为什么地球科学由所有这些领域组成?
- The study of Earth science includes many different fields, including geology, meteorology, oceanography, and astronomy.