12.15 复制
章节大纲
-
What are the advantages of a water-tight egg?
::紧水蛋有什么好处?Obviously, water-tight eggs can be laid anywhere. They do not have to be kept constantly moist. There is no danger of the developing fetus dehydrating. Shown above is a tortoise hatching.
::显然,密水卵可以在任何地方产下。 它们不必一直保持湿润。 发育中的胎儿脱水没有危险。 上面显示的是一种乌龟孵化。Reptile Reproduction
::复制Most reproduce sexually and have internal fertilization . Males have one or two penises that pass from their cloaca to the cloaca of a female. occurs within the cloaca, and fertilized eggs leave the female’s body through the opening in the cloaca. In a minority of , the eggs are retained inside the female’s body until they hatch. Then the offspring leave the mother’s body through the cloaca opening.
::大部分的生殖是性生殖,并且有体内受精。 男性有一两个阴茎,从她们的阴茎到雌性的阴茎。 在阴茎里,受精的卵从雌性的身体里流出。 在阴茎里,受精的卵从雌性的身体里流出。 在少数的雌性体内,卵在孵化前保留在雌性体内。 然后,后代通过阴茎的开口离开母体。Amniotic Eggs
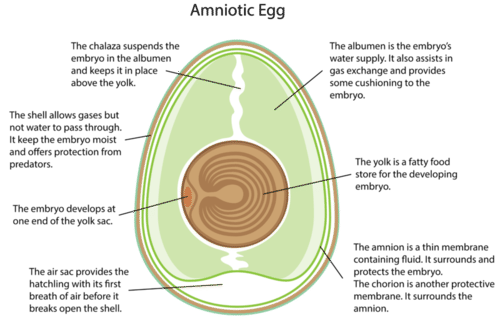
::羊蛋Unlike , reptiles produce amniotic eggs (see Figure ). The shell, membranes, and other structures of an amniotic egg protect and nourish the embryo . They keep the embryo moist and safe while it grows and develops. They also provide it with a rich, fatty food source (the yolk ).
::与爬行动物不同的是,爬行动物产出羊蛋(见图 ) 。 外壳、膜和其他的羊蛋结构保护和养殖胚胎。 它们保持胚胎的湿润和安全,同时胚胎在生长和发育。 它们也为胚胎提供了丰富、脂肪的食物来源(黄蛋 ) 。The amniotic egg is an important adaptation in fully terrestrial vertebrates. It first evolved in reptiles. The shells of reptile eggs are either hard or leathery.
::羊蛋是完全陆地脊椎动物的重要适应。 它首先在爬行动物中演变。 爬行动物蛋的壳状是硬的或皮质的。Reptile Young
::年轻人regtile YoungUnlike amphibians, reptiles do not have a larval stage. Instead, newly hatched reptiles look like smaller versions of the adults. They are able to move about on their own, but they are vulnerable to predators . Even so, most reptile parents provide no care to their hatchlings . In fact, most reptiles don’t even take care of their eggs. For example, female sea lay their eggs on a sandy beach and then return to the ocean. The only exceptions are female crocodiles and alligators. They may defend their nest from predators and help the hatchlings reach the . If the young remain in the area, the mother may continue to protect them for up to a year.
::与两栖动物不同,爬行动物没有幼虫阶段。 相反,新孵化的爬行动物看起来像成人的较小版本。它们可以自己移动,但容易受到食肉动物的伤害。即使如此,大多数爬行动物的父母都不照顾幼崽。事实上,大多数爬行动物甚至不照顾它们的蛋。例如,雌性海藻在沙滩上产卵,然后返回海洋。唯一的例外是雌性鳄鱼和鳄鱼。它们可以保护自己的巢,免受食肉动物的侵扰,帮助孵化动物到达它们。如果年轻人留在这个区域,母亲可以继续保护它们长达一年。Summary
::摘要-
Most reptiles reproduce sexually and have internal fertilization.
::大多数爬行动物性繁殖,并有内脏受精。 -
Reptile eggs are amniotic, so they can be laid on land instead of in water.
::爬虫蛋是羊水,所以可以放在陆地上而不是在水中。 -
Reptiles do not have a larval stage, and their hatchlings are relatively mature.
::爬虫没有幼虫阶段,它们的幼崽相对成熟。 -
Reptile parents provide little if any care to their young.
::爬虫父母对年幼者几乎没有任何照顾。
Review
::回顾-
Outline the structure and function of an amniotic egg.
::概括出一个羊膜蛋的结构和功能。 -
Describe young reptiles.
::描述年轻的爬行动物。
-
Most reptiles reproduce sexually and have internal fertilization.