2.12电磁频谱对空间的研究
章节大纲
-
How do scientists learn about space?
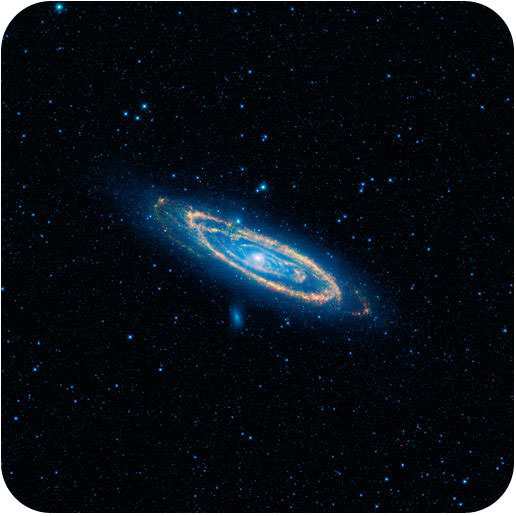
::科学家如何了解空间?Many scientists can touch the materials they study. Most can do experiments to test those materials. Biologists can collect cells, seeds, or sea urchins to study in the laboratory. Physicists can test the strength of metal or smash atoms into each other. Geologists can chip away at and test their chemistry. What can astronomers use to study space? Light and other electromagnetic waves , of course. This is the Andromeda Galaxy as it appeared 2.5 million years ago. Why is the light so old?
::许多科学家可以触摸他们研究的材料。 多数科学家可以做实验来测试这些材料。 生物学家可以收集细胞、种子或海胆,在实验室里研究。 物理学家可以测试金属的强度, 也可以将原子击碎。 地质学家可以解开并测试他们的化学作用。 天文学家可以用什么来研究空间? 光和其他电磁波, 当然。 这是250万年前出现的安朵美达银河系。 为什么光是如此老?Electromagnetic Spectrum
::电磁频谱Earth is just a tiny speck in the . Our planet is surrounded by lots of space. Light travels across empty space. Light is the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum . Astronomers use the light and other energy that comes to us to gather information about the Universe.
::地球只是地球中一个微小的斑点。 我们的星球周围有很多空间。 光穿过空空空间。 光是电磁波谱的可见部分。 天文学家利用光和其他能量来收集宇宙的信息。The Speed of Light
::光的光速In space, light travels at about 300,000,000 meters per second (670,000,000 miles per hour). How fast is that? A beam of light could travel from New York to Los Angeles and back again nearly 40 times in just one second. Even at that amazing rate, objects in space are so far away that it takes a lot of time for their light to reach us. Even light from the nearest star , our , takes about eight minutes to reach Earth.
::光在太空中以每秒30万米(每小时6.70亿英里)的速度行走。它的速度有多快?一束光从纽约到洛杉矶只要一秒钟就能回回回近40次。即使以如此惊人的速度,在太空中的物体也离地球如此之远,它们的光要花很多时间才能到达我们。即使是最近的恒星,我们的光,也需要大约8分钟才能到达地球。Light-Years
::光年We need a really big unit to measure distances out in space because distances between stars are so great. A light-year , 9.5 trillion kilometers (5.9 trillion miles), is the distance that light travels in one year . That’s a long way! Out in space, it’s actually a pretty short distance.
::我们需要一个非常大的单位来测量太空中的距离,因为恒星之间的距离是如此之大。 光年,9.5万亿公里(5.9万亿英里 ) , 光年是光线在一年中行走的距离。 这是一个漫长的路程。 在太空中,它实际上是一个非常短的距离。Proxima Centauri is the closest star to us after the Sun. This near neighbor is 4.22 light-years away. That means the light from Proxima Centauri takes 4.22 years to reach us. Our galaxy, the Milky Way Galaxy , is about 100,000 light-years across. So it takes light 100,000 years to travel from one side of the galaxy to the other! It turns out that even 100,000 light-years is a short distance. The most distant we have detected are more than 13 billion light-years away. That’s over a hundred-billion-trillion kilometers!
::Proxima Centauri是太阳之后最接近我们的恒星。 近邻离太阳只有4. 22光年。 这意味着来自Proxima Centauri的光线需要4. 22年才能到达我们。 我们的银河系,银河系,大约是10万光年。 因此, 从银河的一面到另一面需要10万光年。 事实证明, 即使是10万光年也是短距离。 我们所探测到的最远的距离是130亿光年以上。 这已经超过10亿亿公里!Looking Back in Time
::《回顾时光》When we look at stars and galaxies, we are seeing over great distances. More importantly, we are also seeing back in time. When we see a distant galaxy, we are actually seeing how the galaxy used to look. For example, the Whirlpool Galaxy is about 23 million light-years from Earth ( Figure ). When you see an image of the galaxy what are you seeing? You are seeing the galaxy as it was 23 million years ago!
::当我们观察恒星和星系时,我们看到的距离很远。更重要的是,我们也看到时间。当我们看到一个遥远的星系时,我们实际上看到星系的外观。例如,Whirlpool银河系距地球约2300万光年(图)。当你看到银河系的图像时,你看到了什么?你看到的是银河系,就像2300万年前的银河系一样!The Whirlpool Galaxy as it looked 23 million years ago.
::Whirlpool银河系2300万年前的样子Since scientists can look back in time, they can better understand the Universe's history.
::因为科学家们可以回顾过去, 他们可以更好地了解宇宙的历史。Electromagnetic Waves
::电磁波Light is one type of electromagnetic radiation . Light is energy that travels in the form of an electromagnetic wave. Pictured below is a diagram of an electromagnetic wave ( Figure ). An electromagnetic (EM) wave has two parts: an electric field and a magnetic field . The electric and magnetic fields vibrate up and down, which makes the wave.
::光是电磁辐射的一种类型。光是以电磁波的形式穿行的能量。下面的图示是电磁波的图表(图)。电磁波有两个部分:电场和磁场。电磁场上下振动,形成电波。An electromagnetic wave has oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
::电磁波震动电磁场和磁场。The wavelength is the horizontal distance between two of the same points on the wave, like wave crest to wave crest. A wave’s frequency measures the number of wavelengths that pass a given point every second. As wavelength increases, frequency decreases. This means that as wavelengths get shorter, more waves move past a particular spot in the same amount of time.
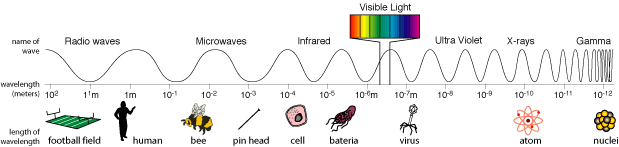
::波长是波上两个相同点之间的水平距离,如波峰的波峰到波峰的波峰。波的频率测量每秒通过一个特定点的波长数量。随着波长的增加,频率会下降。这意味着随着波长的缩短,更多的波浪会在同一时间跨过一个特定点。The Electromagnetic Spectrum
::电磁频谱Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum ( Figure ) that humans can see. Visible light includes all the colors of the rainbow. Each color is determined by its wavelength. Visible light ranges from violet wavelengths of 400 nanometers (nm) through red at 700 nm.
::可见光是人类可以看到的电磁频谱( 图)的一部分。 可见光包括彩虹的所有颜色。 每个颜色由波长决定。 可见光从紫外波长400纳米到红色700纳米不等。Visible light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum. There are parts of the electromagnetic spectrum that humans cannot see. This radiation exists all around you. You just can’t see it! Every star, including our Sun, emits radiation of many wavelengths. Astronomers can learn a lot from studying the details of the spectrum of radiation from a star.
::可见光光只是电磁频谱的一小部分。 有一部分电磁频谱是人类看不见的。 这种辐射存在于你周围。 你看不到它。 每个恒星,包括我们的太阳,都发出许多波长的辐射。 天文学家可以从研究恒星辐射频谱的细节中学到很多东西。The electromagnetic spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays.
::从无线电波到伽马射线的电磁频谱。Many extremely interesting objects can’t be seen with the unaided eye. Astronomers use to see objects at wavelengths all across the electromagnetic spectrum. Some very hot stars emit light primarily at ultraviolet wavelengths. There are extremely hot objects that emit X-rays and even gamma rays . Some very cool stars shine mostly in the infrared light wavelengths. Radio waves come from the faintest, most distant objects.
::许多非常有趣的天体无法在无助眼中看到。 天文学家用电磁波谱以波长看物体。 一些非常热的恒星主要在紫外线波长下发光。 有些极热的天体释放出X射线甚至伽马射线。 一些非常冷淡的恒星主要在红外光波长中发光。 无线电波来自最微弱、最遥远的天体。Summary
::摘要- Electromagnetic radiation is energy transmitted as waves with different wavelengths. This makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.
::电磁辐射是电波和波长不同的波浪所传播的能量,构成电磁波谱。
- Light travels very fast but still takes a long time to get across space. A light-year is the distance light can travel in one year.
::光的移动速度非常快,但仍需要很长的时间才能穿越空间。光年是光的距离,一年后光能穿行。
- From longest wavelengths to shortest wavelengths the electromagnetic spectrum is: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
::从最长波长到最短波长,电磁波谱是:无线电波、微波、红外线、可见光、紫外线、X光和伽马射线。
Review
::回顾- Why do astronomers use light-years as a measure of distance?
::为什么天文学家用光年作为距离的量度?
- In the electromagnetic spectrum, which wavelengths are shorter than visible light? Which are longer than visible light? Which are relatively cooler? Which are relatively hotter?
::在电磁频谱中,哪一种波长比可见光短?哪一种波长比可见光长?哪个波长比可见光长?哪个波长比可见光长?哪个波长相对更冷?哪个波长相对热?
- Why does light we see today tell us something about what happened earlier in the history of the Universe?
::为什么我们今天看到的光告诉我们 宇宙历史早期发生的事情?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
::电磁频谱是什么?
- What type of waves have the shortest wavelengths?
::哪一种波的波长最短?
- What type of waves have the longest wavelengths?
::什么样的波有最长的波长?
- What do electromagnetic waves transmit?
::电磁波传输什么?
- Define wavelength.
::定义波长。
- Define frequency.
::界定频率。
- What type of waves have the lowest frequency?
::哪种波的频率最低?
- What is the visible light region?
::可见光区域是什么?
- How is color produced?
::如何生产彩色?
- What do scientists use the electromagnetic spectrum for?
::科学家使用电磁频谱做什么?
- Electromagnetic radiation is energy transmitted as waves with different wavelengths. This makes up the electromagnetic spectrum.