9.4 印度(2天)
章节大纲
-
Chapter Challenges
::章次 挑战-
Outline the basic activities of British colonialism that affected the realm.
::概述影响王国的英国殖民主义的基本活动。 -
Understand the basic qualities of the rural and urban characteristics of India.
::了解印度城乡特点的基本素质。 -
Summarize the main economic activities and economic conditions in India.
::概述印度的主要经济活动和经济状况。 -
Describe the differences between various geographic regions of India.
::说明印度不同地理区域之间的差异。 -
Explain the measures the Indian government has taken to protect the biodiversity of India.
::解释印度政府为保护印度生物多样性所采取的措施。
Student Learning Objectives
::学生学习目标TEKS Regional Unit 09 South Asia: Chapter 9.4 India
::TERS 区域股 09 南亚:第9.4章WG.2A Describe the human and physical characteristics of the same regions at different periods of time to evaluate relationships between past events and current conditions.
::WG.2A 描述不同时期同一区域的人的和自然的特征,以评估过去事件与当前状况之间的关系。WG.2B Explain how changes in societies have led to diverse uses of physical features.
::WG.2B 解释社会变化如何导致对物理特征的多种利用。WG,4C Explain the influence of climate on the distribution of biomes in different regions.
::工作组,4C 解释气候对不同区域生物群落分布的影响。WG.6B Explain the processes that have caused changes in settlement patterns, including urbanization, transportation, access to and availability of resources, and economic activities.
::WG.6B 解释导致住区模式变化的进程,包括城市化、运输、获得和获得资源以及经济活动。WG.10D Compare global trade patterns over time and examine the implications of globalization, including outsourcing and free trade zones.
::WG.10D 比较一段时间的全球贸易格局,审查全球化的影响,包括外包和自由贸易区。WG.11C Assess how changes in climate, resources, and infrastructure (technology, transportation, and communication) affect the location and patterns of economic activities.
::WG.11C 评估气候、资源和基础设施(技术、运输和通信)的变化如何影响经济活动的地点和模式。WG.22B Generate summaries, generalizations, and thesis statements supported by evidence.
::WG.22B 编写摘要、概述和有证据佐证的论文陈述。WG/22C Use geographic terminology correctly.
::WG/22C 正确使用地理术语。WG.22D Use standard grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation.
::WG.22D 使用标准语法、拼写、句子结构和标点。India
::印度 印度 印度
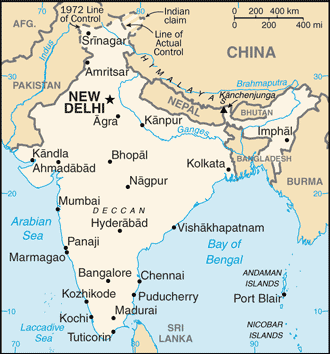
Map of India
::印度地图India and Colonialism
::印度和殖民主义is considered the world’s largest democracy. As the historic geography and the development patterns of India are examined, the complexities of this Hindu state surface. European colonizers of South Asia included the Dutch, Portuguese, French, and, finally, the British. In search of raw materials, cheap labor, and expanding markets, Europeans used their advancements in technology to take over and dominate the regional industrial base.
::南亚的欧洲殖民者 — — 包括荷兰、葡萄牙、法国和英国。 为了寻找原材料、廉价劳动力和不断扩大的市场,欧洲人利用技术进步来接管和支配区域工业基础。The East India Company was a base of British operations in South Asia and evolved to become the administrative government of the region by 1857. The British government created an administrative structure to govern South Asia. Their centralized government in India employed many Sikhs in positions of the administration to help rule over the largely Muslim and Hindu population. The English language was introduced as a lingua franca for the colonies.
::东印度公司是英国在南亚开展业务的基地,到1857年演变成为该地区的行政管理政府,英国政府建立了管理南亚的行政结构,印度的中央政府雇用许多锡克教徒担任行政管理职务,帮助统治主要是穆斯林和印度教徒的人口,英语被作为殖民地的法语。In truth, colonialism did more than establish the current boundaries of South Asia. Besides bringing the region under one central government and providing a lingua franca, India’s colonizers developed the main port cities of Bombay, Calcutta, and Madras (now called Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai, respectively. The names of the port cities have been reverted to their original Hindi forms).
::诚然,殖民主义不仅确定了南亚目前的边界。 除了将该地区置于一个中央政府之下并提供通用语外,印度殖民者还发展了主要港口城市孟买、加尔各答和马德拉斯(分别称为孟买、加尔各答和钦奈 ) 。 港口城市的名称已经恢复到原来的印地语形式。The port cities were access points for connecting goods with markets between India and Europe. Mumbai became the largest city and the economic center of India. In 1912, to exploit the interior of India, the British moved their colonial capital from Kolkata, which was the port for the densely populated Ganges River basin, to New Delhi. Chennai was a port access to southern India and the core of the Dravidian ethnic south.
::孟买成为印度最大的城市和经济中心。 1912年,为了开发印度的内地,英国人将其殖民资本从人口稠密的恒河流域的加尔各答港迁至新德里。 钦奈是印度南部的港口,也是德拉维德族南部的核心。Britain exploited India by extending railroad lines from the three main port cities into the hinterlands, to transport materials from the interior back to the port for export. The Indian Railroad is one of the largest rail networks on Earth. The problem with colonial railroads was that they did not necessarily connect cities with other cities. The British colonizers connected rail lines between the hinterland and the ports for resource exploitation and export of commercial goods. Today, the same port cities act as focal points for the import/export activity of globalization and remain core industrial centers for South Asia. They are now well connected with the other cities of India.
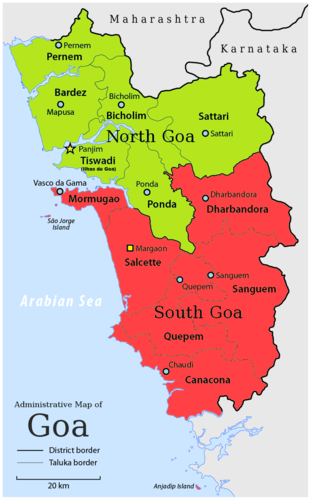
::英国利用印度将铁路线从三个主要港口城市延伸至内地,将内地材料运回出口港口。印度铁路是地球上最大的铁路网之一。殖民铁路的问题在于它们不一定将城市与其他城市连接起来。英国殖民者将内地和港口之间的铁路线连接起来,以便进行资源开采和出口商业货物。今天,这些港口城市是全球化进出口活动的中心点,仍然是南亚的核心工业中心。它们现在与印度其他城市有着密切的联系。Goa is the smallest state of modern-day India. In the 16th century, it was first encountered by Portuguese traders, who annexed it shortly thereafter to become a colony of Portugal, which it was for the next 450 years. Goa was one of the longest-held colonial possessions in the world and was not annexed by India until 1961. By the mid-1800s, most of the population of this tiny area had been forcibly converted to Christianity.
::果阿是现代印度最小的一个国家,在16世纪,葡萄牙贸易商首次发现它,不久后吞并它,成为葡萄牙的殖民地,这是今后450年的葡萄牙殖民地,果阿是世界上拥有时间最长的殖民财产之一,直到1961年才被印度吞并,到1800年代中期,这个小地区的大部分人口被迫皈依基督教。Goa is a state in India within the coastal region known as the Konkan, in Western India. It is bounded by Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its Western coast. It is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population.
::果阿是印度沿海地区内的一个邦,称为印度西部的孔坎,北与马哈拉施特拉交界,东与南与北与卡纳塔卡交界,阿拉伯海形成西海岸,按地区划分是印度最小的邦,按人口划分是第四最小的邦。
Although many Hindu traditions survived the colonial period, and Hindu holidays are celebrated here, Goa is known for its Christian holiday celebrations, especially Christmas and Easter. The cathedral and secular architecture in many of the historic buildings of Goa are European in style, reflecting its Portuguese origins.
::尽管许多印度教传统在殖民时期得以延续,印度教节日也在这里庆祝,但果阿以基督教节日庆祝活动而闻名,特别是圣诞节和复活节。 许多古老的果阿建筑的教堂和世俗建筑是欧洲风格,反映了其葡萄牙血统。Hindu-Christianity Unity Memorial at Miramar Beach in Goa, India.
::印度果阿米拉马尔海滩的印度基督教团结纪念馆。The People of India
::印度人民Contrasts in India are explicitly evident in the regional differences of its human geography. The north-south contrasts are apparent through the lingua franca and ethnic divisions. The main lingua franca in the north is Hindi. In the Dravidian-dominated south, the main lingua franca is English. The densely populated core region along the Ganges River, anchored on each end by Delhi/New Delhi and Kolkata, has traditionally been called the heartland of India.
::印度的对立点明显体现在其人文地理的区域差异上,北南的对比通过语言法语和族裔分歧明显可见。北南的主要语言法语为印地语。在德拉维迪亚人占统治地位的南部,主要语言为英语。恒河沿岸人口稠密的核心地区以德里/新德里和加尔各答为起点,传统上被称为印度的心脏地带。The south is anchored by the port city of Chennai and the large city of Bangalore. Chennai has been a traditional industrial center. The industrial infrastructure has shifted to more modern facilities in other cities, giving over to a “rustbelt” syndrome for portions of the Chennai region. India is a dynamic country, with shifts and changes constantly occurring. Any attempt to stereotype India into cultural regions would be problematic.
::南部由港口城市钦奈和大型城市班加罗尔环绕。 钦奈是一个传统的工业中心。 工业基础设施已经转移到其他城市的现代化设施,让钦奈地区部分地区出现了“入侵带”综合症。 印度是一个充满活力的国家,不断变化变化。 任何将印度刻板化为文化区的企图都会有问题。Hindi is the official language of the government, and both Hindi and English are the lingua franca.
::印地语是政府的官方语言,印地语和英语都是法语语言。
In 2017, India had almost 1.3 billion people, which is about one-sixth of the human population of the earth. An 80 percent majority follow Hindu beliefs. About 13 percent of the population is Muslim. Thirteen may not seem like a high percentage, but in this case it equates to about 140 million people. This is equivalent to all the Muslims who reside in the countries of Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Syria, and Egypt combined. India is sometimes called the third-largest Muslim country in the world, after Indonesia and Pakistan, because of its large Muslim minority.
::2017年,印度有近13亿人口,约占全球人口的六分之一。 80%的印度人信仰印度教。 大约13%的人口是穆斯林。 13人似乎并不高,但在此情况下相当于约1.4亿人。 这相当于居住在伊拉克、沙特阿拉伯、叙利亚和埃及等国家的所有穆斯林人口。 印度有时被称作世界第三大穆斯林国家,仅次于印度尼西亚和巴基斯坦,因为印度是穆斯林少数民族。-
Population trends for major religious groups in India (1951–2011)
::印度主要宗教团体的人口趋势(1951年至2011年)
Religious
groupPopulation
% 1951Population
% 1961Population
% 1971Population
% 1981Population
% 1991Population
% 2001Population
% 2011Hinduism 84.1% 83.45% 82.73% 82.30% 81.53% 80.46% 79.80% Islam 9.8% 10.69% 11.21% 11.75% 12.61% 13.43% 14.23% Christianity 2.3% 2.44% 2.60% 2.44% 2.32% 2.34% 2.30% Sikhism 1.79% 1.79% 1.89% 1.92% 1.94% 1.87% 1.72% Buddhism 0.74% 0.74% 0.70% 0.70% 0.77% 0.77% 0.70% Jainism 0.46% 0.46% 0.48% 0.47% 0.40% 0.41% 0.37% Zoroastrianism 0.13% 0.09% 0.09% 0.09% 0.08% 0.06% n/a Others/Religion not specified 0.43% 0.43% 0.41% 0.42% 0.44% 0.72% 0.9%
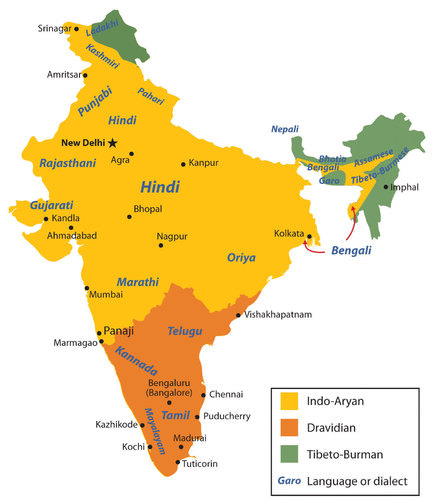
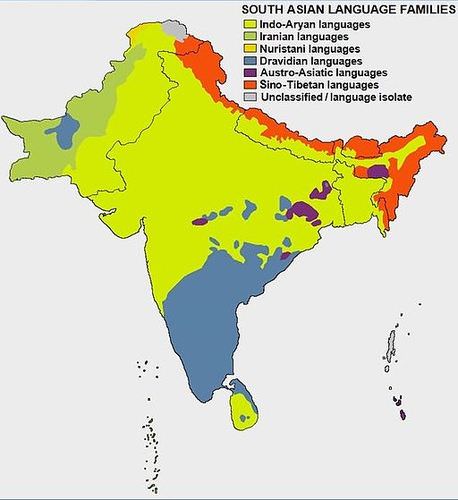
India essentially has two lingua francas: English and Hindi, of which Hindi is the official language of the Indian government. India has 28 states and 14 recognized major languages. Many different languages are spoken in rural areas. The languages of northern India are mainly based on the Indo-European language family. Languages used in the south are mainly from the Dravidian language family. A few regions that border Tibet in the north use languages from the Sino-Tibetan language family.
::印度主要有两种法语语言:英语和印地语,其中印地语是印度政府的官方语言;印度有28个邦和14种公认的主要语言;农村地区使用多种不同语言;印度北部语言主要以印欧语家庭为基础;南部使用的语言主要来自德拉维迪亚语家庭;北部与西藏交界的少数地区使用中提班语家庭的语言。Languages spoken in India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 76.5 percent of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 20.5 percent of Indians. Languages spoken by the remaining 3 percent of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino-Tibetan, Tai-Kadai, and a few other minor language families. India has the world's second highest number of languages after Papua New Guinea.
::印度讲的语言属于若干语系,主要为印度76.5%的印度人讲印度阿里亚语和20.5%的印度人讲德拉维迪亚语,其余3%的人口讲的语言属于奥斯特罗亚西语、中提贝坦语、泰卡代语和其他少数语系。印度的语言数量仅次于巴布亚新几内亚,位居世界第二。-
-
First, Second, and Third Languages by Number of Speakers in India (2001 Census)
::按印度发言者人数分列的第一、第二和第三语言,印度(2001年人口普查)
Language First language
speakersFirst language
speakers as a percentageof total population
::占总人口总数Second language
speakersThird language
speakersTotal speakers Total speakers as a percentage of total
::占总数百分比的百分比population
::人口 人口 人口Hindi 422,048,642 41.03 98,207,180 31,160,696 551,416,518 53.60 English 226,449 0.02 86,125,221 38,993,066 125,344,736 12.18 Bengali 83,369,769 8.10 6,637,222 1,108,088 91,115,079 8.86 Telugu 74,002,856 7.19 9,723,626 1,266,019 84,992,501 8.26 Marathi 71,936,894 6.99 9,546,414 2,701,498 84,184,806 8.18 Tamil 60,793,814 5.91 4,992,253 956,335 66,742,402 6.49 Urdu 51,536,111 5.01 6,535,489 1,007,912 59,079,512 5.74 Kannada 37,924,011 3.69 11,455,287 1,396,428 50,775,726 4.94 Gujarati 46,091,617 4.48 3,476,355 703,989 50,271,961 4.89 Odia 33,017,446 3.21 3,272,151 319,525 36,609,122 3.56 Malayalam 33,066,392 3.21 499,188 195,885 33,761,465 3.28 Sanskrit 14,135 <0.01 1,234,931 3,742,223 4,991,289 0.49 Urban versus Rural
::城市对农村Rural and urban life within the Indian Subcontinent varies according to wealth and opportunity. While concentrated in specific areas across the landscape, in general the population in rural areas is discontinuous and spread thinly. In urban areas, the populations are very concentrated with many times the population density found in rural areas. India has six world-class cities: Kolkata, Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, Bangalore, and Hyderabad.
::印度次大陆内的农村和城市生活因财富和机会而异,主要集中在地貌特定地区,但一般而言,农村地区人口不连续,分布不广,在城市地区,人口高度集中,是农村地区人口密度的很多倍,印度有六个世界级城市:加尔各答、孟买、德里、钦奈、班加罗尔和海得拉巴。
Top 25 Cities in India by Population
::按人口分列的印度25个最大城市Rank City Population
(2011)Population
(2001)State or union territory 1 Mumbai 12,442,373 11,978,450 Maharashtra 2 Delhi 11,034,555 9,879,172 Delhi 3 Bangalore 8,443,675 4,301,326 Karnataka 4 Hyderabad 6,993,262 3,637,483 Telangana 5 Ahmedabad 5,577,940 3,520,085 Gujarat 6 Chennai 4,646,732 4,343,645 Tamil Nadu 7 Kolkata 4,496,694 4,572,876 West Bengal 8 Surat 4,467,797 2,433,835 Gujarat 9 Pune 3,124,458 2,538,473 Maharashtra 10 Jaipur 3,046,163 2,322,575 Rajasthan 11 Lucknow 2,817,105 2,185,927 Uttar Pradesh 12 Kanpur 2,765,348 2,551,337 Uttar Pradesh 13 Nagpur 2,405,665 2,052,066 Maharashtra 14 Visakhapatnam 2,035,922 982,904 Andhra Pradesh 15 Indore 1,960,631 1,474,968 Madhya Pradesh 16 Thane 1,818,872 1,262,551 Maharashtra 17 Bhopal 1,798,218 1,437,354 Madhya Pradesh 18 Pimpri-Chinchwad 1,729,359 1,012,472 Maharashtra 19 Patna 1,683,200 1,366,444 Bihar 20 Vadodara 1,666,703 1,306,227 Gujarat 21 Ghaziabad 1,636,068 968,256 Uttar Pradesh 22 Ludhiana 1,613,878 1,398,467 Punjab 23 Coimbatore 1,601,438 930,882 Tamil Nadu 24 Agra 1,585,704 1,275,134 Uttar Pradesh 25 Madurai 1,561,129 928,869 Tamil Nadu
India’s interior is mainly composed of villages. In rural villages, much of the economy is based on subsistence strategies, primarily agriculture and small cottage industries. The lifestyle is focused on the agricultural cycles of soil preparation, sowing, and harvesting as well as tending animals, particularly water buffalo, cattle, goats, and sheep. About 65 percent of the population lives in rural areas and makes a living in agriculture.
::印度内地主要由村庄组成。 在农村乡村,大部分经济都以自给战略为基础,主要是农业和小型家庭工业。 生活方式的焦点是土壤准备、播种、收割以及饲养动物(特别是水牛、牛、山羊和羊)的农业周期。 大约65%的人口居住在农村地区,以农业为生。About 35 percent of the population—which is equal to the entire US population—is urbanized. India is rapidly progressing toward urbanization and industrialization. Changes in technology, however, tend to be slow in dispersing to the rural villages. More than half the villages in India do not have road access for motor vehicles. For residents of those villages, walking, animal carts, and trains are the main methods of transportation. Agricultural technology is primitive. Diffusion of new ideas, products, or methods can be slow. Modern communication technology is helping connect these remote regions.
::大约35%的人口——相当于整个美国人口——城市化。印度正在迅速走向城市化和工业化。然而,技术的变化往往在向农村分散方面缓慢。印度一半以上的村庄没有机动车辆的公路。对于这些村庄的居民来说,主要交通方式是步行、畜车和火车。农业技术是原始的。新思想、产品或方法的传播可能缓慢。现代通信技术正在帮助这些偏远地区连接。Plowing the field the traditional way in Manthralaya, AP, India.
::在印度AP的Manthralaya以传统方式耕种田地。
India’s cities are dynamic places, with millions of people, cars, buses, and trucks all found in the streets. In many areas of urban centers, traffic may be stopped to await the movement of a sacred cow or a donkey or bullock cart loaded with merchandise. Indian cities are growing at an unsustainable rate. Overcrowded and congested, the main cities are modernizing and trying to keep up with global trends.
::印度的城市是充满活力的地方,街道上有数百万人、汽车、公共汽车和卡车。 在城市中心的许多地区,交通可能会被阻拦,等待圣牛或装满商品的驴或牛车的移动。 印度城市正在以不可持续的速度增长。 过度拥挤和拥挤,主要城市正在现代化并努力跟上全球趋势。A crowd of people on a street in Mumbai, India.
::印度孟买街上一群人。
Traditionally, family size was large. Large family size results in a swell of young people migrating to urban areas to seek greater opportunities and advantages. In modern times, family size has been reduced to about three children, an accomplishment that did not come easily because of the religious beliefs of most of India’s people. If current trends continue, India will overtake China as the most populous country in the world in about 50 years.
::传统上,家庭规模是巨大的。 家庭规模大导致年轻人大量迁移到城市地区寻求更多机会和优势。 在现代,家庭规模已经减少到大约三个孩子,这一成就并不容易实现,因为印度大多数人的宗教信仰。 如果目前的趋势继续下去,印度将超过中国,成为50年来世界上人口最多的国家。
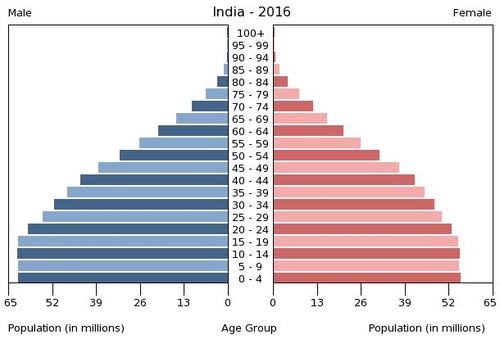
India's Population Pyramid
::印度人口金字塔Age Structure of India: 0-14 years: 27.34 percent (male 186,087,665/female 164,398,204); 15-24 years: 17.9 percent (male 121,879,786/female 107,583,437); 25-54 years: 41.08 percent (male 271,744,709/female 254,834,569); 55-64 years: 7.45 percent (male 47,846,122/female 47,632,532); 65 years and over: 6.24 percent (male 37,837,801/female 42,091,086)
::印度年龄结构:0-14岁:27.34 % (男性 186 087 665女性 164 398 204); 15-24岁: 17.9% (男性 121 879 786女性 107 583 437); 25-54岁: 41.08% (男性 271 744 709/女性 254 834 569); 55-64岁: 7.45% (男性 47 846 122/女性 47 632 532); 65岁及以上: 6.24% (男性 37 837 801/女性 42 091 086)
The level of official governmental control is usually different in an urban setting from what it is in the rural areas. There may be more police or military personnel in areas of heavy traffic or in urban areas that need extra control. A central feature of many Indian cities is an older central city that represents the protected part of the city.
::官方政府控制水平通常在城市环境中与农村地区不同,在交通繁忙地区或城市地区可能有更多的警察或军事人员需要额外控制,许多印度城市的中心特征是代表城市受保护部分的旧中央城市。In Delhi, for example, New Delhi represents the new construction of government buildings that was begun during the British occupation of the region as part of the British Empire. Old Delhi represents the old markets, government buildings, palaces, fortresses, and mosques that were built during the Mogul Empire, between the mid-1500s and the mid-1800s.
::例如,在德里,新德里代表了英国占领该地区期间作为大英帝国的一部分开始的政府建筑新建设。 旧德里代表了老市场、政府建筑、宫殿、堡垒和清真寺,这些建筑都是在1500年代中期至1800年代中期在莫古尔帝国时期建造的。The front view of National Museum New Delhi India.
::印度新德里国家博物馆前视线。
These older parts of the cities, particularly the markets, are bustling with activities, merchants, shoppers, cab drivers, and pedal and motor rickshaws. Rickshaws are either bicycle-driven cabs or cabs based on enclosed motor scooters.
::这些城市的老地方,特别是市场,正忙碌着活动,包括商人、买家、出租车司机、踏板车和摩托车等。 瑞克肖车要么是自行车驱动的出租车,要么是以封闭的摩托车为基础的计程车。Carts parked on the spice market, Khari Baoli Road in Old Delhi, India.
::Carts停在印度新德里的Khari Baoli路的香料市场。
In urban areas, there is a socioeconomic hierarchy of a small group of people who are wealthy and can afford all the amenities we associate with modern life—electricity, clean water, television, computers, and the like. One of the things that characterize modern Indian cities is an expanding middle class. Many young people see the kinds of material goods that are available in the West and are creating job markets and opportunities to allow them to reach or maintain this type of lifestyle. One of the major markets to support this burgeoning middle class is the information technology field, as well as outsourcing in many of the cities of peninsular India.
::在城市地区,一小撮富人拥有社会经济等级,他们可以负担现代生活、清洁用水、电视、计算机等与现代生活相关的所有福利设施。现代印度城市的特点之一是一个不断扩大的中产阶级。许多年轻人看到西方现有的物质产品种类,并正在创造就业市场和机会,使他们能够达到或维持这种生活方式。支持这一新兴中产阶级的主要市场之一是信息技术领域,以及印度半岛许多城市的外包。India is a country with considerable contrast between the wealthy urban elites and the poor rural villagers, many of whom move to the cities and live in slums and work for little pay. Low labor costs have enabled Indian cities to industrialize in many ways similar to Western cities, complete with computers, Internet services, and other modern communications services.
::印度是一个富裕的城市精英和贫穷的农村村民之间有着相当大差异的国家,他们中许多人搬到城市,生活在贫民窟中,工作报酬很低。 低劳动成本使得印度城市能够以与西方城市类似的许多方式实现工业化,完成计算机、互联网服务和其他现代通信服务。India’s growing middle class is a product of educational opportunities and technological advancements. This available skilled labor base has allowed India’s industrial and information sectors to take advantage of economic opportunities in the global marketplace to grow and expand their activities. Development within India is augmented by outsourcing activities by American and European corporations to India. Service center jobs created by are in high demand by skilled Indian workers.
::印度不断增长的中产阶级是教育机会和技术进步的产物。 这种技术熟练的劳动力基础使得印度工业和信息部门能够利用全球市场中的经济机会来增长和扩大它们的活动。 印度内部的发展因美国和欧洲公司向印度的外包活动而得到加强。 熟练的印度工人对服务中心创造就业的需求很大。India’s Economic Situation
::印度的经济状况In the past decade, India has possessed the second fastest growing economy in the world, after China. India’s economy continues to rapidly expand and have a tremendous impact on the world economy. In spite of the size of the economy, India’s population has a low average per capita income. Approximately one-fourth of the people living in India live in poverty. The classifies India as a low-income economy.
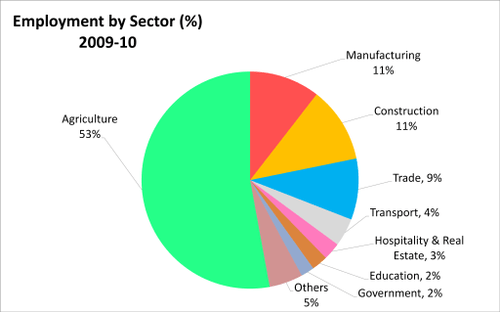
::在过去十年中,印度拥有继中国之后的世界上第二大增长最快的经济体。 印度经济继续快速扩张,并对世界经济产生巨大影响。 尽管印度经济规模庞大,印度人口人均收入却很低。 印度大约四分之一的人口生活在贫困之中。 印度将印度归类为低收入经济体。This chart shows the distribution of labor among India's official major economic categories.
::该图显示了印度官方主要经济类别的劳动力分布情况。
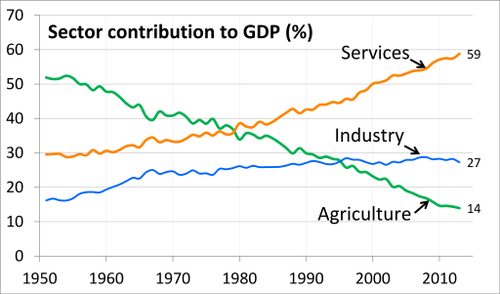
Contribution to the GDP of India by economic sectors of the Indian economy has evolved between 1951 and 2013, as its economy has diversified and developed.
::1951年至2013年期间,印度经济部门对印度国内生产总值的贡献随着经济的多样化和发展而演变。
India has followed a central economic model for most of its development since it declared independence. The central government has exerted strict control over private sector economic development, foreign trade, and foreign investment. Through various economic reforms since the 1990s, India is beginning to open up these markets by reducing government control on foreign investment and trade. Many publicly owned businesses are being privatized. Globalization efforts have been vigorous in India. There has been substantial growth in information services, health care, and the industrial sector
::印度自宣布独立以来,大部分发展都遵循了中央经济模式,中央政府严格控制了私营部门经济发展、对外贸易和外国投资,自1990年代以来,印度通过各种经济改革开始开放这些市场,减少政府对外国投资和贸易的控制,许多公有企业正在私有化,印度的全球化努力十分有力,信息服务、保健和工业部门大幅度增长。Mumbai is the entertainment, fashion and commercial center of India.
::孟买是印度的娱乐、时尚和商业中心。
The economy is extremely diverse and has focused on agriculture, handicrafts, textiles, manufacturing, some industry, and a vast number of services. A 60 percent majority of the population earns its income directly from agriculture and agriculture-related services. Land holdings by individual farmers are small, often less than five acres. When combined with the inadequate use of modern farming technologies, small land holdings become inadequately productive and impractical.
::经济极为多样化,侧重于农业、手工业、纺织品、制造业、某些工业和大量服务,60%的人口直接从农业和与农业有关的服务中赚取收入,农民个人拥有的土地面积小,往往不到五英亩,加上不充分利用现代农业技术,小块土地的产量低,不切实际。Monsoons are critical for the success of India’s agricultural crops during any given season. Because the rainfall of many agricultural areas is tied to the monsoon rains of only a few months, a weak or delayed rainfall can have disastrous effects on the agricultural economy. Agricultural products include commercial crops such as coffee and a variety of spices. An essential product for perfume and incense is sandalwood, harvested primarily in the dense forests of the state of Karnataka, in southwestern India. Bamboo, rice, and lentils provide an important basis for the local economy as well.
::季风对于印度在任何特定季节的农业作物的成功至关重要。 由于许多农业地区的降雨与仅仅几个月的季风雨相关,降雨量的疲软或延迟会对农业经济产生灾难性影响。 农产品包括咖啡和各种香料等商业作物。 香水和香料的基本产品是砂木,主要在印度西南部卡纳塔克州茂密的森林中收获。 竹子、大米和扁豆也为当地经济提供了重要的基础。The history of Agriculture in India dates back to Indus Valley Civilization Era and even before that in some parts of Southern India.
::印度农业的历史可追溯到印度河谷文明时代,甚至在印度南部的一些地区,甚至在此之前。
Over the last two decades, information technology and related services are transforming India’s economy and society. In turn, India is transforming the world’s information technologies in terms of production and service as well as the export of skilled workers in financial, computer hardware, software engineering, and software services. Manufacturing and industry are becoming a more important part of India’s economy as it begins to expand.
::在过去二十年中,信息技术和相关服务正在改变印度的经济和社会。 反过来,印度在生产和服务以及金融、计算机硬件、软件工程和软件服务的熟练工人出口方面正在改变世界的信息技术。 随着制造业和工业开始扩张,它们正在成为印度经济中更重要的一部分。Manufacturing and industry account for almost one-third of the gross domestic product (GDP) and contribute jobs to almost one-fifth of the total workforce. Major economic sectors such as manufacturing, industry, biotechnology, telecommunications, aviation, shipbuilding, and retail are exhibiting strong growth rates.
::制造业和工业占国内生产总值(GDP)的近三分之一,为劳动力总数的近五分之一提供了就业机会,制造业、工业、生物技术、电信、航空、造船和零售等主要经济部门正在呈现强劲的增长率。A large number of educated young people who are fluent in English are changing India into a “back office” target for global outsourcing for customer services. These customer services focus on computer-related products but also include service-related industries and online sales companies. The level of outsourcing of information activity to India has been substantial.
::大量受过教育、英语流利的年轻人正在将印度变成全球客户服务外包的“后台办公室”目标,这些客户服务侧重于计算机相关产品,但也包括与服务有关的行业和在线销售公司,向印度外包信息活动的数量相当大。Any work that can be conducted over the Internet or telephone can be outsourced to anywhere in the world that has high-speed communication links. Countries that are attractive to BPO are countries where the English language is prominent, where employment costs are low, and where there is an adequate labor base of skilled or educated workers that can be trained in the services required. India has been the main destination for BPO activity from the United States. Firms with service work or computer programming are drawn to India because English is a lingua franca and India has an adequate skilled labor base to draw from.
::可以通过互联网或电话进行的任何工作都可以外包给世界上任何拥有高速通信连接的任何地方。对BPO有吸引力的国家是英语突出、就业成本低、有受过所需服务培训的熟练或受过教育的工人拥有足够劳动力基础的国家。印度一直是BPO活动的主要目的地美国。有服务工作或计算机编程的公司被吸引到印度,因为英语是一个通用语,印度拥有足够的熟练劳动力基础。About 2.8 million people work in outsourcing sector in India.
::大约280万人在印度外包部门工作。
Tourism has always been an important part of India’s economy and has been focused on the unique natural environments as well as historical cities, monuments, and temples found throughout the country. Of particular importance are the Mogul-period tombs, palaces, and mosques in Delhi, Agra, and Jaipur, India’s “Golden Triangle” of tourism.
::旅游业一直是印度经济的重要组成部分,并一直关注独特的自然环境以及全国各地的历史城市、古迹和寺庙。 尤其重要的是位于德里、阿格拉和印度 " 金三角 " 旅游的莫古尔时期坟墓、宫殿和清真寺。India is a country of contrasts. Scenic beauty abounds from the Eastern and Western Ghats to the high mountains of the Himalayas. The monsoon rains provide abundant agricultural crops for densely populated regions such as the Ganges River basin. On the other hand, places such as the Thar Desert are sparsely inhabited.
::印度是一个反差的国家,从东部和西盖茨到喜马拉雅山高山,风季雨为诸如恒河流域等人口稠密地区提供了丰富的农作物,而恰尔沙漠等地区则人烟稀少。There is a wide gap between the wealthy elite and the massive numbers of people who live in poverty. Mumbai has some of the largest slums in Asia, yet it is the financial capital of India, teeming with economic activity. As incomes rise for the middle class in India, the price of automobiles becomes more accessible. On the downside, an escalation in the numbers of motor vehicles in use tends to lead to an escalation in the levels of air pollution and traffic congestion.
::富裕的精英阶层和大量贫困人口之间存在巨大差距。 孟买是亚洲最大的贫民窟之一,但它是印度的金融资本,充满了经济活动。 随着印度中产阶级收入的上升,汽车价格更加容易获得。 在下行方面,正在使用的机动车辆数量的上升往往导致空气污染和交通堵塞水平的上升。Similarly, an expansion of transportation systems increases the use of fossil fuels. India is a major competitor for fossil fuels exported from the Persian Gulf and other sources. The continued industrialization and urbanization in India foretell an increase in demand for energy. Rising energy costs and demand, combined with economic growth, have caused a serious problem for India.
::同样,运输系统的扩大也增加了矿物燃料的使用,印度是波斯湾和其他出口来源矿物燃料的主要竞争者,印度持续的工业化和城市化预示着能源需求的增加,能源成本和需求的上升,加上经济增长,给印度造成了严重问题。Many areas will be without power as they are shut off the power grid for hours or days, a process known as load-shedding. This allows industry and manufacturing to use energy resources during peak times. In general, India is poor in natural gas and oil resources and is heavily dependent on coal and foreign oil imports. India is rich in alternative energy resources, such as solar, wind, and biofuels. However, alternative energy resources have not been sufficiently developed.
::许多地区将失去电力,因为它们关闭电网数小时或数天,这是一个称为断压的过程,使工业和制造业能够在高峰时期使用能源资源,一般来说,印度天然气和石油资源贫乏,严重依赖煤炭和外国石油进口,印度拥有太阳能、风能和生物燃料等替代能源资源丰富,但替代能源资源尚未充分开发。Vehicle Manufacturing
::车辆制造
The Nano is considered the world’s most inexpensive car.
::纳诺被认为是世界上最便宜的汽车。
An example of India’s growing economic milieu is motor vehicle manufacturing. India’s vehicle manufacturing base is expanding rapidly. Vehicle manufacturing companies from North America, Europe, and East Asia are all active in India, and India also has its own share of vehicle manufacturing companies. For example, Mumbai-based . is the country’s foremost vehicle production corporation and it claims to be the second-largest commercial vehicle manufacturer in the world.
::印度日益增长的经济环境的一个例子就是机动车辆制造。 印度的机动车辆制造基地正在迅速扩张。 来自北美、欧洲和东亚的机动车辆制造公司都在印度活动,印度也有自己在汽车制造公司中的份额。 比如,孟买是印度最大的汽车生产公司,它自称是世界上第二大商用车辆制造商。Tata Motors is India’s largest designer and manufacturer of commercial buses and trucks, and it also produces the most inexpensive car in the world, the Tata Nano. Tata Motors manufactures mid-sized and larger automobiles, too. The company has expanded operations to Spain, Thailand, South Korea, and the United Kingdom. The company is an example of an Indian-based international corporation that is a force in the global marketplace. In 2010, India was recognized as a major competitor with Thailand, South Korea, and Japan as the fourth main exporter of autos in Asia.
::塔塔汽车公司(Tata Motors)是印度最大的商用大客车和卡车设计师和制造商,也是全世界最廉价的汽车Tata Nano。塔塔汽车公司(Tata Nano )也制造中大型汽车。 该公司将业务扩展到西班牙、泰国、韩国和联合王国。 该公司是印度一家国际公司在全球市场上的一股力量。 2010年,印度被公认为与泰国、韩国和日本为亚洲第四大汽车出口国的主要竞争者。The Indian Cinema
::印度电影院Cinema makes up a large portion of the entertainment sector in India. India’s cinema industry is often referred to as “Bollywood,” a combination of Bombay and Hollywood. Technically, Bollywood is only the segment of the Indian cinema that is based out of Bombay (Mumbai), but the title is sometimes misleadingly used to refer to the entire movie industry in India.
::电影业在印度的娱乐部门中占很大比例。 印度电影业常常被称为“博莱伍德 ” , 这是孟买和好莱坞的结合。 从技术上讲,博莱伍德只是印度电影院中位于孟买(孟买 ) 外的部分,但该标题有时被误导地用来指整个印度电影业。Bollywood is the leading movie maker in India and has a world-class film production center. In the past few years, India has been producing as many as one thousand films annually. The highest annual output for the US film industry is only about two-thirds of what India produces. According to the Guinness Book of World Records, India’s city of Hyderabad has the most extensive film production center in the world. The Telugu film industry operates the studio in Hyderabad.
::宝莱坞是印度主要的电影制片人,拥有世界级电影制作中心。 在过去几年里,印度每年制作的电影多达一千部。 美国电影业的最高年产出只占印度生产的三分之二左右。 根据《吉尼斯世界纪录》,印度的海得拉巴市拥有世界上最广泛的电影制作中心。 特卢古电影业在海得拉巴经营演播室。Bollywood actresses in Mumbai.
::孟买的宝莱坞女演员
Indian films are produced in more than a dozen languages and appeal to a wide domestic and international audience. Indian movies range from long epic productions with stories within stories to dramas, musicals, and theatrical presentations. Their popularity extends beyond South Asia. Indian movies with modest dress, lack of explicit sexual scenes, and a focus on drama are popular in places such as Egypt, the Middle East, and other African countries.
::印度电影以十多种语言制作,吸引广泛的国内和国际观众。 印度电影从故事中故事的长篇大论制作到戏剧、音乐剧和戏剧表演。 电影的流行程度超越南亚。 印度电影穿得体、缺乏明确的性场景和关注戏剧的电影在埃及、中东和其他非洲国家很受欢迎。Movie stars are energetically promoted and enjoy celebrity in India, as is the case with the entertainment industry in the United States and Europe. The cinema is part of the cultural experience in Indian society. Urban life in India reserves a large presence for the entertainment industry, particularly the Indian film industry. One of the prime artistic endeavors in urban India is movie posters depicting all the glory of the latest Bollywood movie. Most of these colorful posters are painted by hand and they tend to be large. Some are several stories high.
::电影明星在印度得到积极宣传并享有名人,美国和欧洲的娱乐业就是一例。电影是印度社会文化经历的一部分。印度的城市生活为娱乐业,特别是印度电影业保留了大量的存在。印度城市的主要艺术活动之一是展示最新宝莱坞电影所有荣耀的电影海报。这些彩色的海报大多是手工画的,而且往往是大型的。有些是一些高档故事。India: East and West
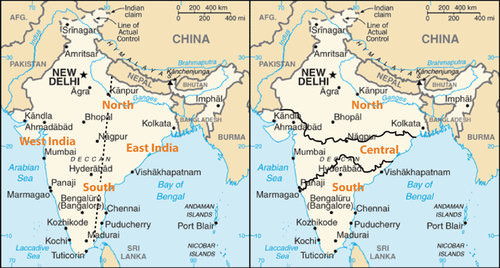
::印度:东部和西部India makes up the largest physical area of the South Asia realm. Another way of looking at the physical and human landscapes of India is to study spatial characteristics. Additionally, the economic side of the equation can be illustrated by dividing India between east and west according to economic development patterns. To do this, on a map of India draw an imaginary line from the border with Nepal in the north, near Kanpur, to the Polk Strait border with Sri Lanka in the south. This division of India illustrates two sides of India’s economic pattern: an economically progressive West India and an economically stagnant East India.
::印度是南亚地区最大的自然区。 研究印度自然和人类景观的另一种方式是研究空间特征。 此外,根据经济发展模式将印度分为东西两部分可以说明等式的经济方面。 为了做到这一点,印度在一张地图上从北部与尼泊尔接壤的边界(坎普尔附近)到南部与斯里兰卡接壤的波尔克海峡边界(斯里兰卡南部 ) 划出一条假想的界线。 印度的这一划分显示了印度经济格局的两个方面:经济进步的西印度和经济停滞的东印度。
India can be divided either along north/south dimensions or along east/west dimensions.
::印度可以沿北/南层面或东/西层面进行划分。
The progressive western side of India is anchored by Mumbai and its surrounding industrial community. Mumbai is the economic giant of India with the country’s main financial markets. It has been a magnet for high-tech firms and manufacturing. Mumbai’s port provides access to global markets and is connected to international trade networks. Auto manufacturing, the film industry, and computer firms all have major centers in the large urban metropolitan areas of the west.
::印度进步的西面以孟买及其周边工业界为根基。 孟买是印度经济巨头,拥有印度的主要金融市场。 孟买是印度经济巨头,是高科技公司和制造业的磁铁。 孟买的港口提供进入全球市场的机会,并与国际贸易网络连接。 汽车制造业、电影业和计算机公司在西部大城市都拥有主要中心。Large industrial cities such as Bangalore and Hyderabad have established themselves as high-tech production centers, attracting international business in the computer industry and the information sector. Chemical processing has been ongoing in Bhopal, which is noted for an environmental disaster, a gas leak in 1984 that resulted in the deaths of as many as 10,000 people.
::班加罗尔和海得拉巴等大型工业城市已经建立高科技生产中心,吸引了计算机工业和信息部门的国际商业,博帕尔的化学加工一直在进行,因为1984年发生了环境灾难,煤气泄漏,造成多达10,000人死亡。The nation’s capital is located in New Delhi, which borders the massive city of (Old) Delhi. The western half of India has been progressing along a pattern with a positive economic outlook that views the global community outside of India as a partner in its success.
::印度首都位于新德里,与大型城市德里(Old)相邻。 印度西部一直沿着积极经济前景发展,将印度以外的全球社会视为成功伙伴。The eastern half of India has not been as prosperous as the west in its economic growth. The renowned city of Kolkata has traditionally anchored the eastern sector, but its factories have deteriorated into rustbelt status with aging and outdated heavy industries. The high-intensity labor activities of textile and domestic goods manufacturing are not as economically viable as they were in the past.
::印度的东半部经济增长不如西方繁荣。 著名的加尔各答市传统上以东区为主,但其工厂随着老化和过时的重工业而恶化为生锈的隐蔽状态。 纺织和国内商品制造业的高强度劳动活动不像过去那样具有经济可行性。The stagnant economic scene in the east is signified by the low average income levels of many of the states in the eastern region. Neighboring Bangladesh offers little in support of economic growth, and Myanmar, another neighbor to the east, has its own set of problems and lacks support for East India. The eastern half of India does not have strong partnerships with the global economy found in the west and thus relies more on internal resources for survival.
::东部经济停滞的征兆是东部地区许多邦的平均收入水平低。 邻国孟加拉国对经济增长的支持很少,而另一个东部邻国缅甸也有自己的问题,缺乏对东印度的支持。 印度东半部与西部的全球经济没有牢固的伙伴关系,因此依赖国内资源维持生存。India: North and South
::印度:南北There are differences in the geographic patterns between the northern and southern halves of India as well as between the eastern and western halves—depending on the criteria used to compare them. Climate patterns, for example, are more diverse in the north, with a wide range of temperatures throughout the seasons. Winter temperatures in the mountainous north are cold and summer temperatures in the Thar Desert can be extremely high.
::印度北部和南部两半之间以及东部和西部之间在地理格局上存在差异,这取决于用来比较这些差异的标准,例如,北方的气候格局更为多样化,整个季节的气温范围很广,北山区的冬季气温寒冷,塔尔沙漠的夏季温度可能极高。Southern India has a more moderate range of temperatures throughout the year. The far north has high mountains. The south has only the low-lying Eastern and Western Ghats. The north has the extensive Ganges River basin. The south has different drainage networks based on the plateaus of the region.
::印度南部全年气温比较温和,远北高山高,南部只有低地东部和西加茨,北部有广阔的恒河流域,南部有以该地区高原为基础的不同排水网络。Besides the physical aspects, there are cultural differences between the north and south as well. India is a complex societal mix of many ethnic groups, languages, and traditions. There are some recognizable trends that have been commonly stated between the northern and southern parts of India. The north is portrayed as a competitive, faster-paced society. The south has been portrayed as more relaxed and less competitive.
::印度是一个复杂的社会组合,包括许多种族群体、语言和传统,印度北部和南部之间经常出现一些明显的趋势,北部被描绘成一个竞争激烈、速度更快的社会,南部被描绘为更加宽松、竞争力更低的社会。Indo-European languages are mainly spoken in the north and Dravidian languages are predominantly spoken in the south. Hindi is more commonly the lingua franca of the north, while English is more frequently the lingua franca of the south. People in the north are of Indo-Aryan descent, while the people in the south have a Dravidian heritage. Hinduism dominates all of India, but the north has a wider diversity of religions, such as Sikhism, Buddhism, and Islam, practiced by a large number of people. The south has a substantial Christian population along its west coast.
::印度-欧洲语言主要在北方使用,德拉维迪语主要在南方使用,印地语更常见于北方的通用语,而英语更常见于南方的通用语,北部的人为印-阿里亚人后裔,而南部的人有德拉维迪人的传统,印度教主导着整个印度,但北方的宗教多样性更为广泛,例如锡克教、佛教和伊斯兰教,许多人信奉这些宗教,南部沿西海岸有大量的基督教人口。Food is an important part of the culture of societies, and there are clear distinctions between the cuisine of the north and of the south in India. Indian cooking is primarily vegetarian, emphasizing aspects of Hinduism. However, many dishes, particularly in North India, contain goat, chicken, lamb, fish, and other meats. Beef is not eaten by Hindus, while pork and some species of fish are not traditionally eaten by Muslims.
::食物是社会文化的重要组成部分,印度北部和南部的烹饪有明显的区别,印度烹饪主要是素食,强调印度教的各个方面,但许多菜菜,特别是在印度北部,含有山羊、鸡、羊肉、鱼和其他肉,印度教徒不吃牛肉,穆斯林传统上不吃猪肉和某些鱼类。North India has more wheat-based products and less rice. Their dishes are prepared with spices and herbs, including chili peppers. Northern Indian food is characterized by its use of dairy products, such as yogurt, milk, homemade cheeses, and clarified butter. Onions, ghee, and spices are the common base for different types of curries. Griddles are used for preparing different types of flat bread, like chapattis, naan, and kulcha. Rice, lentils, and chickpeas are a staple part of the diet in North India.
::北印度的麦类产品较多,大米较少,菜菜菜中配有香料和药草,包括辣椒。 北印度食品的特点是使用乳制品,如酸奶、牛奶、自制奶酪和澄清黄油。 洋葱、芝士和香料是不同种类的咖喱的共同基础。 大饼用于制作不同种类的扁面包,如小麦、玉米和木薯。 稻米、扁豆和小鸡豆是北印度饮食的主要部分。North Indian cuisine is a part of Indian cuisine, from the region of Northern India which includes the Pakistani provinces. This dish is called Boondi Ka Laddu.
::北印度菜是印度菜的一部分,来自印度北部地区,包括巴基斯坦各省。 这个菜叫做Boondi Ka Laddu。
Food in the southern parts of India includes more rice as a staple, and seafood is common along the coastal areas. Coconut oil is used as a basis for cooking. Sambar, a stew made of peas and vegetables, is an important staple of the region. Rice and idlis (a type of cake or bread made from steaming fermented black lentils) is a staple in the cuisine as well. Chili peppers are also common in South Indian cooking.
::印度南部的食品包括更多的大米作为主食,沿海地区海产食品很常见,椰子油被用作做饭的基础,青豆和蔬菜做的炖菜Sambar是该地区的重要主食,大米和idlis(一种由蒸发的发酵黑扁豆制成的蛋糕或面包)也是烹饪的主食,辣椒在南印度烹饪中也很常见。Sambar is a lentil-based vegetable stew or chowder popular in South Indian cuisine.
::Sambar是南印度菜食中流行的扁豆炖菜或陶器。Biodiversity and the Environment
::生物多样性与环境Because of population growth and resource depletion, India struggles with major environmental problems. Water pollution along the Ganges is severe and affects the largest concentration of people in India. India is the second-largest consumer of coal in the world, coal that is mainly burned to produce electricity. Burning coal adds significantly to air pollution. A rise in the number of vehicles in use, combined with few emission controls, destroys the air quality. Deforestation also adds to the issues of environmental degradation in India.
::由于人口增长和资源枯竭,印度面临严重的环境问题:恒河沿岸的水污染严重,影响到印度人口的最大集中;印度是世界上煤炭第二大消费国,煤炭主要是为发电而燃烧的;燃烧煤炭大大增加了空气污染;使用中的车辆数量增加,加上排放控制少,破坏了空气质量;砍伐森林也加剧了印度的环境退化问题。India has a number of rare animal species that need habitat if they are going to survive. A few of the larger animals include the Indian Rhinoceros, Clouded Leopard, Indian Leopard, Snow Leopard, Asiatic Lion, Bengal Tiger, Asian Water Buffalo, Asian Elephant, Striped Hyena, and the Red Panda. Many species are endangered or threatened along with many other lesser-known organisms. The high human population growth throughout South Asia places a strain on the natural habitat of wild animals. Habitat loss caused by human development makes holding on to the wide array of biodiversity difficult.
::印度有一些稀有动物物种,如果它们要生存下去,就需要栖息地。一些较大的动物包括印度的犀牛、云豹、印度的豹、印度的豹、雪豹、亚洲狮、孟加拉虎、亚洲水牛、亚洲大象、被剥离的海纳和红熊猫。许多物种与其他许多较不为人知的生物一起受到威胁或威胁。整个南亚的人类人口高速增长给野生动物的自然栖息地带来了压力。由于人类的发展而导致的生境损失使得生物多样性难以保持。The Indian Leopard is a near-threatened species that once lived throughout South Asia.
::印度豹是一种近乎受威胁的物种,曾经生活在整个南亚。
India has instituted measures designed to preserve its biodiversity. The Indian government has created sanctuaries for threatened or endangered species. National parks were established before India declared independence and were substantially expanded in recent decades. In 1972, The Wildlife Protection Act was instituted to create critical habitat for tigers and other rare species. There are hundreds of protected wildlife areas and 15 biosphere reserves in India. Four of the biospheres were created in conjunction with the .
::印度制定了保护生物多样性的措施,印度政府为受威胁或濒危物种建立了保护区,印度宣布独立之前建立了国家公园,近几十年来,国家公园得到大幅扩展。1972年,印度制定了《野生动物保护法》,为老虎和其他稀有物种创造关键的栖息地。印度有数百个受保护的野生生物区和15个生物圈保护区。其中4个生物圈是与该生物圈共同建立的。The Indian government has established protected areas throughout the country, many of which are in the highland regions and the northern mountains. For example, the Gir Wildlife Sanctuary, including an area preserved for Asian Lions, is located on the Kathiawar Peninsula north of Mumbai, which juts out into the Arabian Sea. India is the only place left with Asian Lions in the wild. Tigers, elephants, rhinos, and leopards can be found in the sanctuaries.
::印度政府在全国各地建立了保护区,其中许多位于高原地区和北部山区,例如,吉尔野生动物保护区,包括为亚洲狮子保留的一个区域,位于孟买以北的Kathiawar半岛,该半岛向外延伸至阿拉伯海,印度是唯一在野外留下亚洲狮子的地方,老虎、大象、犀牛和豹可以在保护区中找到。The country has about 92 national parks, which are also home to rare wildlife species, and more than 350 wildlife sanctuaries of all sizes. There are about 28 tiger reserves in India. The country also has a number of marine reserves and protected areas along its coastlines.
::印度约有92个国家公园,它们也是稀有野生生物物种的栖息地,有350多个各种规模的野生生物保护区,印度约有28个老虎保护区,印度沿海还有一些海洋保护区和保护区。The efforts of the Indian government to protect the country’s biodiversity constitute an admirable environmental undertaking. The government has stepped up law enforcement efforts to combat poaching, which is a major cause of the decrease in numbers of rare species. Poachers kill animals such as tigers, leopards, elephants, and rhinos for their hides, horns, or body parts, which are sold on the black market in Asia for large sums of money.
::印度政府保护印度生物多样性的努力构成了令人钦佩的环境事业。 印度政府加大了打击偷猎的执法力度,这是稀有物种数量减少的主要原因。 偷猎者杀死老虎、豹子、大象和犀牛等动物,因为它们的隐藏物、角或人体器官,在亚洲黑市上以大笔金钱出售。Many of the rare, threatened, or endangered species of India would not have a chance of survival without the government efforts to protect and provide for them. Balancing finding resources for rapid human population growth with wildlife management will continue to be a challenge in the years ahead for India and all countries of the planet.
::印度的许多稀有、受威胁或濒危物种如果没有政府保护和供给这些物种的努力,就不可能生存。 在未来几年中,为人类快速人口增长寻找资源与野生动物管理之间的平衡将继续是印度和地球上所有国家面临的一个挑战。
Key Takeaways
::密钥外出-
Colonialism had a tremendous impact on South Asia and its people. Colonial development patterns were implemented to control the people and to extract resources, not necessarily to benefit the realm.
::殖民主义对南亚及其人民产生了巨大影响,实施殖民发展模式是为了控制人民和开采资源,不一定是为了造福整个王国。 -
India has a wide disparity between its poor rural areas with agricultural economies and its wealthier bustling cities with expanding business sectors.
::印度的贫困农村地区与农业经济相比,与富裕的城市与不断扩大的商业部门相比,差距很大。 -
Various urban centers of India have positioned themselves well to take advantage of the global economy and expand their manufacturing and industrial base. India is becoming a major manufacturing country for vehicles and high-tech industries.
::印度各城市中心已经做好了利用全球经济和扩大制造业和工业基础的良好准备。 印度正在成为汽车和高科技工业的主要制造国。 印度正在成为全球制造业的主要制造国。 -
There are noticeable economic differences between the more progressive Western India and the stagnant economic conditions of Eastern India. There is also a noticeable cultural difference between the North and the South in India in the categories of language, ethnicity, food, and society.
::较进步的印度西部与停滞的印度东部经济条件之间存在明显的经济差异,印度南北之间在语言、种族、食物和社会类别方面也存在明显的文化差异。 -
The Indian government has created national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and game reserves to help protect rare, threatened, or endangered species.
::印度政府建立了国家公园、野生动物保护区和狩猎保护区,以帮助保护稀有、受威胁或濒危物种。
Vocabulary Terms
::词汇术语术语Chapter 9.4 India
::第9.4章 印度Aryan
::雅利扬a member of an Indo-European people who crossed into India around 1500 B.C.
::一名印度裔欧洲人的成员,在公元前1500年左右越境进入印度。Dharma
::达摩The religious and moral duties of the Hindus
::印度教徒的宗教和道德义务Harappan
::哈拉潘Civilization
::文明化Ancient Indian culture, dating back to 2500 B.C., that included the people of the entire Indus River region
::古印度文化可追溯到公元前2500年,包括整个印度河地区人民meditate
::冥想To focus the mind inward in order to find spiritual awareness
::集中内心的心灵,以便找到精神意识migrate
::移徙移民To move from one place to settle in another
::从一个地方搬到另一个地方定居missionary
::传教士A person who spreads his or her religious beliefs to others
::向他人传播其宗教信仰的人Mohandas Gandhi
::穆罕默德·甘地A leader who used nonviolence to oppose the British rule of India
::一位利用非暴力反对英王统治印度的领导人Monsoon
::季风A strong wind that blows across East Asia at certain times of the year
::一年中某些时间吹遍东亚的强风Nirvana
::尼尔瓦纳The lasting peace that Buddhist seek by giving up selfish desires
::佛教通过放弃私欲寻求的持久和平Siddhartha Gautama
::西迪达尔塔·高塔马an Indian prince who founded Buddhism; also known as Buddha.
::一位印度王子,他创建了佛教,也被称为佛祖。subcontinent
::次大陆A large landmass that juts out from a continent
::大陆上的大陆地Applying Knowledge
::应用知识Discussion and Study Questions
::讨论和研究问题-
Outline the main ways in which British colonialism impacted South Asia.
::概述英国殖民主义影响南亚的主要方式。 -
What are the three main language families in India? What is the lingua franca?
::印度三种主要语言家庭是什么? -
List the main qualities that are different between the rural and urban areas of India.
::列出印度农村和城市地区不同的主要特点。 -
How did British colonizers transport resources from the hinterland to the port cities for export back to Great Britain? How has this system changed since 1947?
::英国殖民者如何将资源从内地运回港口城市出口到大不列颠? 自1947年以来,这种制度如何改变? -
Explain the various ways in which the rapid population growth is impacting India.
::解释人口快速增长如何影响印度。 -
Why is India a major target for BPO?
::为什么印度是BPO的主要目标? -
List various ways the Indian film industry impacts India and the world.
::印度电影业对印度和世界有不同的影响。 -
How is economic development different between Western India and Eastern India?
::经济发展在西印度和东印度之间有何不同? -
Outline some cultural differences between the North and the South in India.
::概括了印度南北之间的一些文化差异。 -
How has the government of India worked to protect the biodiversity of the natural environment? What are some of the animals that are being protected?
::印度政府如何保护自然环境的生物多样性? 哪些动物受到保护?
Real-World Geography Exercise
::现实世界地理演习-
Using
, complete the following activities:
-
Locate each place on the bulleted list below.
::在下面的子弹名单上 找到每个地方 -
Find the nearest city with an international airport in proximity to each location on the bulleted list below.
::找到最近的城市,在下面子弹清单上每个地点附近有一个国际机场。 -
Calculate the distance and travel time by plane to each city from the
in Phoenix, Arizona.
::计算从亚利桑那的凤凰城 飞往每个城市的 飞机距离和旅行时间
::使用,完成以下活动: 确定以下子弹清单上的每个地点; 找到最近的城市, 在下面子弹清单上的每个地点附近有一个国际机场。 计算从亚利桑那凤凰城飞往每个城市的飞机距离和飞行时间。 -
Locate each place on the bulleted list below.
-
Using
, determine the latitude and longitude for each location on the bulleted list below.
::使用,确定以下子弹列表中每个位置的纬度和经度。 -
Be prepared to share and discuss your answers.
::准备分享和讨论你的答案
-
Agra
::阿格拉 -
Bangalore
::班加罗尔 -
Bombay (Mumbai)
::孟买(孟买) -
Bhopal
::博帕尔 -
Calcutta (Kolkata)
::加尔各答( 加尔各答) Name -
Delhi
::德里德里 -
Goa
::果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 果 -
Hyderabad
::海得拉巴 -
Jaipur
::斋浦尔 -
Kathiawar Peninsula
::卡希亚瓦尔半岛 -
Madras (Chennai)
::马德拉斯( Chennai) -
New Delhi
::新德里
Current Events
::当前事件Videos for Geography Enrichment
::地理丰富视频Helpful Websites for the Study of Geography
::地理研究有用网站is an encyclopedia funded by the Canadian government covering all branches of knowledge. Their scholarly collection includes interactive materials.
::该百科全书由加拿大政府资助,涵盖所有知识分支,其学术收藏包括交互式材料。provides information on the people, history, government, economy, energy, geography, communications, transportation, military, and transnational issues for the world's entities.
::向世界各实体提供关于人民、历史、政府、经济、能源、地理、通信、运输、军事和跨国问题的资料。is a US government website where you can find federal legislation, past and present, as well as information about the US legal system.
::是一个美国政府的网站,您可以在此找到过去和现在的联邦立法以及关于美国法律制度的信息。is a government agency website that provides current news, resources, topics of interest, information about drugs, careers in the DEA, and a tip hotline.
::是一个政府机构网站,提供最新消息、资源、感兴趣的话题、毒品信息、在缉毒局的职业以及一条小费热线。is the largest library in the world and provides manuscripts, files, information, pictures, and videos.
::图书馆是世界上最大的图书馆,提供手稿、文件、信息、图片和录像。is a US government agency website that allows users to search for and retrieve satellite images of Earth.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,用户可以搜索和检索地球的卫星图像。is a US government website that provides historical documents, photos, records, publications, and educator resources.
::这是一个美国政府网站,提供历史文件、照片、记录、出版物和教育资源。is a US government agency website that provides weather-related information and ocean research.
::是一个提供气象信息和海洋研究的美国政府机构网站。is a website by the United States Geological Survey and other federal, state, and local agencies that delivers topographic information for the United States.
::这是美国地质调查局和其他联邦、州和地方机构为美国提供地形信息的网站。is a massive central data source and a handy way to graphically compare nations.
::是一个庞大的中央数据源,是用图形比较国家的一种方便方式。is a website that measures most locations in the world for air pollution in real time.
::是一个实时测量世界上大多数空气污染地点的网站。is a unique statistical database, which allows you to research and compare a multitude of different data on US states.
::这是一个独特的统计数据库, 使你能够研究和比较关于美国各州的多种不同数据。is an international organization founded in 1945 and made up of 193 member states. The UN maintains international peace and security, protects human rights, delivers humanitarian aid, promotes sustainable development, and upholds international law.
::联合国是一个国际组织,成立于1945年,由193个成员国组成。 联合国维护国际和平与安全,保护人权,提供人道主义援助,促进可持续发展,维护国际法。is a US government agency that provides a population clock, data, surveys, statistics, a library with information and infographics, news about the economy, and much more.
::这是一个美国政府机构,它提供人口钟、数据、调查、统计、一个拥有信息和信息资料的图书馆、关于经济的新闻,以及更多。is a US government agency website that provides scientific information about the natural hazards that threaten lives, the natural resources we rely on, the health of our ecosystems and environment, and the impacts of climate and land-use change.
::这是一个美国政府机构的网站,提供科学信息,说明威胁生命的自然危害、我们赖以生存的自然资源、生态系统和环境的健康以及气候和土地使用变化的影响。is a US government website that provides the latest presidential news, information about the budget, policy, defense, and many more topics.
::提供最新总统新闻、预算、政策、国防等资讯, 以及更多议题。is under the United Nations and provides leadership on matters critical to health, shapes the research agenda on health, and monitors the health situation and assessing health trends around the world. Their website provides information on the state of health around the world, outbreaks, current health news, and more.
::网站提供世界各地卫生状况、疫情爆发、最新卫生新闻等信息。is an intergovernmental organization that regulates international trade. The website provides information on the history of the multilateral trading system, featured videos, news and events, trade topics, and more.
::该网站提供关于多边贸易体系历史的信息、视频、新闻和事件、贸易专题等等。 -
Outline the basic activities of British colonialism that affected the realm.