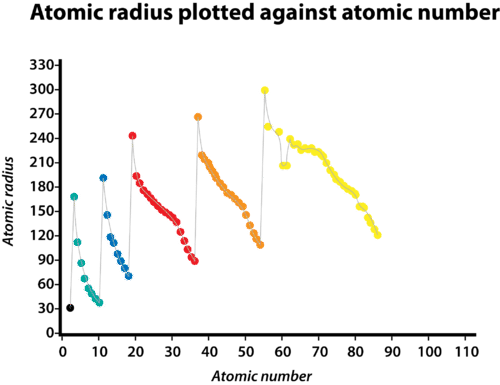6.15 周期趋势:原子半径
章节大纲
-
How can all of these people fit in such a small space?
::这些人怎么会都住在这么小的空间里?Events draw large numbers of people to them. Even an outdoor event can fill up so that there is no room for more people. The crowd capacity depends on the amount of space in the venue, and the amount of space depends on the size of the objects filling it. We can get more people into a given space than we can elephants, because the elephants are larger than people. We can get more squirrels into that same space than we can people for the same reason. Knowing the sizes of objects we are dealing with can be important in deciding how much space is needed.
::事件吸引了众多人。 即使是户外活动也能让更多的人挤满。 人群的能力取决于场地空间的大小, 空间的大小取决于填满场地的物体的大小。 我们可以让更多的人进入一个特定的空间, 因为大象比人大。 我们可以让更多的松鼠进入这个空间, 而不是为了同样的原因让更多的人进入这个空间。 了解我们所处理的物体的大小对于决定需要多少空间很重要 。Atomic Radius
::原子半径The size of atoms is important when trying to explain the behavior of atoms or compounds. One of the ways we can express the size of atoms is with the atomic radius . This data helps us understand why some molecules fit together and why other molecules have parts that get too crowded under certain conditions.
::当试图解释原子或化合物的行为时,原子的大小很重要。我们可以表达原子大小的方法之一是原子半径。这些数据有助于我们理解为什么某些分子相容,为什么其他分子的某些部分在某些条件下过于拥挤。The size of an is defined by the edge of its . However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact, are variable under different conditions. In order to standardize the measurement of atomic radii , the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together is measured. The atomic radius is defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms that are bonded together.
::一个人的大小由它的边缘来界定。 但是, 轨道界限模糊, 事实上在不同条件下是可变的。 为了对原子辐射的测量标准化, 要测量两个相同原子的核质之间的距离。 原子半径被定义为同一原子的核质之间的半径的一半。 原子半径被定义为连接在一起的同一原子的核质之间的半径 。The atomic radius (r) of an atom can be defined as one-half the distance (d) between two nuclei in a diatomic molecule. Atomic radii have been measured for . The units for atomic radii are picometers, equal to 10 -12 meters. The Figure gives the approximate atomic radii of the non- up to radon.
::已测量到原子半径。原子半径的单位是光度计,等于10-12米。图中给出了非雷达的近似原子半径。Atomic radii of the representative elements measured in picometers. Periodic Trend
::定期趋势The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. There are some small exceptions, such as the bismuth (Bi) radius being slightly greater than the polonium (Po) radius. Within a period, are added to the nucleus as electrons are being added to the same principal energy level. These electrons are gradually pulled closer to the nucleus because of its increased positive charge. Since the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons increases, the size of the atoms decreases. The effect lessens as one moves further to the right in a period because of electron- repulsions that would otherwise cause the atom’s size to increase.
::原子原子的原子半径一般会在一个时期从左向右下降。 有一些小的例外, 比如双甲苯(Bi)半径比(Po)半径略高。 在一段时间内, 电子被添加到相同的主能量水平, 这些电子会逐渐被拉近到核。 由于电荷增加, 这些电子会逐渐拉近核。 由于核与电子的吸引力增加, 原子的体积会缩小。 效果会随着电击在一段时间内向右移动而减弱, 否则会使原子的体积增加。Group Trend
::群群趋势The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group. As the increases down a group, there is again an increase in the positive nuclear charge. However, there is also an increase in the number of occupied principle energy levels. Higher principal energy levels consist of orbitals which are larger in size than the orbitals from lower energy levels. The effect of the greater number of principal energy levels outweighs the increase in nuclear charge and so atomic radius increases down a group.
::原子的原子半径一般会在一个组内从上到下增加。随着一个组的上升,正核电量再次增加。然而,占用的能源主要水平也在增加。高主要能源水平包括轨道,其大小大于低能源水平的轨道。主要能源水平的增多,其影响大于核电量的增加,因此原子半径会向下增加一个组。A graph of atomic radius plotted versus atomic number. Each successive period is shown in a different color. As the atomic number increases within a period, the atomic radius decreases. Summary
::摘要-
Atomic radius is defined as one-half of the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together.
::原子半径的定义是两个相同原子的核之间的半径。 -
The atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period.
::原子原子的原子半径在一段时间内一般会从左向右下降。 -
The atomic radius of atoms generally increases from top to bottom within a group.
::原子原子的原子半径通常在一个组内从上到下增加。
Review
::回顾-
Define “atomic radius.”
::“原子半径”的定义。 -
What are the units
of
measurement
for
atomic radius?
::原子半径的测量单位是什么? -
How does the atomic radius of different elements change across a period?
::不同元素的原子半径在一段时间内是如何变化的? -
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom within a group?
::原子半径在组内如何从上向下变化? -
Explain why the atomic radius of hydrogen is so much smaller than the atomic radius
of
potassium.
::解释为什么氢原子半径 要比钾原子半径小得多
-
Atomic radius is defined as one-half of the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms bonded together.