4.2矿物组
章节大纲
-
What would you do with this mineral?
::你会怎么处置这些矿物质?Imagine you are in charge of organizing more than 100 for a museum exhibit. You know that people learn more if they see the minerals together in groups. So how would you group the minerals together in the exhibit? What are some of the possibilities? Size? Shape? Color?
::想象一下你负责组织超过100个博物馆展览。 你知道人们如果把矿物放在一起看, 会学到更多的东西。 那么在展览中, 你会如何将矿物聚集在一起? 哪些可能性? 大小? 形状? 颜色?Learn about the minerals behind modern life with .
::了解现代生活背后的矿物Mineral Groups
::矿物集团Mineralogists are scientists who study minerals. They divide minerals into groups based on chemical composition. Even though there are over 4,000 minerals, most minerals fit into one of eight mineral groups.
::矿物学家是研究矿物的科学家,他们根据化学成分将矿物分成几组,尽管有4 000多个矿物,但大多数矿物属于八个矿物组之一。Silicate Minerals
::硅矿物Silicates are the largest mineral group. About 1,000 silicate minerals are known. Silicate minerals are also extremely common. They make up over 90% of Earth's crust!
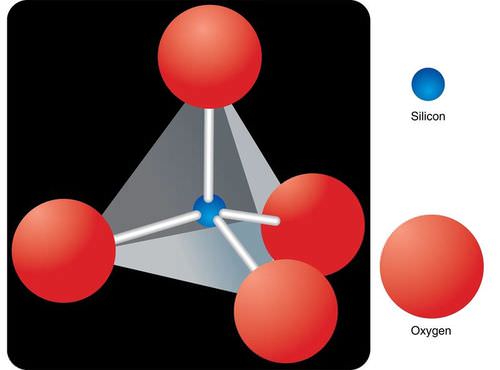
::硅酸盐是最大的矿物质组。已知的硅酸盐矿约1,000种,硅酸盐矿也极为常见,占地球地壳的90%以上!Silicates contain silicon atoms and oxygen atoms. One silicon atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms. These atoms form a tetrahedron ( Figure ). The silica tetrahedron is the building block of silicate minerals. Most silicates contain other elements . These elements include calcium, iron, and magnesium.
::硅化物含有硅原子和氧原子。一个硅原子与四个氧原子相连接。这些原子形成四面形(图)。硅四面形是硅化物矿物的构件。大多数硅化物含有其他元素。这些元素包括钙、铁和镁。One silicon atom bonds to four oxygen atoms to form a pyramid Silicate minerals are divided into six smaller groups. In each group, the silicate pyramids join together differently. The pyramids can stand alone. They can form into connected circles called rings. Some pyramids link into single and double chains. Others form large, flat sheets. Some join in three dimensions.
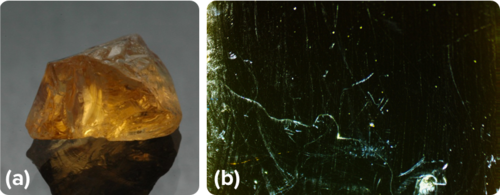
::硅酸盐矿物分为六小类。 每组中,硅酸盐金字塔的组合不同。 金字塔可以单独存在。它们可以形成连结圈,称为环。一些金字塔连接成单链和双链。另一些则形成大型扁床单。有些则分三个维。Feldspar and quartz are the two most common silicates. In beryl, the silicate pyramids join together as rings. In biotite mica, the silicate pyramids come together to create thin, flexible sheets. Compare the beryl and the biotite pictured below ( Figure ).
::Feldspar 和 Quartz 是两种最常见的硅酸盐。 在 beryl 中, 硅酸盐金字塔以环状形式结合在一起。 在 生物地皮 MIca 中, 硅酸盐金字塔聚集在一起, 以创造薄薄、 柔软的床单。 比较以下的白醇和生物地图( 图 ) 。Beryl (a) and biotite (b) are both silicate minerals. Native Elements
::土著元素Native elements contain only atoms of one type of element. They are not combined with other elements. There are very few examples of these types of minerals. Some native elements are rare and valuable. Gold, silver, sulfur, and diamond are examples.
::土著元素只含有一种元素的原子,没有与其他元素结合,这类矿物的例子很少,有些本地元素稀有而珍贵,金、银、硫和钻石就是例子。Carbonates
::碳酸碳酸碳酸碳酸What do you guess carbonate minerals contain? If you guessed carbon, you would be right! All carbonates contain one carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms. Carbonates may include other elements. A few of these are calcium, iron, and copper.
::你猜碳酸盐矿物质含有什么?如果你猜到碳,你会说对了!所有碳酸盐都含有一个碳原子,连接到三个氧原子。碳酸盐可能包含其他元素。其中有一些是钙、铁和铜。Carbonate minerals are often found where seas once covered the land. Some carbonate minerals are very common. Calcite contains calcium, carbon, and oxygen. Have you ever been in a limestone cave or seen a marble tile? Calcite is in both limestone and marble. Azurite and malachite are also carbonate minerals. They contain copper instead of calcium. They are not as common as calcite. Malachite and azurite are used in jewelry; as you can see, they are very colorful ( Figure ).
::碳酸盐矿经常在曾经覆盖过陆地的海洋中发现碳酸盐矿物质,有些碳酸盐矿物质非常常见。碳酸盐含有钙、碳和氧。你曾经在石灰岩洞中或见过大理石砖吗?碳酸盐既存在于石灰岩中,也存在于大理石中。硫酸盐和麦酸盐也是碳酸矿物质,它们含有铜而不是钙。它们不像钙一样常见。马拉奇特和硫酸盐被用于珠宝;如你所见,它们非常多彩(图示 ) 。(a) The deep blue mineral is azurite and the green is malachite. (b) This red rhodochrosite is a carbonate mineral. Rhodochrosite is usually pink; the red crystals are rare. Halides
::卤化物Halide minerals are salts. They form when salt water evaporates. This mineral class includes more than just table salt. Halide minerals may contain the elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, or iodine. Some halide minerals combine with metal elements. Common table salt is a halide mineral that contains the elements chlorine and sodium. Fluorite is a type of halide that contains fluorine and calcium. Fluorite can be found in many colors. If you shine an ultraviolet light on fluorite, it will glow!
::卤化物矿物质是盐类。 当盐水蒸发时, 它们会形成。 这种矿物质不仅包括桌盐。 卤化物矿物质可能含有氟、 氯、 溴或碘元素。 一些卤化物矿物质与金属元素结合。 普通桌盐是一种卤化物矿物质, 含有氯和钠元素。 氟化物是一种卤化物, 含有氟和钙。 氟化物可以在许多颜色中找到。 如果您在氟化物上点亮紫外线, 它会发光 !Oxides
::氧化氧化物Earth’s crust contains a lot of oxygen. The oxygen can combine with other elements to create oxide minerals. Oxides contain one or two metal elements combined with oxygen. Oxides are different from silicates, because they do not contain silicon. Many important metals are found as oxides. For example, hematite and magnetite are both oxides that contain iron. Hematite (Fe 2 O 3 ) has a ratio of two iron atoms to three oxygen atoms. Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) has a ratio of three iron atoms to four oxygen atoms. Notice that the word “magnetite” contains the word “magnet." Magnetite ( Figure ) is a magnetic mineral.
::地球的地壳含有大量的氧气。 氧可以与其他元素结合, 以产生氧化物矿物质。 氧化物含有一两个金属元素和氧。 氧化物与硅不同, 因为它们不含硅。 许多重要的金属被发现为氧化物。 例如, 热铁和磁铁都是含铁的氧化物。 甲基铁( Fe2O3) 与三个氧原子的比例为两个铁原子与三个氧原子之比。 磁铁( Fe3O4) 与四个氧原子之比为三个铁原子。 注意“ 磁铁” 一词包含“ 磁铁 ” 。 磁铁( Figure) 是磁矿物 。Magnetite is one of the most distinctive oxides since it is magnetic. Phosphates
::磷酸盐Phosphate minerals have a structure similar to silicates. In silicates, an atom of silicon is bonded to oxygen. In phosphates , an atom of phosphorus, arsenic, or vanadium is bonded to oxygen. There are many types of phosphate minerals, but phosphate minerals are rare. The composition of phosphates is complex. For example, turquoise contains copper, aluminum, and phosphorus ( Figure ).
::磷酸盐矿物的结构类似于硅酸盐,在硅酸盐中,硅原子与氧结合,在磷酸盐中,磷、砷或原子与氧结合,磷酸盐矿物有多种类型,但磷酸盐矿物很少见,磷酸盐的成分很复杂,例如,硫酸盐含有铜、铝和磷(图)。Turquoise is a phosphate mineral with a beautiful blue color. The stone is not as rare as some minerals and is commonly used for jewelry. Sulfates
::硫酸盐Sulfate minerals contain sulfur atoms bonded to oxygen atoms. Like halides, they can form in places where salt water evaporates. Many minerals belong in the sulfate group, but there are only a few common sulfate minerals. Gypsum is a common sulfate mineral that contains calcium, sulfate, and water. Gypsum is found in various forms. For example, it can be pink and look like it has flower petals. However, it can also grow into very large white crystals. Gypsum crystals that are 11-meters-long have been found. That is about as long as a school bus! Gypsum forms at the Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone National Park ( Figure ).
::硫酸盐矿物质含有硫磺原子, 与氧原子相连接。 和卤化物一样, 它们也可以在盐水蒸发的地方形成。 许多矿物属于硫酸盐组, 但只有少量常见硫酸盐矿。 硫酸盐是一种常见硫酸盐矿, 含有钙、 硫酸盐和水。 硫化物以多种形式出现。 例如, 它可以是粉色, 看起来像有花瓣。 但是, 它也可以发展成非常大的白晶体。 已经发现了11米长的石膏晶。 这大概是一辆校车! 在黄石公园( Figure ) 的Mammoth热泉( Gypum) 。Gypsum is the white mineral that is common around hot springs. This is Mammoth Hot Springs in Yellowstone National Park. Sulfides
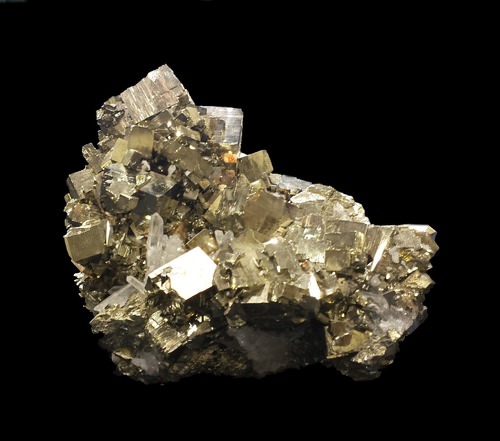
::硫化物Sulfides contain metal elements combined with sulfur. Sulfides are different from sulfates. They do not contain oxygen. Pyrite is a common sulfide mineral ( Figure ). It contains iron combined with sulfur. Pyrite is also known as “fool’s gold.” Gold miners have mistaken pyrite for gold because pyrite has a greenish gold color.
::硫化物含有金属元素和硫磺。硫化物与硫酸盐不同,不含氧气。 硫化物是一种常见硫化物矿物质(图 ) 。 硫化物含有铁和硫。 硫化物也被称为“泡沫的黄金 ” 。 金矿开采者误用金矿,因为金矿的金色是绿色的。Pyrite has a similar color to gold. The appearance of the striations make pyrite different from gold. Summary
::摘要- Silicates, made of building blocks of silica tetrahedrons, are the most abundant minerals on Earth.
::由硅四面线构成的硅石构成的硅石是地球上最丰富的矿物。
- Silica tetrahedrons combine together in six different ways to create rings, single and double chains, large flat sheets, or 3-dimensional structures.
::硅四面体以六种不同方式结合在一起,形成环、单链和双链、大片平板或三维结构。
- Other mineral groups have other chemical components like carbonates, oxides, or phosphates.
::其他矿类有碳酸盐、氧化物或磷酸盐等其他化学成分。
- Minerals that are native elements are made of only one element.
::作为本地元素的矿物只由一个元素组成。
Review
::回顾- On what basis are minerals divided into groups?
::矿物以什么为基础分为几组?
- What are the chemical characteristics of the most common mineral group?
::最常见矿物质组的化学特性是什么?
- How are the silicates categorized?
::硅酸盐分类如何?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- How are minerals classified?
::矿物分类如何?
- What do silicate minerals contain?
::硅酸盐矿含有什么?
- Where are silicate minerals found?
::在哪里发现硅酸盐矿?
- List three examples of silicates.
::列举三个硅酸盐的例子。
- What do non-silcate minerals contain?
::非溶液矿物含有哪些内容?
- What is a native element?
::什么是本地元素?
- What are native elements used in?
::使用哪些本地元素?
- List examples of carbonates.
::碳酸盐的例子清单。
- What are halide minerals used for?
::卤化物矿物用于什么?
- What are oxides used for?
::氧化物用于什么?
- What are sulfate minerals used for?
::硫酸盐矿物用于什么?
- What are sulfide minerals used for?
::硫化物矿物用于什么?
- Silicates, made of building blocks of silica tetrahedrons, are the most abundant minerals on Earth.