9.9 多种原子离子共值保债
章节大纲
-
How do we extend basic principles?
::我们如何推广基本原则?The United States Supreme Court has the unenviable task of deciding what the law is. This responsibility can be a major challenge when there is no clear principle involved or where there is a new situation not encountered before. Chemistry faces the same challenge in extending basic concept to fit a new situation. Drawing of Lewis structures for polyatomic uses the same approach, but tweaks the process a little to fit a somewhat different set of circumstances.
::美国最高法院承担着决定什么是法律的不可推崇的任务,当没有明确的原则或以前没有遇到新的情况时,这一责任可能是一项重大挑战。 化学在扩大基本概念以适应新情况时也面临着同样的挑战。 多方形的刘易斯结构的绘制使用同样的方法,但使这一过程稍有改变,以适应一些不同的情况。Polyatomic Ions
::多质离子Recall that a polyatomic ion is a group of atoms that are covalently bonded together and which carry an overall electrical charge. The ammonium ion, NH 4 + , is formed when a hydrogen ion (H + ) attaches to the lone pair of an ammonia (NH 3 ) molecule in a .
::多原子离子是一组原子,共价结合在一起,并带有总电荷。当氢离子(H+)附着在氨(NH3)分子的单对一分子上时,便形成氢离子(NH4+ ) 。The ammonium ion. When drawing the Lewis structure of a polyatomic ion, the charge of the ion is reflected in the number of total in the structure. In the case of the ammonium ion:
::当绘制多原子离子的刘易斯结构时,离子的荷载反映在结构中的总数中。
::1 N 原子=5 valence eenns4 H 原子=4x1=4 valence evalence evalence eurenssupptrate 1 电子,用于在离子中加装8 valence 电子共8个离子It is customary to put the Lewis structure of a polyatomic ion into a large set of brackets, with the charge of the ion as a superscript outside the brackets.
::通常的做法是将多原子离子的刘易斯结构置于一大批括号中,将离子作为上标的权责置于括号之外。Sample Problem: Lewis Electron Dot Structure of a Polyatomic Ion
::样本问题:多元离子的刘易斯电点结构Draw the Lewis dot structure for the sulfate ion.
::为硫酸盐离子绘制 Lewis点结构。Step 1: List the known quantities and plan the problem.
::第1步:列出已知数量并规划问题。Known
::已知已知
::硫酸盐离子=SO42-1 S原子=6 valence eenns4 O原子=4×6=24 valence eennsadd 2 economs 2 - 电离共32 valence eensThe less electronegative sulfur is the central atom in the structure. Place the oxygen atoms around the sulfur atom, each with a single covalent bond . Distribute lone pairs to each oxygen atom in order to satisfy the . Count the total number of atoms. If there are too many electrons in the structure, make multiple bonds between the S and O.
::结构中的中心原子是电阴性硫磺。 将氧原子放在硫磺原子周围, 每个原子都有单一的共价连接。 将单对单对分配到每个氧原子, 以满足 。 计算原子的总数。 如果结构中存在太多电子, 则在 S 和 O 之间设置多个链接 。Step 2: Solve.
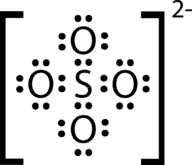
::步骤2:解决。The sulfate ion. Step 3: Think about your result.
::步骤3:想想你的结果。The Lewis structure for the sulfate ion consists of a central sulfur atom with four single bonds to oxygen atoms. This yields the expected total of 32 electrons, but there is still a small problem. As shown in the Figure , the charges in this structure are somewhat unbalanced.
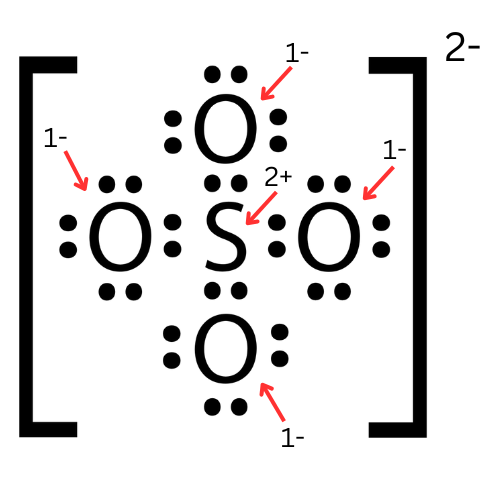
::硫酸盐离子的刘易斯结构由中央硫磺原子组成,与氧原子有4个单一的连接点。这产生了32个电子的预期总数,但仍然存在一个小问题。如图所示,这一结构中的电荷有些不平衡。This structure uses all of the electrons, but a better structure brings as many of these charges to 0 as possible. Step 4: Balance charges.
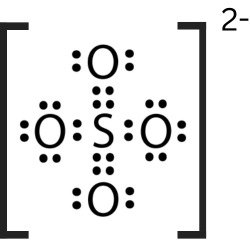
::第4步:平衡费用。The correct Lewis structure for sulfate ( Figure ) moves electrons off two of the oxygen atoms to form an additional bond between them and the sulfur atom. This brings the charge of these three atoms to 0 and leaves -1 charges on the remaining two oxygen atoms. This structure is more stable because more atoms are neutral in charge.
::正确的硫酸盐 Lewis 结构( 图) 将两个氧原子的电子从两个氧原子移走, 形成它们与硫磺原子之间的额外连接。 这使得这三个原子的电荷达到0, 其余两个氧原子的电荷为1。 这个结构比较稳定, 因为更多的原子在负责中性 。The correct Lewis structure for sulfate shows two double bonds between the central sulfur atom and two of the outer oxygen atoms. Summary
::摘要-
Lewis structures for polyatomic ions follow the same rules as those for other covalent compounds.
::多原子离子的刘易斯结构遵循与其他共价化合物相同的规则。
Review
::回顾-
What are two characteristics of polyatomic ions?
::多原子离子的两个特征是什么? -
Which atom becomes the central atom in the structure?
::哪些原子成为结构的中心原子? -
Where is the charge on an ion placed in a lewis dot diagram?
::利维斯点形图中的离子上的电荷在哪里?
-
Lewis structures for polyatomic ions follow the same rules as those for other covalent compounds.