9.19 氢联结
章节大纲
-
What’s the difference between these two molecules?
::这两种分子之间有什么区别?A rough rule of thumb is that higher molecular- weight materials have higher boiling points than their lower molecular weight counterparts. More energy is needed to move the larger molecule from the state to the vapor state. However, ammonia has a boiling point of -33.34°C and a molecular weight of 17 while nitrogen (molecular weight 28) has a boiling point of -195.8°C. The lighter ammonia molecule must have other factors that influence its .
::粗略的拇指规则是,较高的分子量材料的沸点高于较低的分子量当量。 将较大的分子从州移动到蒸气状态需要更多能量。 然而,氨的沸点为-33.34°C,分子量为17,而氮(分子量28)的沸点为-195.8°C。 较轻的氨分子必须有影响它的其他因素。Hydrogen Bonding
::氢联结The attractive force between water molecules is a dipole interaction. The hydrogen atoms are bound to the highly electronegative oxygen (which also possesses two lone pair sets of electrons, making for a very polar bond. The partially positive hydrogen atom of one molecule is then attracted to the oxygen atom of a nearby water molecule (see Figure ).
::水分子之间的吸引力是一种极分子相互作用。氢原子与高电阴性氧密不可分(它也拥有两组单对电子,形成极极联结。 一个分子的局部正氢原子随后被附近水分子的氧原子吸引(见图 )。A hydrogen bond in water occurs between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the lone pair of electrons on an oxygen atom of a neighboring water molecule.
::一个水分子的氢原子与一个相邻水分子的氧原子上的单对电子之间发生氢在水中的联结。A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular attractive force in which a hydrogen atom that is covalently bonded to a small, highly electronegative atom is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on an atom in a neighboring molecule. Hydrogen bonds are very strong compared to other dipole interactions. The strength of a typical hydrogen bond is about 5% of that of a .
::氢联结是一种分子间诱导力,其中氢原子与一个小的、高电阴性原子交织在一起,被相邻分子中原子上的单对电子吸引。 氢联结与其他二极相互作用相比非常强大。 典型氢联结的强度约为一原子的5%。occurs only in molecules where hydrogen is covalently bonded to one of three : fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen. These three elements are so electronegative that they withdraw the majority of the density in the covalent bond with hydrogen, leaving the H atom very electron-deficient. The H atom nearly acts as a bare , leaving it very attracted to lone pair electrons on a nearby atom.
::只有在分子中才会发生,在分子中,氢被共价结合为三分之一:氟、氧或氮。这三个元素的电阴性非常强,以至于它们撤回了与氢的共价结合的密度,使H原子极电子衰竭。H原子几乎是光着的,让附近的原子中的单对电子吸引它。The hydrogen bonding that occurs in water leads to some unusual, but very important properties. Most that have a mass similar to water are at room temperature . Because of the strong hydrogen bonds, water molecules are able to stay condensed in the liquid state. Figure shows how the bent shape and two hydrogen atoms per molecule allows each water molecule to be able to hydrogen bond to two other molecules.
::在水中发生的氢联结导致一些不同寻常但非常重要的特性。大多数质量与水相似的氢在室温下。由于氢联结的强力,水分子能够保持液态凝结。图显示每个分子的弯曲形状和两个氢原子如何使每个水分子能够将氢联结到另外两个分子。Multiple hydrogen bonds occur simultaneously in water because of its bent shape and the presence of two hydrogen atoms per molecule.
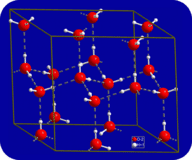
::多氢联结在水中同时发生,原因是其弯曲形状和每个分子存在两个氢原子。In the liquid state, the hydrogen bonds of water can break and reform as the molecules flow from one place to another. When water is cooled, the molecules begin to slow down. Eventually, when water is frozen to ice, the hydrogen bonds become permanent and form a very specific network (see Figure ).
::在液态中,水的氢联结会随着分子从一个地方流向另一个地方而破裂和改变。当水被冷却时,分子开始减慢。 最终,当水被冰冻时,氢联结会成为永久的,形成一个非常具体的网络(见图 ) 。When water freezes to ice, the hydrogen bonding network becomes permanent. Each oxygen atom has an approximately tetrahedral geometry – two covalent bonds and two hydrogen bonds.
::当水冻结到冰层时,氢联结网络就成为永久的。 每个氧原子都有大约四面形几何 — — 两个共价键和两个氢联结。The bent shape of the molecules leads to gaps in the hydrogen bonding network of ice. Ice has the very unusual property that its solid state is less dense than its liquid state. Ice floats in liquid water. Virtually all other substances are denser in the solid state than in the liquid state. Hydrogen bonds play a very important biological role in the physical structures of and .
::分子的弯曲形状导致冰氢结合网络的缺口。 冰有非常不寻常的特性, 其固态比液态低密度。 冰在液态中漂浮。 几乎所有其他物质在固态比液态更稠密。 氢结层在物理结构以及物理结构中发挥着非常重要的生物作用 。Why does water form droplets? Hint: it has to do with the attraction between water molecules. Learn more (and see how many drops of water you can get a penny can hold) in this simulation:
::水滴为何形成? 提示 : 它与水分子之间的吸引有关。 在此模拟中学习更多( 看看有多少滴水可以维持 ) :Summary
::摘要-
Hydrogen bonds form when a H attached to a N, O, or F atom interacts with another N, O, or F atom.
::当与N、O或F原子相连的H与另一个N、O或F原子发生相互作用时,氢键形成。
Review
::回顾-
How strong is a hydrogen bond?
::氢联结有多强? -
What happens when H is covalently bonded to N, O, or F?
::当H和N、O或F连结在一起时会怎样? -
How does the shape of the water molecule affect the properties of ice?
::水分子的形状如何影响冰的特性?
-
Hydrogen bonds form when a H attached to a N, O, or F atom interacts with another N, O, or F atom.