10.6 Avogadro的假设和摩尔卷
Section outline
-
How do scuba divers know if they will run out of gas?
::潜水潜水员怎么知道他们会不会用完汽油?Knowing how much is available for a dive is crucial to the survival of the diver. The tank on the diver’s back is equipped with gauges to tell how much gas is present and what the pressure is. A basic knowledge of gas behavior allows the diver to assess how long to stay under water without developing problems.
::了解潜水的可用量对于潜水员的生存至关重要。 潜水员背部的潜水池配备了测量仪,以判断有多少气体存在以及什么是压力。 有关气体行为的基本知识使得潜水员能够评估在水中停留多久而不出现问题。Avogadro’s Hypothesis and Molar Volume
::阿沃加德罗的假说和摩尔卷Volume is a third way to measure the amount of matter, after item count and mass. With and solids, volume varies greatly depending on the density of the substance . This is because solid and liquid particles are packed close together with very little space in between the particles. However, gases are largely composed of empty space between the actual gas particles (see Figure ).
::音量是测量物质数量的第三种方式,在项目计数和质量之后。与固体和固体相比,音量差异很大,取决于物质的密度。这是因为固体和液体颗粒被紧紧包装在一起,颗粒之间的空间很小。然而,气体主要由实际气体颗粒之间的空空空空间组成(见图 )。Gas particles are very small compared to the large amounts of empty space between them.
::与它们之间的大量空隙相比,气体粒子很小。In 1811, Amedeo Avogadro explained that the volumes of all gases can be easily determined. Avogadro’s hypothesis states that equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of particles. Since the total volume that a gas occupies is made up primarily of the empty space between the particles, the actual size of the particles themselves is nearly negligible. A given volume of a gas with small light particles such as hydrogen (H 2 ) contains the same number of particles as the same volume of a heavy gas with large particles such as sulfur hexafluoride, SF 6 .
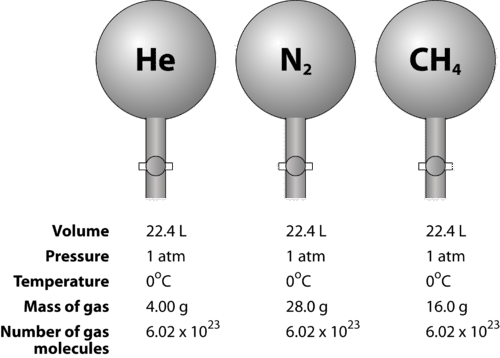
::1811年,阿梅德奥·阿沃加德罗(Amedeo Avogadro)解释说,所有气体的数量都可以很容易地确定。阿沃加德罗的假设是,所有气体在相同的温度和压力下的数量都相等,含有同等数量的颗粒。由于一个气体占据的总量主要由粒子之间的空空隙组成,粒子本身的实际大小几乎可以忽略不计。氢(H2)等小光粒子气体的一定数量与六氟化硫(SF6)等大型颗粒的重气体的相同数量。Gases are compressible, meaning that when put under high pressure, the particles are forced closer to one another. This decreases the amount of empty space and reduces the volume of the gas. Gas volume is also affected by temperature. When a gas is heated, its molecules move faster and the gas expands. Because of the variation in gas volume due to pressure and temperature changes, the comparison of gas volumes must be done at one standard temperature and pressure . Standard temperature and pressure (STP) is defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atm pressure. The molar volume of a gas is the volume of one mole of a gas at STP. At STP, one mole (6.02 × 10 23 representative particles) of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L ( Figure ).
::气体是压缩的,这意味着在高压下,粒子被迫相互靠近。这减少了空空空间的数量并减少了气体的体积。气体体积也受到温度的影响。当气体加热时,其分子移动更快,气体膨胀。由于压力和温度变化造成的气体体积变化,气体体积的比较必须在一个标准温度和压力下进行。标准温度和压力(STP)的定义是:0°C(273.15K)和1°压力。气体的摩尔体积是STP的一个气体摩尔体积。在STP,任何气体的摩尔体积(6.02×1023有代表性的粒子)为22.4升(Figure)。A mole of any gas occupies 22.4 L at standard temperature and pressure (0°C and 1 atm).
::任何气体的摩尔在标准温度和压力(0°C和1 atm)下均占22.4升。Figure illustrates how molar volume can be seen when comparing different gases. Samples of helium (He), nitrogen (N 2 ), and methane (CH 4 ) are at STP. Each contains 1 mole or 6.02 × 10 23 particles. However, the mass of each gas is different and corresponds to the of that gas: 4.00 g/mol for He, 28.0 g/mol for N 2 , and 16.0 g/mol for CH 4 .
::图中显示了在比较不同气体时如何看到摩尔体积的图示。在STTP中,有(He)、氮(N2)和甲烷(CH4)的样本。每个样本都含有1摩尔或6.02×1023颗粒。然而,每种气体的质量不同,与气体质量相对应:He为4.00克/摩尔,N2为28.0克/摩尔,CH4为16.0克/摩尔。Avogadro’s hypothesis states that equal volumes of any gas at the same temperature and pressure contain the same number of particles. At standard temperature and pressure, 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 L.
::阿沃加德罗的假设指出,在相同的温度和压力下,任何气体的同量含有相同数量的颗粒。 在标准温度和压力下,任何气体的1毫尔占22.4升。Summary
::摘要-
Equal volumes of gases at the same conditions contain the same number of particles.
::同一条件下同等数量的气体含有相同数量的颗粒。 -
Standard temperature and pressure is abbreviated (STP).
::标准温度和压力缩微(STP)。 -
Standard temperature is 0°C (273.15 K) and standard pressure is 1 atm.
::标准温度为0°C(273.15K),标准压力为1小时。 -
At STP, one mole of any gas occupies a volume of 22.4 L
::在保护受威胁人民党,任何气体的一毫里尔占22.4升的体积。
Review
::回顾-
A container is filled with gas, what do we know about the space actually taken up by a gas?
::装满气体的容器 我们对气体实际占用的空间了解多少? -
Why do we need to do all our comparisons at the same temperature and pressure?
::为什么我们需要在相同的温度和压力下 做我们所有的比较呢? -
At standard temperature and pressure, 1 mole of gas is always equal to how many liters?
::在标准温度和压力下,1毫升气体总等于多少升?
-
Equal volumes of gases at the same conditions contain the same number of particles.