13.5 平均动能和温度
章节大纲
-
How much energy does it take to hit a baseball?
::打棒球需要多少能量?is the energy of motion. Any object that is moving possesses kinetic energy. Baseball involves a great deal of kinetic energy. The pitcher throws a ball, imparting kinetic energy to the ball. When the batter swings, the motion of swinging creates kinetic energy in the bat. The collision of the bat with the ball changes the direction and speed of the ball, with the idea of kinetic energy being involved again.
::运动的能量。 任何移动的物体都拥有动能。 棒球涉及大量的动能。 投手投球, 给球注入动能。 当击手挥动时, 挥动运动在球棒中产生动能。 球棒与球的碰撞改变了球的方向和速度, 动能的想法又被卷入了。Kinetic Energy and Temperature
::动能和温度As stated in the kinetic-molecular theory , the temperature of a substance is related to the average kinetic energy of the particles of that substance. When a substance is heated, some of the absorbed energy is stored within the particles, while some of the energy increases the motion of the particles. This is registered as an increase in the temperature of the substance.
::正如动能分子理论所述,物质的温度与该物质的颗粒的平均动能有关,当一种物质变暖时,部分吸收的能量储存在粒子中,而部分能量增加粒子的动能,这被记录为该物质的温度上升。Average Kinetic Energy
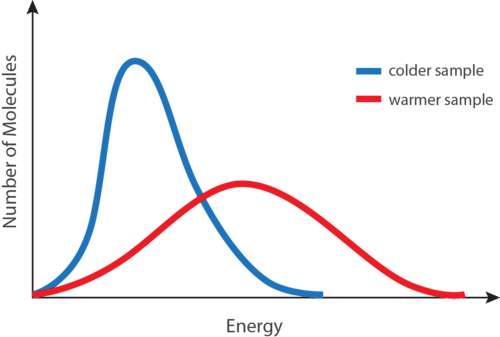
::平均动能At any given temperature, not all of the particles of a sample of matter have the same kinetic energy. Instead, the particles display a wide range of kinetic energies. Most of the particles have a kinetic energy near the middle of the range. However, a small number of particles have kinetic energies a great deal lower or a great deal higher than the average (see Figure ).
::在任何特定温度下,并非所有物质样本的粒子都具有相同的动能。相反,这些粒子展示了广泛的动能。大多数粒子在射程的中间都有动能。然而,少数粒子的动能大大低于或大大高于平均值(见图 )。A distribution of molecular kinetic energies as a function of temperature. The blue curve is for a low temperature, while the red curve is for a high temperature.
::分子动能的分布是温度的函数。蓝色曲线是低温,红色曲线是高温。The blue curve in the figure above is for a sample of matter at a relatively low temperature, while the red curve is for a sample at a relatively high temperature. In both cases, most of the particles have intermediate kinetic energies, close to the average. Notice that as temperature increases, the range of kinetic energies increases and the distribution curve “flattens out.” At a given temperature, the particles of any substance have the same average kinetic energy.
::上图中的蓝色曲线是相对低温物质样本,红色曲线是相对高温物质样本,两种情况下,大多数颗粒都具有接近平均值的中间动能。请注意,随着温度的上升,动能范围的扩大和分布曲线“向外拉动 ” 。 在特定温度下,任何物质的粒子都有相同的平均动能。Absolute Zero
::绝对绝对零As a sample of matter is continually cooled, the average kinetic energy of its particles decreases. Eventually, one would expect the particles to stop moving completely. Absolute zero is the temperature at which the motion of particles theoretically ceases. Absolute zero has never been attained in the laboratory, but temperatures on the order of 1 × 10 -10 K have been achieved. The Kelvin temperature scale is the scale that is based on molecular motion and so absolute zero is also called 0 K. The Kelvin temperature of a substance is directly proportional to the average kinetic energy of the particles of the substance. For example, the particles in a sample of hydrogen at 200 K have twice the average kinetic energy as the particles in a hydrogen sample at 100 K.
::随着物质的样本不断冷却,其粒子的平均动能会下降。最终,人们会预计粒子将完全停止移动。绝对零是粒子在理论上停止运动的温度。在实验室中从未达到绝对零,但已经达到1×10-10K的温度。克尔文温度尺度是以分子运动为基础的尺度,因此绝对零也称为0K。一种物质的凯尔文温度与该物质的粒子的平均动能直接成比例。例如,200K的氢样本中的粒子比100K的氢样本中的粒子具有两倍的平均动能。Helium gas liquefies at 4 K or four degrees above absolute zero. Liquid helium is used as a coolant for large superconducting magnets and must be stored in insulated metal canisters.
::液态用作大型超导磁铁的冷却剂,必须储存在隔热金属罐中。Summary
::摘要-
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
::动能是运动的能量 -
At a given temperature, individual particles of a substance have a range of kinetic energies.
::在特定温度下,物质的个别粒子具有一系列动能。 -
The motion of particles theoretically ceases at absolute zero.
::粒子的运动理论上以绝对零停止。
Review
::回顾-
What is kinetic energy?
::什么是动能? -
If the temperature increases, will particles move faster or slower
than
they would at a lower temperature?
::如果温度上升,粒子的移动速度会比低温时更快或更慢吗? -
What is absolute zero?
::什么是绝对零?
-
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.