14.4 《查尔斯法》
章节大纲
-
How do you bake bread?
::你怎么烤面包的?Everybody enjoys the smell and taste of freshly-baked bread. It is light and fluffy as a result of the action of yeast on sugar. The yeast converts the sugar to carbon dioxide, which at high temperatures causes the dough to expand. The end-result is an enjoyable treat, especially when covered with melted butter.
::人人都喜欢新鲜面包的味道和味道。 酵母对糖的动作是轻而易举的。 酵母将糖转化为二氧化碳,在高温下导致面团膨胀。 最终结果是一种令人愉快的治疗,特别是被融化的黄油覆盖时。Charles’s Law
::查尔斯法As a container of confined gas is heated, its molecules increase in kinetic energy and push the movable piston outward, resulting in an increase in volume.
::随着一个封闭气体容器的加热,其分子的动能增加,将动活塞推向外,导致体积增加。French physicist Jacques Charles (1746-1823) studied the effect of temperature on the volume of a at constant pressure . Charles’s law states that the volume of a given mass of gas varies directly with the absolute temperature of the gas when pressure is kept constant. The absolute temperature is temperature measured with the Kelvin scale. The Kelvin scale must be used because zero on the Kelvin scale corresponds to a complete stoppage of molecular motion.
::法国物理学家雅克·查尔斯(Jacques Charles (1746-1823) 研究温度对恒定压力下一个气体体积的影响。 查尔斯的法律规定,当压力保持不变时,特定气体质量的量与气体的绝对温度直接不同。 绝对温度是用凯尔文的温度测量的。 使用凯尔文的比值必须使用凯尔文的比值,因为克尔文的比值为零,相当于分子运动完全停止。Mathematically, the direct relationship of Charles’s law can be represented by the following equation:
::从数学上讲,查尔斯法律的直接关系可以用下列方程式来表示:
::VT=k(k)As with Boyle’s law , is constant only for a given gas sample. Table shows temperature and volume data for a set amount of gas at a constant pressure. The third column is the constant for this particular data set and is always equal to the volume divided by the Kelvin temperature.
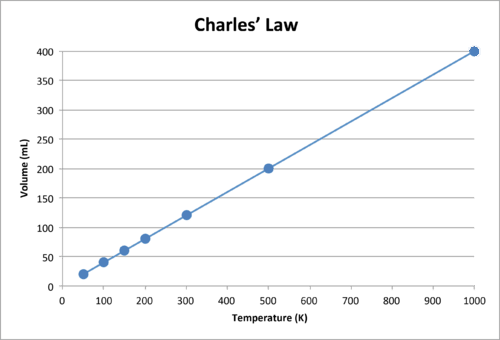
::与 Boyle 的法律一样, k 仅对特定气体样本是恒定的。表格显示在恒定压力下一组气体的温度和体积数据。第三列为该特定数据集的常数,总和Kelvin温度所除的体积相等。Temperature-Volume Data Temperature (K) Volume (mL) 50 20 0.40 100 40 0.40 150 60 0.40 200 80 0.40 300 120 0.40 500 200 0.40 1000 400 0.40 When this data is graphed, the result is a straight line, indicative of a direct relationship, shown in Figure .
::当用图表绘制这一数据时,结果为直线,显示直接关系,如图6所示。The volume of a gas increases as the Kelvin temperature increases.
::随着开尔文温度的上升,气体的量会增加。Notice that the line goes exactly toward the origin, meaning that as the absolute temperature of the gas approaches zero, its volume approaches zero. However, when a gas is brought to extremely cold temperatures, its molecules would eventually condense into the state before reaching absolute zero . The temperature at which this change into the liquid state occurs varies for different gases.
::注意该线完全朝着源头前进,这意味着当气体的绝对温度接近零时,其体积接近零。 但是,当气体进入极端寒冷的温度时,其分子最终会在达到绝对零之前凝聚到状态。 不同气体的液体状态发生这种变化的温度各不相同。Charles’s Law can also be used to compare changing conditions for a gas. Now we use and to stand for the initial volume and temperature of a gas, while and stand for the final volume and temperature. The mathematical relationship of Charles’s Law becomes:
::查尔斯法(Charles Law)也可以用来比较气体不断变化的条件。 现在,我们用V1和T1代表气体的初始体积和温度,而V2和T2代表最终体积和温度。 查尔斯法的数学关系是:
::V1T1=V2T2This equation can be used to calculate any one of the four quantities if the other three are known. The direct relationship will only hold if the temperatures are expressed in Kelvin. Temperatures in Celsius will not work. Recall the relationship that K = °C + 273.
::如果已知其他三个数量,此方程式可用于计算四个数量中的任何一个。 只有当温度以克尔文表示时, 直接关系才会保持。 摄氏温度不会起作用 。 回顾 K = °C + 273 之间的关系 。Sample Problem: Charles’s Law
::抽样问题:查尔斯法A balloon is filled to a volume of 2.20 L at a temperature of 22°C. The balloon is then heated to a temperature of 71°C. Find the new volume of the balloon.
::气球在22°C的温度下填充到2.20升的体积。 气球然后加热到71°C的温度。 找到气球的新体积。Step 1: List the known quantities and plan the problem.
::第1步:列出已知数量并规划问题。Known
::已知已知-
::V1=2.20升 -
::T1=22°C=295K -
::T2=71C=344K
Unknown
::未知-
::V2=L吗?
Use Charles’s law to solve for the unknown volume . The temperatures have first been converted to Kelvin.
::使用Charles的法律解决未知体积(V2),Step 2: Solve.
::步骤2:解决。First, rearrange the equation algebraically to solve for .
::首先,重新排列方程式代数以解析 V2 。
::V2=V1xT2T1Now substitute the known quantities into the equation and solve.
::现在将已知数量替换为方程式和解析 。
::V2=2.20 Lx344 K295 K=2.57 LStep 3: Think about your result.
::步骤3:想想你的结果。The volume increases as the temperature increases. The result has three .
::随着温度的上升,数量会增加。结果有3个。Summary
::摘要-
Increasing the temperature of a gas at constant pressure will produce and increase in the volume.
::以恒定压力提高气体的温度将产生和增加气体的体积。
Review
::回顾-
Explain Charles’s Law in terms of the kinetic molecular theory.
::从动能分子理论的角度解释一下查尔斯的法律。 -
Why does the temperature need to be in Kelvin?
::为什么温度需要在开尔文? -
Does Charles’s law hold when the gas becomes a liquid?
::当气体变成液体时,查尔斯的法律是否维持不变?
-