16.4饱和和不饱和和不饱和解决办法
章节大纲
-
How do you make sure a compound is pure?
::你如何确保化合物纯净?When compounds are synthesized, they often have contaminating materials mixed in with them. The process of recrystallization can be used to remove these impurities. The crystals are dissolved in a hot solvent , forming a solution. When the solvent is cooled the is no longer as soluble and will precipitate out of solution, leaving other materials still dissolved.
::当化合物被合成后,它们往往会污染混合在一起的材料。内晶化过程可以用来清除这些杂质。晶体溶解于热溶剂中,形成溶液。溶剂被冷却后,溶剂就不再可以溶解,会从溶液中解脱出来,其他材料仍然溶解。Saturated and Unsaturated Solutions
::饱和和和不饱和解决方案Table salt (NaCl) readily dissolves in water. Suppose that you have a beaker of water to which you add some salt, stirring until it dissolves. So you add more and that dissolves. You keep adding more and more salt, eventually reaching a point that no more of the salt will dissolve no matter how long or how vigorously you stir it. Why? On the molecular level, we know that action of the water causes the individual to break apart from the salt crystal and enter the solution, where they remain hydrated by water molecules. What also happens is that some of the dissolved ions collide back again with the crystal and remain there. Recrystallization is the process of dissolved solute returning to the solid state. At some point the rate at which the solid salt is dissolving becomes equal to the rate at which the dissolved solute is recrystallizing. When that point is reached, the total amount of dissolved salt remains unchanged. Solution equilibrium is the physical state described by the opposing processes of dissolution and recrystallization occurring at the same rate. The solution equilibrium for the dissolving of sodium chloride can be represented by one of two equations.
::盐 容易溶解于水中。 假设你有一个水杯, 将一些盐添加到水中, 搅拌到溶解中。 所以, 你增加更多, 溶解。 你不断增加更多盐, 最终达到一个点, 无论多久或多么激烈地搅拌, 盐都不会溶解。 为什么? 在分子一级, 我们知道水的作用导致个人脱离盐晶, 进入溶液中, 那里仍然有水分子。 溶解的离子再次与水晶交融在一起, 并且留在水晶中。 矩形化是溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶溶液返回固体状态的过程。 在某个点, 固化盐的溶解速度等于溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶液的速度。 当达到该点时, 溶解盐的总量没有变化。 溶解平衡度是反溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解的物理状态, 与溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解的溶解溶解溶解溶解溶解的平衡的溶解溶解溶解的平衡的平衡由两种方方体形成一个等方体代表。NaCl ( s ) ⇄ NaCl ( a q )
::NaCl NaCl (aq)While this shows the back and forth between solid and aqueous solution , the preferred equation also shows the that occurs as an ionic solid dissolves.
::虽然这显示了固态和水溶液之间的背和背,但偏好方程式也显示了离子固态溶解时发生的情况。NaCl ( s ) ⇄ Na + ( a q ) + Cl − ( a q )
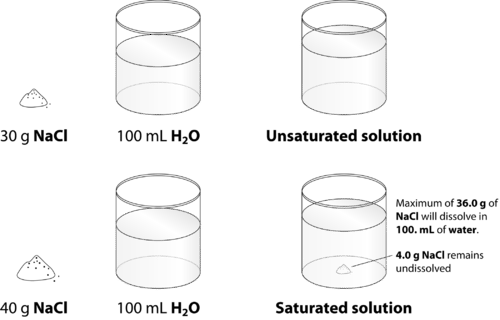
::NaClNa+(aq)+Cl-(aq)When the solution equilibrium point is reached and no more solute will dissolve, the solution is said to be saturated. A saturated solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved. At 20°C, the maximum amount of NaCl that will dissolve in 100. g of water is 36.0 g. If any more NaCl is added past that point, it will not dissolve because the solution is saturated. What if more water is added to the solution instead? Now more NaCl would be capable of dissolving in the additional solvent. An unsaturated solution is a solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved. Figure illustrates the above process and shows the distinction between unsaturated and saturated.
::当溶液平衡点达到而不再溶解时,溶液据说是饱和的。饱和的溶液是含有能够溶解的溶液最大量的溶液。在 20 °C 时,以100 克水溶解的纳氏最大量为36.0克。如果再增加NaCl,它不会溶解,因为溶液是饱和的。如果将更多的水添加到溶液中,又会怎样?现在更多的纳氏能溶解额外的溶剂。不饱和的溶液是一种溶解量低于能溶解的溶液最大量的溶液的溶液。图显示上述过程,并显示不饱和的溶液之间的区别。When 30.0 g of NaCl is added to 100 ml of water, it all dissolves, forming an unsaturated solution. When 40.0 g is added, 36.0 g dissolves and 4.0 g remains undissolved, forming a saturated solution.
::当 NaCl 的 30.0 克添加到 100 毫升的水中, 它会溶解, 形成不饱和的溶液。 当添加 40.0 克时, 36.0 克溶解 和 4.0 克 仍然未溶解, 形成饱和的溶液 。How can you tell if a solution is saturated or unsaturated? If more solute is added and it does not dissolve, then the original solution was saturated. If the added solute dissolves, then the original solution was unsaturated. A solution that has been allowed to reach equilibrium but which has extra undissolved solute at the bottom of the container must be saturated.
::您如何判断溶液是饱和的还是不饱和的? 如果添加了更多的溶液而不溶解, 那么原始溶液是饱和的。 如果添加的溶液溶解了, 那么原溶液是不饱和的。 允许达到平衡但容器底部有额外未溶解溶液的解决方法必须饱和 。Summary
::摘要-
Saturated and unsaturated solutions are defined.
::界定饱和和不饱和的解决办法。 -
Solution equilibrium exists when the rate of dissolving equals the rate of recrystallization.
::当溶解率等于内吸附率时,即存在溶解平衡。
Review
::回顾-
Why is the preferred equation for solution equilibrium of NaCl an equilibrium between solid NaCl and the ions?
::为什么NaCl的解决方案平衡偏好方程式是固态NaCl和离子之间的平衡? -
If I add water to a saturated sucrose solution, what will happen?
::如果我把水加到饱和的苏格罗斯溶液中 会发生什么呢? -
If I heat a solution and remove water, I see crystals at the bottom of the container. What happened?
::如果我加热溶液,除去水, 我可以看到水晶在容器的底部。
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。-
What is the initial solution used?
::最初使用的解决办法是什么? -
What is the heat source for evaporation?
::蒸发的热源是什么? -
Why does the salt precipitate out of solution?
::为什么盐会从溶液中抽出?
-
Saturated and unsaturated solutions are defined.