1.2 人体组织
章节大纲
-
Muscle, connective, skeletal, and epithelial. What do these have in common?
::肌肉、连接、骨骼和上皮骨,这些有什么共同点?Tissues
::组织组织A tissue is a group of connected that have a similar function within an organism . The simplest living, , , are made of many specialized types of cells that work together for a common goal. Such cell types include digestive cells, tubular pore cells, and epidermal cells. Though the different cell types create a large organized, multicellular structure—the visible sponge—they are not organized into true tissues. If a sponge is broken up by passing it through a sieve, the sponge will reform on the other side.
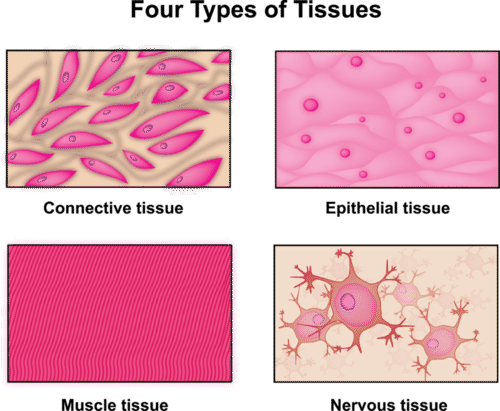
::一种组织是由有机体内具有类似功能的连接体组成的群体,最简单的活体是由许多专门类型的细胞组成的,它们为了一个共同的目标而共同工作。这种细胞类型包括消化细胞、管状孔细胞和上皮细胞。虽然不同的细胞类型创造了一个大型的有组织的多细胞结构——可见海绵,但它们没有组织成真正的组织。如果海绵通过一个筛子通过一个筛子将海绵分解,那么海绵就会在另一侧进行改造。More complex organisms, such as jellyfish, coral, and sea anemones, have a tissue level of organization. For example, jellyfish have tissues that have separate protective, digestive, and sensory functions. There are four basic types of tissues in the bodies of all including the . These make up all the organs , structures, and other contents of the body. Figure shows an example of each tissue type. The four basic types of tissues are epithelial, muscle, nervous, and connective.
::更复杂的有机体,如水母、珊瑚和海葵等,具有组织层次的组织。例如,水母组织具有单独的保护、消化和感官功能。在包括水母在内的所有身体中,有四种基本的组织类型。它们构成身体的所有器官、结构和其他内装物。图显示了每个组织类型的一个实例。四种基本组织类型是上皮、肌肉、神经和连接。The human body consists of these four tissue types.
::人体由这四种组织组成(a) A scanning electron micrograph (SEM) image of lung trachea epithelial tissue. (b) A transmission electron micrograph (TEM) image of skeletal muscle tissue. (c) A light microscope image of neurons of nervous tissue. (d) Red blood cells, a connective tissue.
:b) 骨骼肌肉组织传输电子显微镜(TEM)图像。 (c) 神经组织神经元的光显微镜图像。 (d) 红血细胞,一种连接组织。
Epithelial tissue is made up of a layer or layers of tightly packed cells that line the surfaces of the body. The largest example of epithelial tissue (also the largest organ in the human body) is the skin. Mammalian skin consists of stratified epithelium, which has several layers of cells. The outermost layers of cells, called squamous cells, are flat plate-like cells, while the deeper layers are roughly cube shaped and called cuboidal cells. Epithelial tissue has multiple functions, but it serves primarily to protect, absorb, and secrete. As you probably already know, our skin organ covers our entire body and protects underlying tissues from , chemicals, and other injury. Epithelial cells also line the where they absorb nutrients , and similar cells in the glands secrete and .
::皮层组织由一层或一层紧密的细胞组成,紧密的细胞排列在身体表面。皮层组织的最大例子(也是人体中最大的器官)是皮肤。哺乳动物的皮肤由分层的皮层组成,有几层细胞。最外层的细胞,称为光滑的细胞,是平的板状细胞,而更深层的细胞大致是立方体形状,称为结骨细胞。皮层组织有多种功能,但主要用于保护、吸收和秘密。正如你们已经知道的那样,我们的皮肤器官覆盖着我们整个身体,保护底部组织免受化学和其他伤害。外层细胞也排在吸收营养素的地方,以及腺中类似的细胞。Muscle tissue encompasses not only the , such as those in our legs or fingers, that we actively control, but also the tissue that forms most of our internal organs. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. tissue forms what we think of as our muscles; it is attached to our by our tendons and can be relaxed or contracted voluntarily. Similar in structure to skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle is found exclusively in the walls of the heart. The major difference, however, is that cardiac muscle is involuntary and cannot be actively controlled. Similarly, smooth muscle , which forms the muscle layers in internal organs such as the digestive tract and bladder , is an involuntary tissue. Smooth muscle tissue controls slow involuntary movements such as stomach wall contractions and the contractions of arteries to regulate flow.
::肌肉组织不仅包括我们积极控制的腿部或手指部的肌肉组织,还包括构成我们大部分内器官的组织。肌肉组织有三种类型:骨骼、心脏和光滑。组织组成了我们所认为的肌肉;它被我们的管子连接在我们的肌肉上,可以放松或自愿缩减。在与骨骼肌肉结构类似的结构中,心脏肌肉完全在心脏的墙壁中发现。但主要区别在于心脏肌肉是非自愿的,不能积极控制。同样,构成内器官肌肉层的光滑肌肉,如消化道和膀胱,是一种非自愿的组织。肌肉组织控制着不自觉的动作,如胃壁收缩和动脉收缩以调节流动。Nervous tissue is made up of the nerve cells (neurons) that form the , including the brain and spinal cord . These cells are especially responsive to stimuli , allowing nervous tissue to transmit stimuli from the brain to the body extremely rapidly.
::神经组织由构成神经细胞(中子)组成的神经细胞组成,包括大脑和脊髓。 这些细胞对刺激反应特别敏锐,神经组织可以极快地将刺激从大脑传输到身体。Connective tissue connects, supports, or separates other tissues and organs. Connective tissue proper, a form of connective tissue, can be either loose or dense. Adipose tissue, or fat, is loose connective tissue, while tendons and ligaments , composed of collagen , are examples of dense connective tissue. Other forms of connective tissue include blood (fluid connective tissue) and cartilage and bone (both forms of supporting connective tissue).
::连接组织连接、支撑或隔开其他组织和器官。连接组织本身是一种连接组织的形式,可以是松散的,也可以是稠密的。脂肪或脂肪是松散的连接组织,而由科兰根组成的圆锥形和长颈是稠密的连接组织的例子。其他连接组织形式包括血液(流感连接组织)、软骨和骨头(两种支持连接组织的形式)。Summary
::摘要-
Tissues are composed of cells, and multiple tissues together constitute an organ.
::组织由细胞组成,多个组织合在一起构成器官。 -
The human body has four types of tissues: nervous, muscle, connective, and epithelial
::人体有四类组织:神经、肌肉、连接和上皮组织。
Review
::回顾-
What are the four types of tissues? Give an example of each.
::四种组织是什么类型的?请举一个例子。 -
What is the difference between tissue and cellular level organization?
::组织和细胞一级的组织之间有什么区别? -
Are there any organisms that do not have tissue structures? If yes, what organism(s)?
::是否有任何生物没有组织结构?如果有,什么生物?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the video above to answer the following questions:
::使用以上视频回答下列问题:-
What are some different types of connective tissue?
::什么是某种不同类型的连接组织? -
What is the extracellular matrix?
::什么是外细胞矩阵? -
What are the differences between skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissue?
::骨骼、心脏和滑动肌肉组织之间有什么区别?
-
Tissues are composed of cells, and multiple tissues together constitute an organ.