4.3 A空气呼吸
章节大纲
-
Grapes. Why? What do these have in common with a breath of air?
::为什么 这些和呼吸空气有什么共同之处?Shown below are the parts of the lungs where oxygen moves from the lungs into the . If the alveoli below were purple, they could resemble a bunch of grapes. Of course, as the alveoli are in the lungs, they must be very small to provide enough area for the exchange of gases. In fact, there are about 300-600 million alveoli in the adult lung.
::下面显示的是肺部中氧气从肺部转移到肺部的部分。如果下面的叶子是紫色的,它们可以像一堆葡萄一样。当然,由于肺部中的叶子很小,它们必须能提供足够的面积来交换气体。事实上,成人肺中大约有3亿到6亿叶子。The Journey of a Breath of Air
::空中呼吸之旅In air-breathing vertebrates , such as humans, respiration of oxygen includes four stages:
::在呼吸空气的脊椎动物,如人类,呼吸氧气包括四个阶段:-
Ventilation
from the
atmosphere
into the alveoli of the lungs.
::从大气中通风到肺的肺叶 -
Pulmonary gas exchange
from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillaries.
::肺气交换 从肺泡素到肺毛毛毛毛毛毛毛 -
Gas transport from the pulmonary capillaries through the circulation to the
peripheral capillaries
in the
organs
.
::气流通过循环从肺毛毛毛毛毛刺通过器官的边缘毛毛毛刺从肺毛毛毛毛毛毛毛毛刺输送到器官的边缘毛毛毛刺。 -
Peripheral gas exchange from the
tissue
capillaries into the
and
.
::中间气体交换 从组织胶囊 进入和... ...
Ventilation: From the Air to the Alveoli
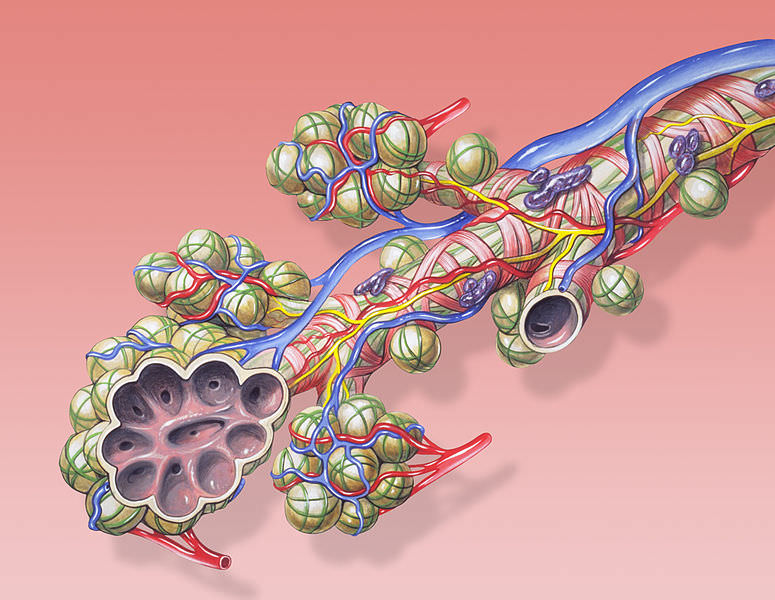
::通风:从空中到阿尔维奥利Air enters the body through the nose where it is warmed, filtered, and passed through the nasal cavity . Air passes the pharynx (which has the epiglottis that prevents food from entering the trachea). The upper part of the trachea contains the larynx . The vocal cords are two bands of tissue that extend across the opening of the larynx. After passing the larynx, the air moves into the trachea. The trachea is a long tube that divides into two smaller tubes called bronchi , which lead into each lung, as shown in Figure . Bronchi are reinforced to prevent their collapse and are lined with ciliated epithelium and mucus-producing cells. Bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles . Bronchioles end in grape-like clusters called alveoli. Alveoli are surrounded by a network of thin-walled capillaries, as shown in Figure .
::空气通过鼻孔进入身体,取暖、过滤和通过鼻腔。空气通过pharynx(有阻止食物进入气管的上皮球),气管的上部含有喉咙。声带是横跨喉咙开口的两根组织带。经过喉咙后,空气进入气管。气管是一条长管,分为两根小管,称为支气管,如图所示,每根肺中都有支气管。Bronchi被加固,以防止其崩溃,并配有结结膜的上部和结膜生成的细胞;Bronchi分枝为小管,称为支气管;Bronchioles在葡萄类聚体中结束;Alveoli被一个薄墙的毛绒网包围,如图所示。Breathing in, or inhaling , is usually an active movement . A contraction of the diaphragm is necessary, and it uses ATP . The diaphragm is a muscle that is found below the lungs. Contraction of the diaphragm causes the volume of the chest cavity to increase, and the air pressure within the lungs decreases. The pressure difference causes air to rush into the lungs. Relaxation of the diaphragm causes the lungs to recoil, and air is pushed out of the lungs. Breathing out, or exhaling, is normally a passive process powered by the elastic recoil of the chest, similar to letting the air out of a balloon.
::呼吸或吸入通常是一种活跃的运动。 隔膜缩缩是必要的, 它使用 ATP 。 隔膜缩缩是肺下发现的肌肉。 隔膜缩缩导致胸腔腔的体积增加, 肺内的空气压力减少。 压力差异导致空气向肺中冲入气压。 隔膜的放松导致肺部回旋, 空气被从肺中挤出。 呼吸或呼吸通常是一种被动过程, 其动力来自胸部的弹性后坐力, 类似于让空气从气球中流出。The alveoli are the tiny grape-like structures within the lungs, and they are the site of pulmonary gas exchange.
::藻类是肺里微小的葡萄状结构 它们是肺气交换的场所Pulmonary Gas Exchange: From the Alveoli into the Pulmonary Capillaries
::肺气交换:从阿尔维奥利到肺气罐头Breathing is only part of the process of delivering oxygen to where it is needed in the body. The process of gas exchange occurs in the alveoli by of gases between the alveoli and the blood in the lung capillaries, as shown in Figure . Recall that diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The difference between the high concentration of O 2 in the alveoli and the low O 2 concentration of the blood in the capillaries is enough to cause O 2 molecules to diffuse across the thin walls of the alveoli and capillaries and into the blood. CO 2 moves out of the blood and into the alveoli in a similar way. The greater the concentration difference, the greater the rate of diffusion. Breathing also results in a loss of from the body. Exhaled air has a relative humidity of 100 percent because of the diffusion of water from the moist surfaces of the breathing passages and the alveoli into the warm exhaled air.
::呼吸只是将氧气输送到身体需要的地方的过程的一部分。气交换过程在藻类中发生,如图所示,气交换过程在藻类中发生,气体在藻类和肺毛毛血管中的血液中产生气体。回顾,物质的扩散是物质从高浓度地区向低浓度地区的迁移。在藻类中的O2高浓度和在毛皮室血液中的O2低浓度之间的差别足以导致O2分子扩散到藻类的薄壁和毛细和血管中。CO2以类似的方式从血液中流出,进入藻类中。浓度差异越大,扩散速度越快。呼吸力也会导致身体的流失。吸入空气的相对湿度为100%,因为呼吸道的湿度表水和藻类渗入温暖的空气中。Alveoli are tiny sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
::Alveoli是发生气体交换的肺部的小囊囊。In the lungs, oxygen diffuses across the thin membranes of the alveoli and capillary walls and is attracted to the hemoglobin molecules within red blood cells .
::在肺部中,氧弥漫在藻类薄膜和毛细墙的薄膜上,并被红细胞中的血红蛋白分子所吸引。After leaving the lungs, the oxygenated blood returns to the heart to be pumped through the aorta and around the body. The oxygenated blood travels through the aorta to the smaller arteries , arterioles, and finally the peripheral capillaries where gas exchange occurs.
::离开肺部后,氧化血液返回心脏,通过动脉和身体周围抽取。 氧化血液通过动脉、动脉、小动脉、动脉,最后是发生气体交换的边缘毛细血管,穿过动脉。Peripheral Gas Exchange: From Capillaries into Cells, and from Cells into Capillaries
::外围气体交换:从胶囊进入细胞,从胶囊进入胶囊The oxygen concentrations in are low, while the blood that leaves the lungs is 97 percent saturated with oxygen. So, oxygen diffuses from the blood into the body cells when it reaches the peripheral capillaries (the capillaries in the systemic circulation).
::氧气浓度较低,而肺部的血液则有97%饱和氧气。 因此,当氧气到达周围的毛细血管(系统循环中的毛细血管)时,血液中的氧气会扩散到身体细胞中。Carbon dioxide concentrations in metabolically active cells are much greater than in capillaries, so carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the capillaries. Most of the carbon dioxide (about 70 percent) in the blood is in the form of bicarbonate (HCO 3 - ). A small amount of carbon dioxide dissolves in the water of the plasma to form carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ). Carbonic acid and bicarbonate play an important role in regulating the pH of the body.
::新陈代谢活性细胞中的二氧化碳浓度远远大于毛细纤维中的二氧化碳浓度,因此二氧化碳从细胞中扩散到毛细血管中。血液中的大多数二氧化碳(约70%)以碳酸(HCO3-)的形式出现。 少量二氧化碳在等离子体水中溶解,形成碳酸(H2CO3)。 碳酸和碳酸双碳酸在调节身体pH方面发挥着重要作用。In order to remove CO 2 from the body, the bicarbonate is picked up by red blood cells and is again turned into carbonic acid. A water molecule (H 2 O) is then taken away from the carbonic acid, and the remaining CO 2 molecule is expelled from the red blood cells and into the alveoli where it is exhaled. The following equation shows this process:
::为了清除体内的二氧化碳,红细胞吸收了碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸三碳酸二碳酸二碳酸三碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸二碳酸HCO 3 - + H + ⇌ H 2 CO 3 ⇌ CO 2 + H 2 O
::HCO3 - + H+ + H2CO3 + CO2 + H2OGas exchange between your body and the environment occurs in the alveoli. The alveoli are lined with pulmonary capillaries, the walls of which are thin enough to permit the diffusion of gases. Inhaled oxygen diffuses into the pulmonary capillaries where it binds to hemoglobin in the blood. Carbon dioxide diffuses in the opposite direction—from capillary blood to alveolar air. At this point, the pulmonary blood is oxygen-rich, and the lungs are primarily holding carbon dioxide. Exhalation follows, thereby ridding the body of the carbon dioxide and completing the cycle of respiration.
::你的身体和环境之间的气体交换发生在alveoli。alveoli 与肺毛毛毛的毛毛毛粘结在一起,其壁薄足以扩散气体。吸入的氧气扩散到肺毛毛毛的毛细,与血液中的血红蛋白结合。二氧化碳向相反的方向扩散——从毛细血液到肺气。此时,肺血富含氧,肺部主要含有二氧化碳。随后,吸入后,释放出二氧化碳,完成呼吸循环。Gas Exchange and Homeostasis
::天然气交换和原气保持The equilibrium between carbon dioxide and carbonic acid is very important for controlling the acidity of body fluids. As gas exchange occurs, the pH balance of the body is maintained as part of . If proper respiration is interrupted, two things can occur:
::二氧化碳和碳酸之间的平衡对于控制体液的酸度非常重要。随着气体交换的发生,身体的pH平衡作为部分保持。如果适当的呼吸中断,可以发生两件事:-
Respiratory acidosis, in which arterial blood contains too much carbon dioxide, causing a drop in blood pH.
::呼吸酸中毒,动脉血液含有过多二氧化碳,导致血液pH值下降。 -
Respiratory alkalosis results from increased respiration (or hyperventilation), which causes a drop in the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood plasma. The drop in carbon dioxide concentration causes the blood pH to rise.
::呼吸性肺病是呼吸(或超通风)增加的结果,导致血浆中的二氧化碳含量下降,二氧化碳浓度下降导致血液pH值上升。
Summary
::摘要-
Breathing in, or inhaling, is usually an active movement. Contraction of the diaphragm causes the volume of the chest cavity to increase, and the air pressure within the lungs decreases.
::呼吸或吸入通常是一种积极的运动,隔膜收缩导致胸腔的体积增加,肺内的气压下降。 -
Diffusion is the movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
::传播是指物质从高浓度地区转移到低浓度地区。 -
The process of gas exchange occurs in the alveoli by diffusion of gases between the alveoli and the blood in the lung capillaries.
::气体交换过程在藻类中发生,在藻类和肺刺膜中的血液之间扩散气体。 -
Carbon dioxide concentrations in metabolically active cells are much greater than in capillaries, so carbon dioxide diffuses from the cells into the capillaries.
::新陈代谢活性细胞中的二氧化碳浓度远远大于毛细胞,因此二氧化碳从细胞中扩散到毛细胞。 -
The equilibrium between carbon dioxide and carbonic acid is very important for controlling the acidity of body fluids. As gas exchange occurs, the pH balance of the body is maintained as part of homeostasis.
::二氧化碳和碳酸之间的平衡对于控制体液的酸性非常重要。 随着气体交换的发生,身体的pH平衡作为全能保持的一部分得以保持。
Review
::回顾-
What are the four stages of respiration?
::呼吸的四个阶段是什么? -
Why does breathing result in a loss of water?
::为什么呼吸会导致水的流失? -
What is respiratory acidosis?
::什么是呼吸道酸化? -
What can cause respiratory alkalosis?
::是什么导致呼吸道肺病?
-
Ventilation
from the
atmosphere
into the alveoli of the lungs.