6.2 肾脏和排泄
章节大纲
-
How is it determined what's waste and what's not?
::它如何决定什么是浪费,什么不是浪费?Shown above is a major process of maintaining . Getting rid of waste and excess . Such a basic process is actually very complex. It involves an intricate exchange of materials through the kidneys.
::上面所展示的是一个主要的维持过程。清除浪费和过剩。这样一个基本过程实际上非常复杂,需要通过肾脏进行复杂的材料交换。Kidneys and Excretion
::肾肾和排泄The kidneys are part of the . The kidneys work together with other organs of the urinary system in the function of excretion . The urinary system is shown in Figure .
::肾脏与尿道系统的其他器官一起工作,发挥排泄功能。Components of the Urinary System. The kidneys are the chief organs of the urinary system.
::肾脏是尿道系统的主要器官。Urinary System
::内脏系统In addition to the kidneys, the urinary system includes the ureters , bladder , and urethra . The main function of the urinary system is to filter waste products and excess water from the and remove them from the body. The two kidneys, which are described in detail below, filter the blood and form urine . Urine is the liquid waste product of the body that is excreted by the urinary system.
::除了肾脏外,尿道系统还包括尿管、膀胱和尿道,尿道系统的主要功能是过滤废品和多余的水,从身体上取出,两种肾脏(下文详述)过滤血液和尿液,尿液是被尿道系统排出的身体的液体废物。From the kidneys, urine enters the ureters, which carry it to the bladder. Each ureter is a muscular tube about 25 centimeters long. Peristaltic movements of the of the ureter send urine to the bladder in small spurts.
::尿液从肾脏进入尿囊,然后将尿囊带到膀胱,每根尿囊都是一个肌肉管,大约25厘米长,尿囊的阴性运动将尿液用小刺塞送到膀胱。The bladder is a hollow organ that stores urine. It can stretch to hold up to 500 milliliters. When the bladder is about half full, the stretching of the bladder sends to the sphincter that controls the opening to the urethra. In response to the impulses, the sphincter relaxes and lets urine flow into the urethra.
::膀胱是一种储存尿液的空心器官,可以伸展至500毫升。当膀胱半满时,膀胱的伸展会传到控制尿道开口的螺旋杆上。当脉冲出现时,螺旋杆会放松,让尿液流入尿道。The urethra is a muscular tube that carries urine out of the body. Urine leaves the body through another sphincter in the process of urination . This sphincter and the process of urination are normally under conscious control.
::尿道是一种肌肉管,从身体中撒尿,尿液在尿过程中通过另一根指环离开身体,这种指环和尿过程通常在有意识的控制之下。Kidneys
::肾The kidneys participate in whole-body homeostasis. As mentioned above, one of the primary roles of the kidneys is to remove nitrogenous wastes. The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped, reddish-brown organs about the size of a fist. They are located just above the waist at the back of the abdominal cavity, on either side of the spine. As shown in Figure , the kidneys are protected by the ribcage. They are also protected by a covering of tough connective tissue and two layers of fat, which help cushion them.
::如上文所述,肾脏的主要作用之一是清除氮废物,肾脏是一对与拳头大小相近的豆形红褐色器官,位于脊椎两侧腹腔后部的腰部上方,如图所示,肾脏受肋骨保护,并受到坚固的连接组织及两层脂肪的保护,有助于缓冲。Located on top of each kidney is an adrenal gland, also shown in Figure . The two adrenal glands secrete several . Hormones are chemical messengers in the body that regulate many body functions. The adrenal hormone aldosterone helps regulate kidney functions.
::肾上腺位于每个肾上腺上,图中也显示了这一点。两种肾上腺分泌,若干次。荷尔蒙是管理许多身体功能的体内化学信使。肾上激素 aldosterone有助于调节肾功能。The Kidney. Each kidney is supplied by a renal artery and a renal vein.
::肾脏 每个肾脏都有肾动脉和肾静脉In Figure , you can see that the kidney has three layers. The outer layer is the renal cortex, and the middle layer is the renal medulla. The inner layer, the renal pelvis, is where the renal artery enters the kidney and the renal vein exits the kidney. The renal artery carries blood to the kidney to be filtered, and the renal vein carries the filtered blood away from the kidney. Structures in the kidney called nephrons are also seen in Figure . Each nephron extends from the cortex down into the medulla.
::在图中,可以看到肾有三个层。外层是肾皮层,中间层是肾膜。内层,肾骨盆,是肾动脉进入肾脏,肾静脉从肾脏进入肾脏。肾动脉将血液输送到肾脏过滤,肾静脉将经过滤的血液从肾脏运走。肾脏中的结构也见于图中。每个肾脏都从皮层延伸到脑膜。Nephrons
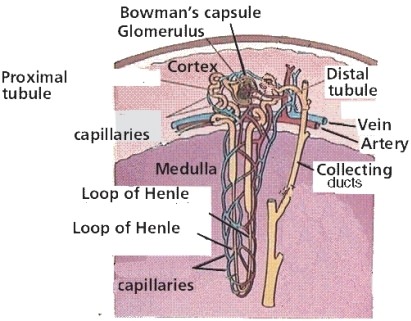
::内环Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the kidneys. A single kidney may have more than a million nephrons. The diagram in Figure represents an individual nephron and shows its main structures and functions. The structures include the glomerulus , Bowman’s capsule , and the renal tubule .
::肾脏是肾的结构和功能单位。 单肾可能拥有100多万个肾。 图中的图表代表了单个肾脏,显示了其主要结构和功能。 结构包括球状体、鲍曼胶囊和肾管。Nephron structures and functions.
::神经结构和功能。-
The glomerulus is a cluster of
arteries
that filters substances out of the blood.
::球状体是一组动脉 从血液中过滤物质 -
Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped structure around the glomerulus that collects the filtered substances.
::鲍曼的胶囊是收集过滤物质环绕球状物的杯状结构。 -
The renal tubule is a long, narrow tube surrounded by capillaries that reabsorbs many of the filtered substances and secretes other substances.
::肾管是一个长而狭窄的管子,四周有刺膜,重新吸收许多过滤过的物质,并分泌其他物质。
Filtration, Reabsorption, and Secretion
::过滤、再吸附和保密The renal arteries, which carry blood into the kidneys, branch into the capillaries of the glomerulus of each nephron. The pressure of blood moving through these capillaries forces some of the water and dissolved substances in the blood through the capillary walls and into Bowman’s capsule. Bowman’s capsule is composed of layers. The space between the layers, called Bowman’s space, fills with the filtered substances.
::将血液带入肾脏的肾动脉是每个肾脏球状体的支流。 通过这些刺状物的血液压力迫使一些水和血液中的溶解物质穿过毛细墙和鲍曼的胶囊。鲍曼的胶囊由层组成。 层间的空间被称为鲍曼的空间,充满了过滤的物质。The process of filtering substances from blood in the glomerulus is called filtration. The fluid that collects in Bowman’s space is called filtrate. It is composed of water, salts, glucose , amino acids , and urea. Larger structures in the blood—including molecules, blood , and platelets—do not pass into Bowman’s space. Instead, they stay in the main circulation.
::从球体中的血液中过滤物质的过程被称为过滤。 在鲍曼空间收集的流体被称为过滤。 它由水、盐、葡萄糖、氨基酸和尿素组成。 血液中的较大结构 — — 包括分子、血液和小板 — — 并不流入鲍曼的空间。 相反,它们停留在主环流中。From Bowman’s space, the filtrate passes into the renal tubule. The main function of the renal tubule is reabsorption. Reabsorption is the return of needed substances in the filtrate back to the bloodstream. It is necessary because some of the substances removed from the blood by filtration—including water, salts, glucose, and amino acids—are needed by the body. About 75 percent of these substances are reabsorbed in the renal tubule.
::从鲍曼的空间,过滤器通过过滤进入肾管。肾管的主要功能是再吸附。再吸附是将过滤器中的必要物质返回血液。 有必要这样做,因为通过过滤从血液中抽取的一些物质 — — 包括水、盐、葡萄糖和氨基酸 — — 是身体所需要的。 这些物质中约有75%被重新吸收到肾管中。As shown in Figure , the renal tubule is divided into three parts: the proximal tubule, the Loop of Henle, and the distal tubule.
::如图3所示,肾管分为三个部分:近似管、Henle环形管和管状管。Parts of the renal tubule and other nephron structures.
::肾管和其他肾元体结构的部件。-
Filtrate first enters the proximal tubule. This is where the most reabsorption takes place. Tiny projections called microvilli line the proximal tubule and increase the surface area for reabsorption. From the proximal tubule, the filtrate passes through the loop of Henle.
::filtarate 首先进入正方块。 这是最常进行再吸附的地方 。 微小的预测称为微小的微小线条, 近似小块块, 并增加可再吸附的表面积 。 从近似小块块, 过滤器通过 Henle 循环 。 -
The loop of Henle carries the filtrate from the cortex down into the medulla and then back up to the cortex again. Its primary purpose is to reabsorb water and salt from the fluid filtrate. The remaining fluid enters the distal tubule.
::Henle的循环将皮层过滤器从皮层往下过滤到中丘,然后又回回到皮层,其主要目的是从液体过滤器中再吸收水和盐。剩下的液体进入阴极管。 -
The distal tubule carries the fluid, now called tubular fluid, from the loop of Henle to a collecting duct. As it transports the fluid, the distal tubule also reabsorbs or secretes substances such as
calcium
and sodium. The process of secreting substances into the tubular fluid is called secretion.
::解剖管管将流体(现称管状液)从Henle循环到收集管,在输送流体时,解剖管管还携带再吸附或分泌物质,如钙和钠,将物质分解到管管液中的过程称为分泌。
Urine Formation
::厕所培养The collecting ducts are the site of urine formation. This process is crucial for water in the body. The collecting ducts reabsorb water from tubular fluid and return it to the blood. The remaining fluid, called urine, has both a smaller volume and a greater concentration than tubular fluid. From the collecting ducts, urine enters a ureter and is eventually excreted from the body.
::收集管道是形成尿液的场所,这一过程对身体的水至关重要。从管状液中收集管状再吸收水,然后将水还给血液。其余的液称为尿液,其体积和浓度均小于管状液。从收集管道中,尿液进入尿液,最终从身体中排出。The reabsorption of water by the collecting ducts is controlled by a negative feedback mechanism. The mechanism involves a hormone secreted by the pituitary gland , called antidiuretic hormone (ADH). ADH makes the collecting ducts more permeable to water, allowing more water to be reabsorbed from tubular fluid. When there is not enough water in the blood, more ADH is secreted, more water is reabsorbed from tubular fluid, and less water is excreted in urine. The opposite happens when there is too much water in the blood.
::取水管道对水的再吸附由负反馈机制控制,这种机制涉及一种被称为抗二尿荷尔蒙(ADH)的低垂腺所隐蔽的荷尔蒙。ADH使取水的管道更容易渗透到水中,使更多的水能够从管状液中再吸附。当血液中没有足够的水时,ADH被秘密化了,更多的水通过管状液再吸附,而尿液中排出的水较少。相反,当血液中水量过大时,情况正好相反。Summary
::摘要-
The urinary system is composed of the kidney, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
::尿道系统由肾脏、尿素、膀胱和尿道组成。 -
The main function of the urinary system is to filter waste products and excess water from the blood and remove them from the body.
::尿道系统的主要功能是从血液中过滤废物和多余的水,并将其从身体中取出。 -
Located on top of each kidney is an adrenal gland. The adrenal hormone aldosterone helps regulate kidney functions.
::肾上腺素是肾上腺素,肾上腺素有助于调节肾功能。 -
The kidney has three layers: the outer renal cortex, the renal medulla, and the inner renal pelvis where the renal artery and vein enter and exit the kidney respectively.
::肾有三层:外肾皮层、内肾膜骨盆和内肾骨盆,肾动脉和血管分别进入和流出肾脏。 -
Bowman’s capsule is composed of layers. The space between the layers, called Bowman’s space, fills with the filtered substances (known as filtrate).
::鲍曼的胶囊由层组成。 层之间的空间被称为鲍曼的空间,充斥着过滤物质(称为过滤剂 ) 。 -
The process of filtering substances from blood in the glomerulus is called filtration.
::在球状体中从血液中过滤物质的过程称为过滤过程。 -
The renal tubule is divided into three parts: the proximal tubule, the Loop of Henle, and the distal tubule. Most reabsorption happens in the renal tubule.
::肾管可分为三部分:近轴管、Henle环和分管管。大多数再吸附都发生在肾管中。 -
The collecting ducts are the site of urine formation; they reabsorb water from tubular fluid and return it to the blood.
::收集的管道是尿液形成的地方;它们用管状液重新吸收水,并将水还给血液。
Review
::回顾-
Which organs compose the urinary system?
::尿道系统是由哪些器官构成的? -
When does your bladder send nerve pulses to initiate urination?
::你的膀胱什么时候会发出神经脉冲 来开始尿? -
What is the function of the adrenal gland?
::肾上腺的功能是什么? -
How is the reabsorption of water controlled?
::如何控制水的再吸收? -
Which part of the renal tubule is responsible for the most reabsorption?
::肾管的哪个部位 负责最大程度的再吸附? -
What is the role of the loop of Henle and the distal tubule (which are parts of the renal tubule)?
::Henle环状管和管状管(是肾管的一部分)的作用是什么?
-
The glomerulus is a cluster of
arteries
that filters substances out of the blood.