7.5 内分泌系统条例
章节大纲
-
On or off?
::开还是关?alter conditions inside the , usually in response to a stimulus . That means they are activated at specific times. So they must be turned on and then turned back off. What turns these hormones and their responses on or off?
::通常为了响应刺激措施, 内部条件会发生变化。 这意味着它们会在特定的时间被激活。 因此它们必须被打开, 然后被关掉。 是什么让这些荷尔蒙和反应开着或关上?Regulation: Feedback Mechanisms
::条例:反馈机制Hormones regulate many cell activities and are important to homeostatic regulation. The rate of hormone production and secretion is often controlled by homeostatic feedback control mechanisms, and the effect of hormones is also controlled by hormone antagonists. Hormone antagonists and hormone receptor antagonists are hormones or other molecules that block the action of hormones and are used by the body to control the action of hormones. They are molecules that mimic hormones and/or bind to hormone receptors, but have no effect. A feedback control mechanism, or a feedback loop, is a signaling system in which a product or effect of the system controls an earlier part of the system, either by shutting the process down or speeding it up. In these ways, the concentrations of hormones and their products are kept within a narrow range, so as to maintain .
::荷尔蒙对抗者和荷尔蒙受体对抗者是阻塞荷尔蒙作用并被身体用于控制荷尔蒙动作的荷尔蒙或其他分子。它们都是模仿荷尔蒙和(或)与荷尔蒙受体结合的分子,但没有任何效果。反馈控制机制或反馈循环是一个信号系统,系统的产品或效果控制系统早期的一部分,要么关闭过程,要么加速过程。在这些方面,荷尔蒙及其产品的浓度保持在狭窄的范围之内,以便维持。Negative Feedback
::负反馈Negative feedback is a reaction in which the system responds in such a way as to reverse the direction of change. Since this tends to keep things constant, it allows for a process to return from a state of imbalance back to a homeostatic equilibrium.
::消极反馈是一种反应,系统在反应中以扭转变化方向的方式作出反应。 由于这种反应往往使情况保持不变,它允许一种过程从不平衡状态返回到自制平衡状态。A common non-biological example of negative feedback happens in a home heating system. When you are home, you set your thermostat to 21˚C (about 70˚F), which is the set point. The thermometer in the thermostat monitors the room temperature and will sense when the temperature drops below the 21˚C set point (the stimulus). The thermometer will then send a message to the thermostat (control center), which in turn sends a message to the furnace to switch on and heat up the room. When the room temperature returns to the set temperature, the thermostat shuts the furnace off. In this home-heating example, the increase in air temperature is the negative feedback that results in the furnace being shut off. In this way, a set room temperature of 21˚C (within a degree or two) is maintained.
::在家庭供暖系统中出现一个常见的非生物的负面反馈实例。 当您在家时,您将自动调温器设为21 °C(约70 °F),这是设定点。自动调温器中的温度计监测室温度,当温度降到21 °C设定点(刺激)以下时将感知温度下降。然后,温度计将向自动调温器(控制中心)发送信息,而温度计又向炉子发送信息,以打开和加热房间。当房间温度恢复到设定温度时,自动调温器将炉关闭。在这个家庭供热的例子中,空气温度的上升是导致炉炉被关闭的负反馈。这样,设定室温度为21 °C(在一定或两个范围内),保持21 °C(在一定或两个范围内)的定位温度。An example of negative feedback in the body is the control of blood- glucose concentrations by insulin . A higher amount of glucose in the (the stimulus) signals the beta cells of the pancreas to release insulin into the blood. Hormone concentration alone cannot trigger a negative feedback mechanism; negative feedback is instead triggered by an overproduction of the effect of the hormone, such as the lowering of blood glucose concentrations (the effect), which causes a decrease in the secretion of insulin by the pancreas.
::体内消极反馈的一个例子是胰岛素对血糖浓度的控制。(刺激)中较多的葡萄糖意味着胰岛素的乙型细胞将胰岛素释放到血液中。光是荷尔蒙浓度不能引发负面反馈机制;相反,负面反馈是因过度生产激素效应引起的,如血液葡萄糖浓度降低(效果),导致胰岛素分泌减少。The thyroid gland is regulated by a negative feedback loop. The loop includes the hypothalamus and pituitary gland in addition to the thyroid.
::甲状腺受负面反馈环圈的调节,除了甲状腺外,甲状腺还包括下脑和脑下腺。Negative Feedback: Regulation of Thyroid Hormones
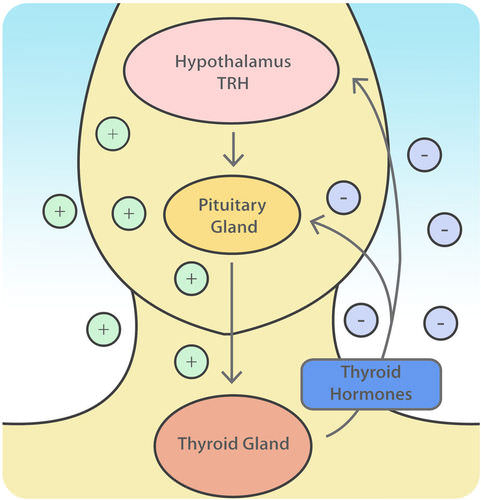
::消极反馈:对甲状腺激素的管制The thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) regulate the rate of metabolism . The production of T4 and T3 is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is released by the anterior pituitary. The thyroid and the TSH-producing cells of the anterior pituitary form a negative feedback loop, as shown in Figure .
::甲状腺激素甲状腺激素甲状腺激素(T4)和三碘二苯乙烯(T3)调节新陈代谢率,T4和T3的生产受甲状腺刺激激素(TSH)调节,该激素由前垂体释放。Thyroid-stimulating hormone production is decreased when the T4 levels are high, and, when TSH levels are high, T4 production is increased. The production and secretion of TSH is in turn controlled by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus . The rate of TRH secretion is increased in situations such as cold temperature because increasing the metabolic rate would generate more heat. Increased levels of T4 and T3 in the blood cause a reduction in TRH secretion. Among other things, TSH secretion is reduced by high levels of thyroid hormones as well as the antagonistic hormone somatostatin. These feedback loops keep the concentrations of thyroid hormones within a narrow range of concentrations.
::甲状腺刺激激素产量在T4水平高时下降,在TH水平高时,T4产量增加;TH的生产和分泌反过来又由甲状腺分泌激素(TRH)控制,甲状腺激素(TRH)是低丘体生成的;在寒冷温度等情况下,TRH分泌率增加,因为增加代谢率会产生更多的热量;血液中的T4和T3含量增加,导致TH分泌减少。除其他外,TH分泌因甲状腺激素和对立激素而减少。这些反馈循环将甲状腺激素的浓度控制在狭窄的浓度范围内。Two negative feedback loops exist in the control of thyroid hormone secretion. (1) Shows the loop between the TSH-producing cells of the anterior pituitary and the thyroid. Increased levels of T4 and T3 in the blood cause a reduction in TSH secretion. (2) Shows that increased levels of T4 and T3 in the blood cause a reduction in TRH secretion.
::在控制甲状腺激素分泌方面存在两个负面反馈循环。 (1) 显示前脑垂体和甲状腺的TSH生成细胞之间的循环,血液中的T4和T3浓度增加导致TSH分泌减少。 (2) 显示血液中的T4和T3浓度增加导致TR分泌减少。Positive Feedback
::积极反馈Positive feedback is a reaction in which the system responds in such a way as to speed up the direction of change. Positive feedback mechanisms are not as common as negative feedback mechanisms because they cause an increase in the initial signal, which would tend to knock many systems out of homeostatic balance . Take, for example, the analogy of the home heating system. If this system were to work on a positive feedback loop, the furnace would not switch off when the temperature reached the set point of 21˚C. Instead, it would keep going and heat the room indefinitely.
::积极的反馈机制不像消极反馈机制那样常见,因为它们导致初始信号增加,这往往会使许多系统失去自闭平衡。例如,将家庭供暖系统比作家庭供暖系统。如果这个系统要形成积极的反馈循环,当温度达到21°C设定点时,炉子就不会关闭。相反,它会无限期地继续运行和加热。An example of a positive feedback mechanism is milk production by a mother for her baby, as shown in Figure . As the baby suckles, nerve messages from the mammary glands cause the hormone prolactin to be secreted by the mother’s pituitary gland . The more the baby suckles, the more prolactin is released, which stimulates further milk production by the mother’s mammary glands. In this case, a negative feedback loop would be unhelpful because the more the baby nursed, the less milk would be produced. Another example of a positive feedback loop is the blood-clotting cascade that happens after a is cut.
::积极的反馈机制的一个例子是母亲为婴儿生产奶制品,如图所示。 哺乳腺的神经信息使荷尔蒙蛋白被母亲的垂体腺掩盖。 婴儿吸食量越多,蛋白素就越多,从而刺激母亲的哺乳腺进一步生产奶制品。 在这种情况下,负面反馈循环将无益,因为婴儿喂养的越多,牛奶的产量就越少。 积极的反馈循环的另一个例子是切除后出现的血层。Production of breast milk is controlled by a positive feedback mechanism.
::母乳的生产受到积极反馈机制的控制。Hormone Antagonists
::激素对敌者Many hormones work with hormone antagonists to control the concentrations of substances in the body. The hormones have opposite actions on the body and are called antagonistic.
::许多荷尔蒙与荷尔蒙对立者合作,控制体内物质的浓度,荷尔蒙对身体有相反作用,被称为对立。Insulin and glucagon make up an antagonistic hormone pair; the action of insulin is opposite that of glucagon. For example, your blood glucose concentration rises sharply after you eat food that contains simple , such as the chocolate chip muffin shown in Figure . The increase in blood glucose levels stimulates beta cells in the pancreas to release insulin into blood. In response to signals by insulin, most take up glucose, which removes it from the blood, and the blood glucose concentration returns to the set point. Later, you have missed eating lunch, and you are hungry and feel a little light-headed. Your blood glucose concentration has dropped below the set point, which causes the release of glucagon from the pancreas. Glucagon causes the release of glucose from liver cells, which increases your blood glucose concentration. If glucagon did not do its job correctly, your blood glucose concentration would continue to drop, and you would develop hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). This antagonistic relationship between the two hormones helps you maintain the narrow range of blood glucose concentration.
::胰岛素和甘蓝素的含量上升刺激了胰岛素中的乙型细胞释放出胰岛素。 根据胰岛素的信号,大部分使用从血液中去除的葡萄糖,而血糖浓度则返回到设定点。例如,在吃含有简单食物的食品(如图中显示的巧克力片松饼)之后,你的血糖浓度急剧上升。血液甘蓝浓度下降到设定点以下,导致胰岛素释放出胰岛素。根据胰岛素的信号,大部分使用葡萄糖,将它从血液中分离出来,而血糖浓度则返回到设定点。后来,你错过了午餐,你饿了,感到有点轻头。你的血糖浓度下降到设定点以下,这导致胰岛素的释放。Glucaon导致肝细胞释放出葡萄糖,这增加了你的血糖浓度。如果葡萄糖浓度不正确,你的血糖浓度会继续下降,你会继续发展低血糖浓度,你会发展出两种血糖浓度关系。Insulin and glucagon work as an antagonistic pair to keep your blood glucose concentration within a narrow range even after you eat food containing carbohydrates, such as a muffin.
::胰岛素和甘油是一对对抗性对,将血液中的葡萄糖浓度控制在狭窄范围内,即使你吃过含有碳水化合物(如松饼)的食物后也是如此。The actions of growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) are opposed by another hypothalamic hormone, somatostatin, also known as "growth hormone inhibiting hormone" (GHIH). Somatostatin and GHRH are secreted alternatively by the hypothalamus, which causes an increase and decrease in the secretion of growth hormone (GH) by the pituitary.
::生长激素释放激素(GHRH)的动作受到另一种低压荷尔蒙(Somatostatain)的反对,后者又被称为“生长激素抑制荷尔蒙(GHIH ) ” ( GHIH ) 。 Somatostatain 和 GHRH被低压抗体(GHH ) , 这导致生长激素(GH)的分泌增加和减少。Many also work together as a group to control body processes. The major endocrine glands coordinate the control of various regulatory systems such as metabolism, osmoregulation, and . Many individual glands are directly controlled by the , and all are in some way controlled by the pituitary and hypothalamus. Some of these glands and their hormone products are listed in Table .
::主要内分泌腺协调对新陈代谢、雌激素调节和...等各种监管系统的控制。许多单个的腺直接受控制,并且都以某种方式受垂体和下丘脑控制。这些腺及其荷尔蒙产品中有一些列于表 。Coordination of the Endocrine Glands in the Control of Body Systems Function Organ or Glands Hormones Nervous System Control Control of the Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland
::水下光学光学TSH, FSH, LH, GH, and prolactin (PRL)
::TH、FHH、LH、GH和丙烯(PRL)Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
::Adrenocortictropic 荷尔蒙(ACTH)ANS (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system) Regulation of Metabolism Thyroid Gland
::甲状腺Parathyroid Glands
::甲虫菊酯Pancreas
::胰腺Pineal Gland
::松果园Liver
::升动器T 3 and T 4
::T3和T4Parathyroid hormone
::抗甲菊酯激荷荷尔蒙Insulin
::胰岛素Glucagon
::Glucagon 浮形Melatonin
::梅拉图宁NameANS (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system) Response to Stress Adrenal Glands Epinepherine
::埃皮涅弗林Norepinepherine
::Norecepinepheine( 异丙丙丙烯酯)Cortisol
::ColorsolANS (sympathetic nervous system) Reproduction Gonads ( ovaries and testes) Androgens (testosterone)
::甲醇(内酯酮)Estrogens
::雌性激素Progestins (progesterone)
::预测值(原原体)ANS (parasympathetic nervous system) Osmoregulation Adrenal Glands
::肾上腺Liver
::升动器Aldosterone
::阿尔多酮ADH
::ABDH 人权协会Angiotensin
::Angiotensin 血管ANS (sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system) Summary
::摘要-
Hormones work in positive and negative feedback loops to maintain homeostasis within the body.
::荷尔蒙在积极和消极反馈循环中发挥作用,以保持体内的常态。 -
Hormone antagonists are pairs of hormones that oppose each other.
::荷尔蒙对立者是一对相互对立的荷尔蒙
Review
::回顾-
Explain the interaction between glucagon and insulin.
::解释葡萄干和胰岛素之间的相互作用。 -
Give an example of a set point in the human body.
::举个例子来说明人体中的定点。 -
Is breastfeeding a positive or negative feedback loop?
::母乳喂养是正面的还是负面的反馈循环?
-
Hormones work in positive and negative feedback loops to maintain homeostasis within the body.