6.5造山
章节大纲
-
How do plate motions create mountains?
::盘子运动如何创造山峰?Plate tectonic processes create some of the world's most beautiful places. The North Cascades Mountains in Washington State are a continental volcanic arc. The mountains currently host some . There are many features left by the more abundant Ice Age glaciers. Changes in altitude make the range a habitable place for many living organisms.
::板块构造过程创造了世界上一些最美丽的地方。 华盛顿州的北卡卡德斯山脉是一座大陆火山弧。 山区目前聚集着一些山体。 冰河时代冰川的丰富留下许多特征。 高度的变化使山脉成为许多生物体的可居住地点。Stress and Mountain Building
::压力与山区建设Many processes create mountains. A mountain is a rocky landform that rises significantly above the surrounding terrain (land). If an elevated landform is not very high or steep, it may be classified as a hill . Most mountains form along plate boundaries . A few mountains, such as hotspot , may form in the middle of a plate.
::许多过程创造山区。 山是一个岩石状的地形, 大大高于周围的地形( 陆地 ) 。 如果高地形态不高或陡峭, 则可以划为山丘。 大多数山沿板块边界形成。 几个山峰, 如热点, 可能形成板块中间 。Continent-Continent Convergence
::大陆 -- -- 大陆汇合Most of the world’s largest mountains form as plates collide at convergent plate boundaries. Continental crust is too buoyant to get pushed down into the mantle. So when the plates smash together, the crust crumples upward. This creates mountains. Folding and faulting in these collision zones makes the crust thicker.
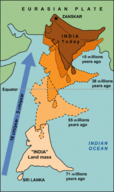
::全世界最大的山峰大多以板块在聚点板块边界相撞的形式形成。 大陆地壳过于活跃,无法被推入地壳。 因此,当板块相撞时,地壳会向上倾斜。 这创造了山峰。 在这些碰撞区发生折叠和断裂会让地壳变厚。The world’s highest mountain range, the Himalayas, is growing as India collides with Eurasia. About 80 million years ago, India was separated from Eurasia by an ocean ( Figure ). As the plates collided, pieces of the old were forced over the Asian continent . This old seafloor is now found high in the Himalayas ( Figure ).
::全世界最高的山脉 — — 喜马拉雅山 — — 正在随着印度与欧亚的碰撞而增长。 大约8000万年前,印度与欧亚被海洋(图 ) 隔开。 随着板块相撞,亚洲大陆上被迫出现一些老的碎片。 如今,在喜马拉雅山(图 ) , 这块旧的海底已经高居不下。As India rams into Eurasia, the Himalaya Mountains rise. The Himalayas. Oceanic Plate Subduction
::海洋板本潜水Volcanic mountain ranges form when oceanic crust subducts into the mantle at convergent plate boundaries. The Andes Mountains are a chain of coastal volcanic mountains. They are forming as the Nazca plate subducts beneath the South American plate ( Figure ).
::火山山脉形成时,海洋结壳渗入汇合板块边界的地壳。安第斯山脉是沿海火山山脉的链条,形成南美板块下方的纳斯卡板块下方(图 ) 。Cotopaxi is in the Andes Mountains of Ecuador. The 19,300 foot tall mountain is the highest active volcano in the world. Rifting
::断裂Mid-ocean ridges form at . As the ocean floor separates an enormous line of volcanoes is created.
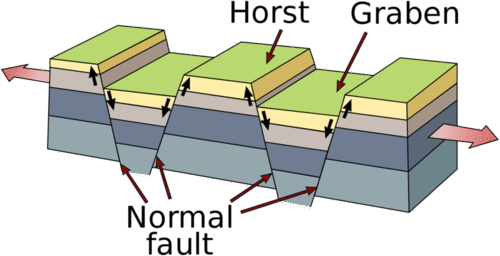
::洋底隔开一连串巨大的火山,Continents can also rift apart in a process called continental rifting . When continental crust is pulled apart, it breaks into blocks that are separated by normal ; this is known as block faulting . During block faulting, blocks slide up or down, resulting in alternating mountain ranges and areas of low land called valleys ; this topography is known as basin-and-range ( Figure ). The area near Death Valley, California, is the center of a classic basin-and-range province ( Figure ).
::大陆也可以在一个称为大陆裂裂的过程中分裂。 当大陆地壳被拉开时,它会破碎成由正常隔开的区块;这被称为块断裂。在块断裂时,块块向上或向下滑动,导致山脉和低地称为山谷的地区交替变化;这种地形被称为盆地和山脉(图 )。加利福尼亚死谷附近的地区是典型盆地和山脉省份的中心(图 )。This diagram shows how a basin-and-range forms. This photograph was taken from a basin with a range in the distance near Death Valley, California. Summary
::摘要- Converging or diverging plates cause mountains to grow.
::汇合或交错的板块导致山峰增长。
- Subduction of oceanic crust beneath a continental or oceanic plate creates a chain of volcanoes.
::在大陆或海洋板块下沉积海洋地壳,形成一连串火山。
- Tensional forces bring about block faulting. This creates a basin-and-range valleys and mountains.
::紧张力量导致断层断层,造成流域和山脉的山谷和山峰。
Review
::回顾- Describe how plates create mountain ranges like the Himalayas.
::描述板块如何创造喜马拉雅山那样的山脉。
- Diagram how pulling apart continental crust could create mountains and basins. What are the mountains and basins called?
::地图显示大陆地壳的分离如何能创造山区和盆地。 山区和盆地叫什么来着?
- Why don't strike slip faults create mountains?
::为何不揭开山坡的错误 来创造山峰呢?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resource below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- What created the landscape we see today on Earth?
::是什么创造了我们今天在地球上看到的地貌?
- What can cause mountains to form?
::是什么使山岳形成?
- What are the Rocky Mountains made of?
::洛基山是由什么构成的?
- How were the Rockies formed?
::落基山脉是如何形成的?
- Why did the Rockies form so far inland from the plate margin?
::为什么落基山脉离板边很远就形成内陆?
- Converging or diverging plates cause mountains to grow.