8.5 周边神经系统
章节大纲
-
How does the signal get to your toes?
::信号怎么到达你的脚趾?If the brain controls practically everything, how does the signal get to your toes? Or your legs? Or arms? By way of the peripheral nervous system: all the nerves shown here other than the brain and spinal cord . Notice that they go everywhere.
::如果大脑实际上控制了一切,信号怎么到达你的脚趾?或者你的腿?或者手臂?通过外围神经系统:除了大脑和脊髓之外,所有神经都显示在这里。注意它们无处不在。The Peripheral Nervous System
::周边神经系统The peripheral nervous system (PNS) consists of the nervous tissue that lies outside the , as shown in Figure . The nervous tissue of the peripheral nervous system serves the limbs and organs . The central nervous system interacts with the peripheral nervous system through twelve pairs of cranial nerves that connect the brain to areas of the head and neck and 31 pairs of spinal nerves that connect the spinal cord (and CNS) to the rest of the body such as the internal organs, arms, and legs. A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of axons . Unlike the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system is not protected by , making it more vulnerable to toxins and injuries.
::如图所示,外围神经系统(PNS)由外部的神经组织组成。边缘神经系统的神经组织为四肢和器官服务。中枢神经系统通过十二对骨骼神经与外围神经系统互动,将大脑连接到头部和颈部,31对脊椎神经连接到身体的其余部分,如内脏器官、胳膊和腿。神经是一个封闭的、像电缆一样的斧子捆包。与中枢神经系统不同,外围神经系统没有受到保护,因此更容易受到毒素和伤害。Spinal nerves originate from the spinal cord. They control functions of the rest of the body. Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ventral root, which are shown in Figure . The dorsal root is the “nerve highway” that carries sensory information from sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. The ventral root contains axons of motor neurons that carry information away from the CNS to the and glands of the body.
::脊椎神经源于脊髓,它们控制着身体其余部分的功能。每个脊椎神经都有一个背根和呼吸根,图中显示了这一点。负根是“神经高速公路”,从身体的感应器携带感官信息到 CNS。呼吸根包含运动神经元的轴,将信息从 CNS 传送到身体和腺部。These two nerve “highways” are actually parts of two subdivisions of the PNS. The sensory division , also known as the afferent division, carries sensory information from sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. The sensory division keeps the CNS constantly updated on events happening inside and outside the body. The motor division , or efferent division, carries from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and organs of the body. The nerve impulses of the motor division cause muscles to contract and cause glands to secrete chemical signals.
::这两个神经“高速公路”实际上是PNS两个分区的一部分。感官分区(又称“远距分区 ” ) 从身体的感应受体向 CNS 传送感官信息。感官分区不断向CNS 通报身体内外发生的事件。发动机分区,或“远距分区”从 CNS 传送到身体的肌肉、腺和器官。运动分区的神经脉冲导致肌肉收缩,并导致腺隐匿化学信号。(Left) The peripheral nervous system (PNS). The peripheral nervous system extends from the CNS and reaches out to all parts of the body, from the cranial nerves found in the head to the plantar nerves in the tips of the toes. (Right) A cross section of the spinal cord. The central, butterfly-shaped area (1, 2, 3) is the gray matter, and the outer cortex is the white matter. Instructions going to the body’s muscles and other areas go through the motor neurons that leave the spinal cord in the ventral roots (11). Sensory information from the body enters the spinal cord through sensory neurons in the dorsal roots (12). Dorsal and ventral roots occur on both sides of the spinal cord; only one side is shown in this diagram.
::边缘神经系统从 CNS 延伸至身体的所有部位,从头部发现的骨髓神经到脚尖尖部位的板骨神经。 (右) 脊髓的交叉部分。中央、蝴蝶形区域(1, 2, 3) 是灰质,外皮层是白色物质。对身体肌肉和其他部分的指示通过运动神经,将脊髓留在腹部根(11)。身体的感官信息通过脊髓根的感官神经进入脊髓(12)。圆脊髓两侧都有角和脑根;本图只显示一面。Somatic and Autonomic Nervous Systems
::体力和自主神经神经系统The motor division of the peripheral nervous system is divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system .
::外围神经系统的运动部分分为体能神经系统和自主神经系统。The somatic nervous system is the part of the PNS that is associated with the conscious (voluntary) control of the body through the movement of and the perception of external stimuli through such as touch, hearing , and sight . The system includes all the that are connected with muscles, skin, and sensory organs. The somatic nervous system is made up of both sensory nerves that receive sensory information from the external environment and motor nerves that are responsible for muscle contractions.
::身体神经系统是PNS的一部分,它通过触摸、听力和视觉等手段,与身体的自觉(自愿)控制相关联,通过感知和感知外刺激,该系统包括与肌肉、皮肤和感官器官相关的所有系统。 身体神经系统由接受外部环境感官信息的感官神经和导致肌肉收缩的运动神经组成。Together with interneurons , sensory and motor neurons are found in reflex arcs. A reflex is an automatic (involuntary) action that is caused by a defined stimulus and is carried out through a reflex arc . For example, a person stepping on a sharp object would start a reflex action through the creation of a stimulus (pain) within specialized pain receptors located in the skin tissue of the foot. The resulting stimulus would be passed along sensory neurons to the spinal cord. This stimulus is usually processed by an interneuron, which creates an immediate response to the stimulus by initiating a motor response in the muscles of the leg that pull the foot away from the object. This reflexive action occurs as the pain sensation is arriving in the brain; thus, the brain is not needed for a reflex arc to occur. A reflex arc is shown in Figure .
::与中中子、感官和运动神经元一起在反射弧中发现。 反射是一种自动( 非自愿) 动作, 由特定刺激因素引起, 并且通过反射弧进行。 例如, 一个人踩着尖锐的物体, 通过在位于脚的皮肤组织内的特殊疼痛受体内创建刺激( 帕) , 开始反射动作。 由此产生的刺激作用将随感应神经元传递到脊髓。 这种刺激通常由中枢处理, 通过在将脚拉离物体的腿部肌肉中启动运动反应, 从而产生对刺激的即时反应。 这种反射动作随着疼痛感在脑中降临而发生; 因此, 大脑不需要来进行反射弧。 图中显示反射弧 。The components of a reflex. A sensory receptor detects a stimulus and sends nerve signals to the spinal cord. These signals activate motor neurons that lead back to the effector (muscle).
::反射的成分。感官受体检测到刺激,并向脊髓发出神经信号。这些信号会激活运动神经元,并引向影响器(肌肉)。The autonomic nervous system ( ANS ) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that maintains in the body. Your body carries out most of these maintenance activities without your conscious control, which is why the autonomic nervous system is also called the involuntary . The ANS has far reaching effects such as the control of heart rate, digestion , respiration rate, salivation, and perspiration. Some autonomic nervous system functions, such as , work in line with the conscious mind.
::自主神经系统(ANS)是身体内维持的外围神经系统的一部分。你的身体在没有意识控制的情况下进行大部分这些维护活动,这就是为什么自主神经系统也被称为非自愿神经系统的原因。ANS具有深远的影响,例如控制心率、消化、呼吸率、流出和呼吸。有些自自主神经系统功能,例如,与意识意识相一致。The ANS is also made up of the sensory and motor neurons that send messages to and from the internal organs. These neurons form reflex arcs that pass through the medulla oblongata. This explains why a person's cerebrum may experience trauma, yet their cardiovascular, digestive, and respiratory functions will continue to function, even if higher level functions, such as awareness and consciousness, are lost. Such a low level of brain functioning is referred to as a vegetative state.
::ANS也由向内脏发送信息的信息的感官和运动神经元组成。这些神经元形成反射弧,穿过脑脑膜,这解释了为什么一个人的脑部可能遭受创伤,然而他们的心血管、消化和呼吸功能会继续起作用,即使更高级的功能,如意识和意识已经丧失。这种低水平的大脑功能被称为植物状态。The ANS has two subdivisions: the sympathetic division and parasympathetic division . The sympathetic division generally stimulates body systems during emergency situations. It gets the body ready for "fight or flight ," which would probably be required in the situation shown in Figure . The parasympathetic division controls non-emergency functions such as digestion. The relationships between the divisions of the nervous system are illustrated in Figure .
::ANS有两个分支:同情分裂和寄生虫分裂。同情分裂通常在紧急情况下刺激身体系统。它使身体准备好“战斗或飞行 ” , 这可能是图所示情况所需要的。寄生虫分裂控制非紧急功能,如消化。神经系统分裂之间的关系在图中说明。Watch out! A situation in which your sympathetic nervous system (and hopefully your somatic nervous system) would be firing at full speed.
::当心! 在这样的情况下,你同情的神经系统( 和希望你的体外神经系统) 将会全速发射。Levels of Organization of the Nervous System
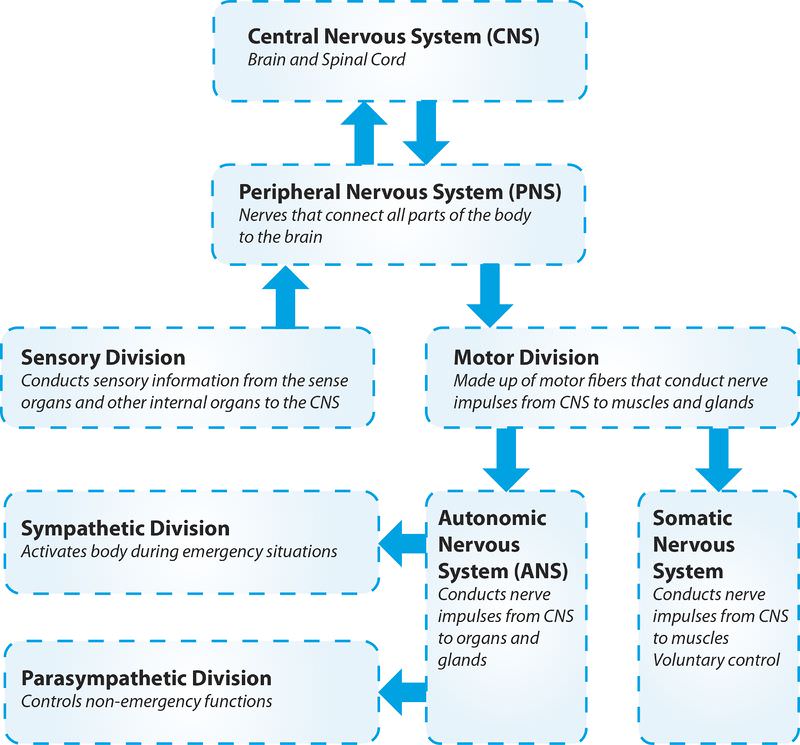
::神经系统组织级别The Levels of Organization in the Nervous System.
::神经系统中的组织级别。Summary
::摘要-
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves that are not within the brain or spinal cord.
::外围神经系统由大脑或脊髓内没有的神经组成。 -
The PNS can be separated into the sensory, or afferent, and motor, or efferent, divisions.
::PNS可分离成感官或感官或感官、运动或感官分裂。 -
The motor division can be separated into the somatic nervous system, which controls conscious movement, and the autonomic nervous system.
::发动机分裂可分离成控制自觉运动的体能神经系统以及自主神经系统。 -
The autonomic nervous system can be separated into the sympathetic (emergency) and parasympathetic (non-emergency) nervous system.
::自主神经系统可分为同情(紧急)和寄生虫(非紧急)神经系统。
Review
::回顾-
Explain the different divisions of the peripheral nervous system.
::解释一下外围神经系统的不同部门。 -
What is a reflex?
::什么是反射? -
What is "fight or flight?"
::什么是"战斗还是飞行?"
-
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves that are not within the brain or spinal cord.