9.3 骨骨形成
章节大纲
-
How do grow?
::如何成长?Bones are hard structures. So how do they grow? Well, bones are living tissue . They have a supply and grow from the cartilage at their ends. You are consistently making new bone. In fact, the human skeleton is replaced every 7-10 years.
::骨骼是坚硬的结构。 那么它们是如何生长的呢? 骨头是活组织。 它们有供养 并且从骨骼的末端生长。 你一直在制造新的骨骼。 事实上,每7到10年,人体骨骼就会被替换一次。Development of Bones
::Bones公司的发展Ossification , or osteogenesis, is the process of bone formation. This process begins early in fetal , usually by the end of the eighth week after conception. By this point, the skeletal pattern is formed by cartilage and connective tissue membranes, and ossification begins.
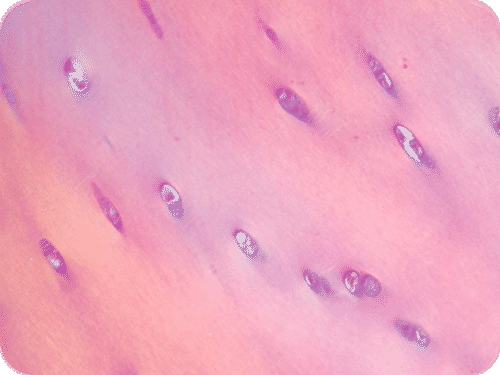
::骨质化或骨骼形成是骨骼形成的过程。这一过程在胎儿早期开始,通常在受孕后第八周结束时开始。此时,骨骼模式由软骨和骨骼组织膜组成,骨质化开始。Early in fetal development, the skeleton is made of cartilage. Cartilage is a type of dense connective tissue that is composed of collagen and/or elastin fibers and called chondrocytes, which are all set in a gel-like substance called the extracellular matrix. Cartilage does not contain any , so nutrients diffuse through the matrix to the chondrocytes. Cartilage serves several functions such as providing a framework upon which bone deposition can begin and supplying smooth surfaces for the movement of bones at a joint. Cartilage is shown in Figure .
::胚胎早期发育时,骨骼由软骨组成。软骨是一种由科林和/或弹性纤维组成、称为体细胞的密闭性结扎组织,它们都以凝胶类物质(称为外细胞基体)组成。软骨不包含任何物质,因此营养物质通过母体扩散到锥体细胞中。软骨可以发挥若干功能,例如提供一个骨沉积的起始框架,并为结关骨的移动提供光滑的表面。图中显示了软骨。A micrograph of the structure of hyaline cartilage, the type of cartilage that is found in the fetal skeleton and at the ends of mature bones.
::在胎儿骨骼和成熟骨骼末端发现的软骨类型。The bones of the body gradually form and harden throughout the remaining gestation period and for years after birth in a process called endochondrial ossification. However, not all parts of the fetal cartilage are replaced by bone; cartilage remains in many places of the body including the , the rib cage, the ears, the tip of the nose, the bronchial tubes, and the discs between vertebrae .
::身体骨骼在其余的妊娠期和出生后的几年里逐渐形成和硬化,其过程称为内分泌硬化,但胎儿的骨骼并非全部被骨头取代;在身体的许多地方,包括骨骼、肋骨笼、耳朵、鼻尖、支气管和脊椎之间的盘片,仍有软骨残存。Endochondral Ossification
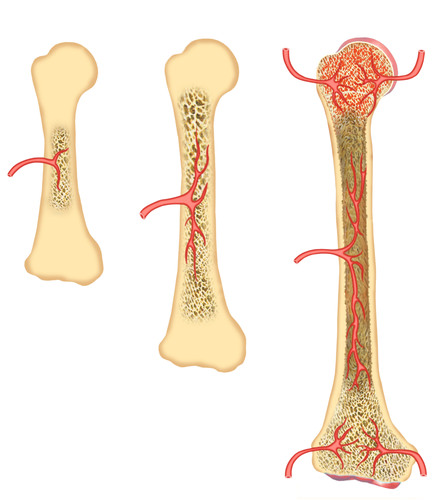
::内分泌化Endochondral ossification is the process of replacing cartilage with bony tissue, as shown in Figure . Most of the bones of the skeleton are formed in this way. During the third month after conception, blood vessels form and grow into the cartilage, transporting osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and cells into the interior. These begin to change the cartilage into bone tissue. The osteoblasts form a bone collar of compact bone around the diaphysis, or central shaft, of the bone. Osteoclasts remove material from the center of the bone and form the central cavity of long bones. Ossification continues from the center of the bone toward the ends of the bones.
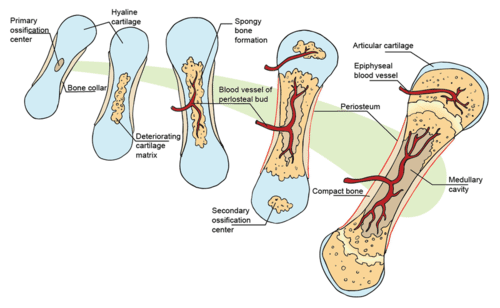
::如图所示,内分层骨化是一种用骨骼组织替换软骨的过程。骨骼的多数骨骼都是以这种方式形成的。在受孕后第三个月,血管形成并生长到软骨中,将骨质激素、骨质激素和细胞运入内部。这些都开始将软骨转化为骨骼组织。骨质激素形成骨骼骨骼紧凑的骨圈,骨骼周围或骨骼中央轴。骨质激素从骨骼中心取出材料,形成长骨骨的中央腔。骨骼中央的骨质化继续从骨骼中心一直持续到骨骼的尾部。The cartilage at the ends of long bones are called the epiphyses. These continue to grow, so the developing bone increases in length. Later, usually after birth, secondary ossification centers form in the epiphyses, as shown in Figure . Ossification in the epiphyses is similar to that in the center of the bone except that the spongy bone is kept instead of being broken down to form a cavity. When secondary ossification is complete, the cartilage is totally replaced by bone except in two areas. A region of cartilage remains over the surface of the epiphysis as articular cartilage, and another area of cartilage remains inside the bone at either end. This area is called the epiphyseal plate or growth region.
::长骨头端端的骨骼被称作骨骼。 这些继续生长, 发育中的骨骼会增加长度。 后来, 通常在出生后, 二级骨骼化中心会形成在骨骼部位中, 如图所示 。 外科的骨骼与骨骨中央的骨质化相似, 但海绵骨不会被折成一个洞穴。 当二次骨骼化完成后, 骨骼会完全被骨头取代, 除了两个区域。 外, 外科外, 外科外科的骨骼表面还有部分骨骼, 外科骨骼的骨骼部位, 以及骨骨骼两端的另一部分的骨骼。 这个区域被称为骨骼板或生长区域。Long bones ossify and get longer as they grow and develop. The process of endochondrial ossification happens when the skeleton is developing during fetal development and in childhood.
::当骨骼在胎儿发育和童年发育期间发育时,内分泌的骨质化过程就会发生。When a bone develops from a fibrous membrane, the process is called intramembranous ossification. Intramembranous ossification usually happens in flat bones such as the cranial bones and the clavicles. During intramembranous ossification in the developing fetus , the future bones are first formed as connective tissue membranes. Osteoblasts migrate to the membranes and secrete osteoid, which becomes mineralized and forms bone matrix . When the osteoblasts are surrounded by matrix, they are called osteocytes. Eventually, a bone collar of compact bone develops, and marrow develops inside the bone.
::当骨骼从纤维质膜中发育出来时,这一过程被称为内膜骨质化。内膜骨质化通常发生在骨骼骨骼和锁骨等扁骨中。在发育中的胎儿体内骨质化过程中,未来的骨骼最初形成为连接组织膜。骨质迁移到膜和秘密骨质组织,这些骨质组织成为矿物并形成骨质矩阵。当骨质组织被矩阵包围时,它们通常被称为骨质组织。最终,骨质组织骨骼的骨圈形成,骨髓在骨骼内部发育。Bone Elongation
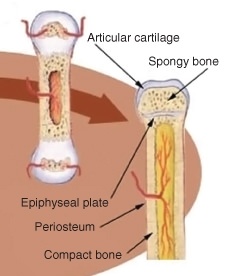
::骨延长An infant is born with zones of cartilage called epiphyseal plates, as shown in Figure , between segments of bone to allow further growth of the bone. When the child reaches skeletal maturity (between the ages of 18 and 25 years), all of the cartilage in the plate is replaced by bone, which stops further growth.
::如图所示,婴儿出生时的骨骼部位在骨骼各部分之间,其骨骼部位被称作肾上腺素板,以便进一步生长。当婴儿骨骼发育成熟(18至25岁)时,板块内的所有软骨都被骨骼取代,停止了进一步生长。The location of the epiphyseal plate in an immature long bone. The chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate are very metabolically active, as they constantly reproduce by mitosis. As the older chondrocytes move away from the plate, they are replaced by osteoblasts that mineralize this new area, and the bone lengthens.
::肾上腺素板在不成熟的长骨头中的位置。 肾上腺素板中的子肾上腺素细胞非常具有代谢性,因为它们经常通过肾上腺素繁殖。 随着旧的子宫素细胞从盘中移走,它们被使这个新区域矿物化的卵巢体和骨头长度所取代。Bones grow in length at the epiphyseal plate by a process that is similar to endochondral ossification. The chondrocytes in the region of the epiphyseal plate grow by and push older chondrocytes down toward the diaphysis. Eventually, these chondrocytes age and die. Osteoblasts move into this region and replace the chondrocytes with bone matrix. This process lengthens the bone and continues throughout childhood and the adolescent years until the cartilage growth slows down and finally stops. When cartilage growth stops (usually in the early twenties), the epiphyseal plate completely ossifies so that only a thin epiphyseal line remains, and the bones can no longer grow in length. Bone growth is under the influence of growth from the anterior pituitary gland and sex hormones from the ovaries and testes .
::骨骼在肾上腺素板上长长, 其过程与内分泌腺骨质化相似。 肾上腺素板所在区域的腺质细胞会生长, 并将老的腺质细胞推向生殖器官。 最终, 这些腺质细胞会衰老和死亡。 骨质细胞会迁移到这个区域, 用骨质矩阵来取代腺质细胞。 这个过程会延长骨头, 持续到整个童年和青少年年, 直到软体生长减缓并最终停止。 当软体生长停止( 通常在20世纪初) , 癫痫细胞细胞会完全萎缩, 以至于只有薄的皮质细胞会留下, 骨头不会长到更长的长。 骨质生长受到来自腹部的脑腺生长以及卵巢和睾丸的性激素的影响 。Even though bones stop growing in length in early adulthood , they can continue to increase in thickness or diameter throughout life in response to stress from increased muscle activity or weight-bearing .
::尽管骨头在成年初期停止长长,但是在肌肉活动或体重增加造成压力的情况下,骨头在整个生命中仍可继续增加厚度或直径。Summary
::摘要-
Bones grow through a process called ossification.
::骨骼通过一个叫骨化的过程生长 -
Long bones consist of a central shaft (the diaphysis) and cartilaginous ends called epiphyses.
::长骨由中央轴(直径)和卷轴端组成,叫做附着。 -
It is at the epiphyses and the epiphyseal plates that chondrocytes undergo mitosis to lengthen the bones.
::正是在肾上腺素和肾上腺素板上,子激素细胞会发生分裂,以延长骨头。
Review
::回顾-
What is ossification?
::什么是骨质化? -
What purpose does matrix serve?
::矩阵服务的目的是什么? -
How do bones grow in length?
::骨头怎么长长?
-
Bones grow through a process called ossification.