6.8变换板块边界地震
章节大纲
-
What does the future of San Francisco hold?
::旧金山的未来能维持什么?One of the largest and most damaging on the San Andreas struck the city of San Francisco in 1906. This magnitude 7.9 quake devastated the city. Based on the long-term movement of the San Andreas fault, scientists estimate an earthquake of this size occurs roughly every 200 years, and there is only a 2 percent chance of it happening within the next 30 years. However, there is a much higher probability of smaller but still damaging earthquakes. What do you think the future holds for San Francisco?
::1906年,圣安德烈亚斯市最大、破坏力最大的地震之一袭击了旧金山市。这一规模的7.9地震摧毁了这座城市。根据圣安德烈亚斯断层的长期变化,科学家估计大约每200年发生一次如此规模的地震,在未来30年中只有2%的可能性发生。然而,地震规模小得多,但破坏力仍然很大。你认为旧金山的未来会如何?Transform Plate Boundaries
::变换板板边框Transform plate boundaries produce enormous and deadly earthquakes. These quakes at transform faults have a shallow focus . This is because the plates slide past each other without moving up or down.
::变形板块边界产生巨大致命的地震。 这些变形断层地震的焦点浅。 这是因为变形板块在不向上或向下滑过对方。The San Andreas Fault that runs through much of California is an enormous transform plate boundary . It is the plate boundary between Pacific and North American plates. The deadliest earthquake on the San Andreas Fault occurred in 1906. The quake's epicenter was just north of in San Francisco. About 3,000 people died and 28,000 buildings were lost, mostly in the fire that followed the earthquake.
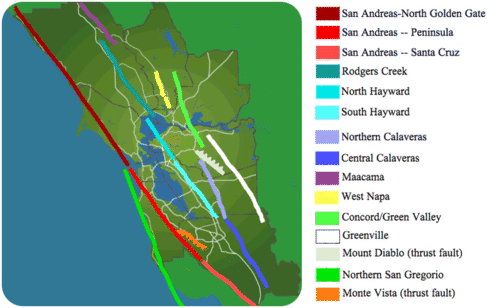
::圣安德烈亚斯断层横跨加利福尼亚州大部分地区,是一个巨大的变形板块边界,是太平洋和北美板块之间的板块边界。1906年,圣安德烈亚斯断层发生最致命的地震。地震中心位于旧金山以北,大约3 000人死亡,28 000栋建筑物失事,大都发生在地震后的火灾中。There are many other faults spreading off the San Andreas, to take up the plate motion. In total the San Andreas Fault system produces around 10,000 earthquakes a year ( Figure ). While most of those earthquakes cannot even be felt by people nearby, occasionally one is very strong. For example, the Hayward Fault, east of San Francisco, was the site of a magnitude 6.8 earthquake in 1868.
::San Andreas号上还有其他许多断层。 San Andreas号上的断层也随着板块运动而扩大。 San Andreas断层系统每年总共造成约10,000次地震(图 ) 。 虽然这些地震大多无法为附近的人所感受到,但偶尔也会发生一次非常强烈的地震。 比如,旧金山以东的Hayward号断层是1868年6.8级地震的发生地。The San Andreas Fault runs through the San Francisco Bay Area. Other related faults cross the region. Lines indicate strike slip faults. Lines with hatches are thrust faults. Other significant earthquakes in California include the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake near Santa Cruz ( Figure ) and the 1994 Northridge earthquake near Los Angeles.
::加利福尼亚州其他重大地震包括1989年圣克鲁斯附近的Loma Prieta地震(图)和1994年洛杉矶附近的Northridge地震。Three people died in this mall in Santa Cruz during the 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake. Although California is prone to many natural hazards, including volcanic eruptions at Mt. Shasta or Mt. Lassen, and landslides on coastal cliffs, the natural hazard the state is linked with is earthquakes. In this video, the boundaries between three different tectonic plates and the earthquakes that result from their interactions are explored.
::尽管加利福尼亚州容易遭受许多自然危害,包括沙斯塔山或拉森山的火山爆发和沿海悬崖的滑坡,但该州与地震相关的自然危害是地震。 在这次视频中,探索了三个不同的构造板块之间的界限以及它们相互作用所产生的地震。New Zealand also has a transform fault with strike- slip motion, causing about 20,000 earthquakes a year! Only a small percentage of those are large enough to be felt. A 6.3 quake in Christchurch in February 2011 killed about 180 people.
::新西兰也有因罢工滑动而变形的断层,每年造成约20,000次地震,其中只有一小部分足够大,可以感觉到。 2011年2月,克赖斯特彻奇发生6.3次地震,导致180人死亡。Summary
::摘要- Transform fault earthquakes have shallow focus because the plates meet near the surface.
::变形断层地震的焦点很浅 因为板块靠近表面
- The San Andreas Fault is actually a fault zone made up of a number of other active faults.
::圣安德烈亚斯断层实际上是一个断层区, 由其他许多主动断层组成。
- New Zealand also has a transform plate boundary.
::新西兰还有一个变形板块边界。
Review
::回顾- Why are earthquakes at transform plate boundaries always shallow focus?
::为什么变形板块边界的地震 总是浅浅的焦点?
- Why are there so many small faults in the San Francisco Bay Area?
::为什么旧金山湾有这么多小故障?
- Why do such large earthquakes take place along the San Andreas Fault?
::为什么在圣安德烈亚斯断层上 发生这么大的地震?
Explore More
::探索更多Use the resources below to answer the questions that follow.
::利用以下资源回答以下问题。- How far does the San Andreas Fault extend?
::圣安德烈亚斯断层延伸到多远?
- If you have one foot on each side of the fault, which plate is each foot on? What regions share each plate?
::如果你的过失两边各有一英尺, 每一英尺的板块是哪个?哪个区域共享每一块板块?
- What type of fault is it?
::这算哪门子的过错?
- What causes an earthquake?
::地震的起因是什么?
- What is a creepmeter? How much movement does the creepmeter in the video sense?
::摄像意义里 脚步计的移动量是多少?
- How many earthquakes occur at the San Andreas fault each year?
::圣安德烈亚斯断层每年发生多少次地震?
- Transform fault earthquakes have shallow focus because the plates meet near the surface.