10.2 肌肉系统结构
章节大纲
-
How do your move?
::你的动作如何?By the contractions and extensions of your skeletal muscles. Notice how the are attached to the bones. The muscles pull on the bones, causing movement .
::你骨骼肌肉的收缩和延伸 注意骨头的附着情况 肌肉拉扯骨骼 导致运动Structure of Muscle Tissue
::肌肉组织结构A whole skeletal muscle is an organ of the muscular system . Each skeletal muscle consists of skeletal muscle tissue , connective tissue , nerve tissue, and . Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. They range from extremely tiny strands, such as the tiny muscles of the middle ear, to large masses such as the quadricep muscles of the thigh.
::整个骨骼肌肉是肌肉系统的一个器官,每个骨骼肌肉由骨骼肌肉组织、连接组织、神经组织以及.骨骼肌肉组成,在纤维大小、形状和排列方面差异很大,从极小的细小的股,如中耳的小肌肉,到大腿的四肢肌肉等大块。Each skeletal muscle fiber is a single large, cylindrical muscle . Skeletal muscle fibers differ from “regular” . They are multinucleated, which means they have many in a single cell. During , many cells, called myoblasts, fuse together to form muscle fibers . Each nucleus in a fiber originated from a single myoblast. Smooth and cardiac muscle fibers do not develop in this way.
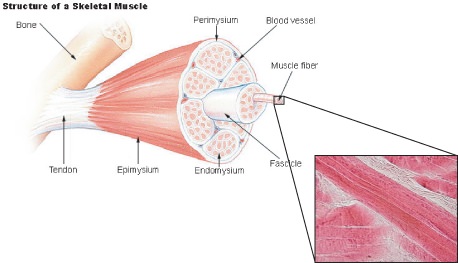
::每个骨骼肌肉纤维都是一个单独的大圆柱形肌肉。骨骼肌肉纤维不同于“常规 ” 。 骨骼肌肉纤维不同于“ 常规 ” 。 它们是多核型的, 也就是说, 在一个单细胞里有很多。 在很多细胞中, 被称为“ 粒子 ” , 结合组成肌肉纤维。 纤维中的每个核都来自一个单粒子。 光滑和心脏肌肉纤维不会以这种方式发展。An individual skeletal muscle may be made up of hundreds, or even thousands, of muscle fibers that are bundled together and wrapped in a connective tissue covering called epimysium. Portions of the epimysium fold inward to divide the muscle into compartments called fascicles. Each fascicle compartment contains a bundle of muscle fibers, as shown in Figure . Fascia, connective tissue outside the epimysium, surrounds and separates the skeletal muscles.
::单骨骼肌肉可能由数百甚至数千根肌肉纤维组成,这些肌肉纤维被捆绑在一起,包裹在一个连接组织中,覆盖的称为上皮子,上皮子的部位向内折叠,将肌肉分割成称为分册的隔间,每个分册包都含有一捆肌肉纤维,如图所示。Fascia、上皮层外的连接组织、环绕和分离骨骼肌肉。Individual bundles of muscle fibers are called fascicles. The cell membrane surrounding each muscle fiber is called the sarcolemma, and beneath the sarcolemma lies the sarcoplasm, which contains the cellular proteins, organelles, and myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of two major types of protein filaments: the thinner actin filament and the thicker myosin filament. The arrangement of these two protein filaments gives skeletal muscle its striated appearance.
::肌肉纤维的个体捆包被称为分册。每根肌肉纤维周围的细胞膜被称为沙科隆玛,沙科隆底部是沙科布拉姆,它包含细胞蛋白、器官和肌膜。我的肌膜由两种主要的蛋白丝组成:薄质丝和厚度的肌质丝。这两种蛋白丝的排列使骨骼肌肉的外形变形。Skeletal muscle fibers, like body cells, are soft and fragile. The connective tissue covering gives support and protection for the delicate cells and allows them to withstand the force of contraction. The coverings also provide pathways for the passage of and nerves. Active skeletal muscle needs efficient delivery of nutrients and oxygen and removal of waste products, both of which are carried out by a rich supply of blood vessels.
::骨骼肌肉纤维,如身体细胞一样,软和脆弱,覆盖的连接组织为脆弱的细胞提供支撑和保护,并允许它们承受收缩的力;遮盖也为神经的通过和神经提供了途径;活跃的骨骼肌肉需要高效地提供养分和氧气,以及清除废物产品,而两者都是由丰富的血管供应进行的。Muscles and Bones
::肌肉和骨头Muscles move the body by contracting against the skeleton. Muscles can only actively contract; they extend (or relax) passively. The ability of muscles to move parts of the body in opposite directions requires that they be attached to bones in pairs that work against each other (called antagonistic pairs). Generally, muscles are attached to one end of a bone, span a joint, and are attached to a point on the other bone of the joint. Commonly, the connective tissue that covers the muscle extends beyond the muscle to form a thick rope-like structure called a tendon , as shown in Figure . One attachment of the muscle, the origin, is on a bone that does not move when the muscle contracts. The other attachment point, the insertion, is on the bone that moves. Tendons and muscles work together and exert only a pulling force on .
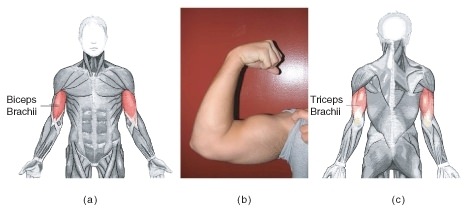
::肌肉通过绑定骨骼来移动身体。 肌肉只能积极结合; 它们可以被动地延伸( 或放松) 。 肌肉将身体的部位向相反方向移动的能力要求它们附在骨骼上, 两对之间相互对立( 称为对对对对) 。 一般而言, 肌肉连接在骨头的一端, 横跨一个关节, 并且连接在骨骼的另一端。 通常, 肌肉的连接组织超越肌肉, 形成一个厚厚厚的绳形结构, 称为“ 弯道 ” , 如图所示 。 肌肉的一个连接点, 其起源在一块骨上, 在肌肉合同时不会移动。 另一个连接点, 插入点, 是在运动的骨头上。 Tendon 和肌肉一起工作, 并且只施加拉动力 。Movement of the elbow joint involves muscles and bones. The contraction of the biceps brachii muscle pulls on the radius, its point of insertion, which causes the arm to bend. To straighten the arm, the triceps brachii muscle contracts and pulls on the ulna. This causes the arm to straighten.
::手肘关节的动作涉及肌肉和骨头。 胸骨肌肉的收缩会拉动半径,即插入点,导致手臂弯曲。 要伸直手臂,胸骨肌肉的三头肌会结合并拉动螺旋。 这会使手臂直直。For example, when you contract your biceps brachii muscle, shown in Figure , the force from the muscle pulls on the radius bone (its point of insertion), causing the arm to move up. This action decreases the angle at the elbow joint (flexion). Flexion of the elbow joint is shown in Figure . A muscle that causes the angle of a joint to become smaller is called a flexor. To extend or straighten the arm, the biceps brachii relaxes, and the triceps on the opposite side of the elbow joint contracts. This action is called extension , and a muscle that causes a joint to straighten out is called an extensor. In this way, the joints of your body act like levers that reduce the amount of effort you have to expend to cause large movements of the body.
::例如,当您用图中显示的双螺旋杆骨质时,肌肉的强度会拉动半径骨(插入点),导致手臂向上移动。这个动作会降低肘合点(伸缩)角。手肘合点的弹性在图中显示。造成联合点角变小的肌肉被称为柔软器。为了伸展或拉伸手臂,Biceps brachii放松,以及肘合点合同对面的三螺旋。这个动作被称为延伸,而导致合点直线的肌肉则被称为伸缩器。这样,你身体的结点就会像拉杆一样,减少你为引起身体大规模移动而必须付出的精力。(a) The position of the biceps brachii. (b) The biceps brachii and triceps brachii act as an antagonistic pair of muscles that move the arm at the elbow joint. The biceps muscle is the flexor, and the triceps, at the back of the arm, is the extensor (c).
:b) biceps brachii 和 tricceps brachii 和 tricceps brachii 充当一对敌对的肌肉,将手臂移动在肘关节上;biceps 肌肉是弹性体;而三肢在手臂后部是伸缩体(c)。
Summary
::摘要-
Individual skeletal muscles are composed of bunches of muscle fibers wrapped together.
::个体骨骼肌肉由捆绑在一起的肌肉纤维组成。 -
Muscles can only contract or pull; antagonistic muscles oppose each other, allowing joints to move in both directions.
::肌肉只能收缩或拉动;对立肌肉相互对立,允许关节双向移动。
Review
::回顾-
What is the difference between a fascicle and the fascia?
::分册和Fascia有什么区别? -
How does a tendon work with a muscle?
::一个长发的肌肉怎么用? -
What is the difference between a flexor and an extensor?
::弹性体和扩展体有什么区别?
-
Individual skeletal muscles are composed of bunches of muscle fibers wrapped together.