6.14测量地震震级
章节大纲
-
Have you ever felt an earthquake?
::你有过地震吗?Small are fairly common in some parts of the world. Depending on the quake, the land, and the setting, people experience them differently. You may wonder why your chair is moving, when you are sitting still. You may think someone is running across the roof. In a skyscraper, you may be swaying. Seismometers quantify this and record the energy released in the quake.
::小在世界上某些地方是相当常见的。根据地震、土地和环境的不同,人们体验它们的方式不同。当你坐着不动的时候,你可能会想为什么你的椅子在动。你可能会觉得有人在跑过屋顶。在摩天大楼里,你可能会摇摆不定。地震仪可以量化这一点,并记录地震释放的能量。Measuring Seismic Waves
::测量地震波are measured on a seismograph . Seismographs contain a lot of information, and not just about earthquakes.
::地震图包含许多信息,而不只是关于地震。Seismometers
::地震仪A seismograph is a machine that records seismic waves. In the past, seismographs produced a seismogram . A seismogram is a paper record of the seismic waves the seismograph received. Seismographs have a weighted pen suspended from a stationary frame. A drum of paper is attached to the ground. As the ground shakes in an earthquake, the pen remains stationary but the drum moves beneath it. This creates the squiggly lines that make up a seismogram ( Figure ).
::地震仪是一种记录地震波的机器。 过去,地震仪产生地震图。 地震仪是地震仪收到的地震波的纸面记录。 地震仪从固定的架子上悬浮了一把加权钢笔。 一块纸桶附在地面上。 当地面在地震中震动时, 笔会保持固定, 但鼓会在其下方移动。 这创造了构成地震图( 图表 ) 的细线 。This seismograph records seismic waves.
::这个地震仪记录了地震波Modern seismometers record ground motions using electronic motion detectors. The data are then kept digitally on a computer.
::现代地震仪使用电子移动探测器记录地面运动,然后将数据数码保存在计算机上。What We Learn from Seismograms
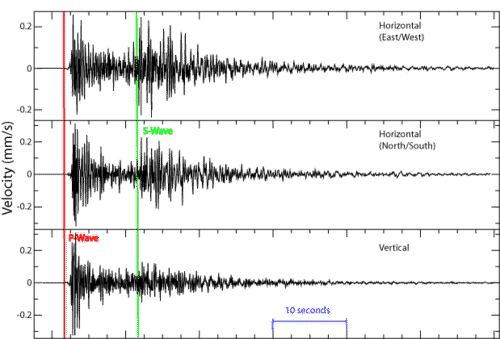
::我们从地震图中学到的东西Seismograms contain a lot of information about an earthquake: its strength, length, and distance. Wave height is used to determine the magnitude of the earthquake. The seismogram shows the different arrival times of the seismic waves ( Figure ). The first waves are P-waves since they are the fastest. S-waves come in next and are usually larger than P-waves. The surface waves arrive just after the S-waves. If the earthquake has a shallow focus , the surface waves are the largest ones recorded.
::地震图包含许多关于地震的信息:地震的强度、长度和距离。波高用来决定地震的强度。地震图显示地震波的不同到达时间(图)。第一个波是P波,因为它们是最快的。S波是下一个波,通常大于P波。地表波是在S波之后到达的。如果地震的焦点很浅,则地表波是记录的最大波。These seismograms show the arrival of P-waves and S-waves.
::这些地震图显示P波和S波的到来。A seismogram may record P-waves and surface waves, but not S-waves. This means that it was located more than halfway around the Earth from the earthquake. What does that mean? Earth's outer core is liquid. S-waves cannot travel through liquid. So the liquid outer core creates an S-wave shadow zone on the opposite side of the Earth from the quake.
::地震图可能记录P波和地表波, 但不记录S波。 这意味着它位于地震后的地球另一半。 这意味着它位于地震后的地球另一半。 这意味着什么? 地球的外核是液体。 S波不能通过液体流动。 因此, 液体外核在地震后的地球对面创建了S波阴影区 。Like most things, seismographs are now digital. Information from seismic waves is fed into computers at seismic stations around the world.
::与大多数情况一样,地震仪现在也是数字化的,地震波的信息被输入世界各地的地震台站的计算机。Further Reading
::继续阅读Summary
::摘要- A seismograph records seismic waves on a seismogram. A seismometer is a digital seismic wave recorder.
::地震仪记录地震波在地震图上。地震仪是数码地震波记录器。
- S-waves do not travel through liquids. So a seismogram with no S-waves is on the other side of the planet from the quake.
::电波不会通过液体流动。因此地震后地球的另一侧就有没有S波的地震图。
- Seismographs yield a tremendous amount of information about an earthquake.
::地震记录了地震的大量信息。
Review
::回顾- Define seismograph, seismogram, and seismometer.
::定义地震、地震图和地震仪。
- What does a seismogram with P-waves but not S-waves mean and why?
::P波的地震图 而不是S波是什么意思? 为什么?
- How can you tell S-wave arrival from the end of the P-wave?
::你如何从P波的尽头得知S波的到来?
Explore More
::探索更多- Why was the Alaska Earthquake on March 27, 1964 so large? How large was it?
::为什么1964年3月27日的阿拉斯加地震这么大?
- Name the types of plate boundaries that experience earthquakes.
::列出发生地震的板块边界类型。
- When geologists discovered new oceanic crust forming at divergent plate boundaries, what two explanations did they come up with?
::当地质学家发现新的海洋地壳 在不同的板块边界形成时 他们提出了两种解释?
- What happens at a subduction zone?
::潜入区发生什么了?
- What is the common cause of all 6 megathrust earthquakes that have been recorded since 1900?
::自1900年以来记录的所有6个大地震的共同原因是什么?
- Why is it impossible (at least at this time) to predict when an earthquake will take place?
::为什么无法(至少此时)预测地震何时会发生?
- A seismograph records seismic waves on a seismogram. A seismometer is a digital seismic wave recorder.