1.6 科学实验
章节大纲
-
Seeing Spots
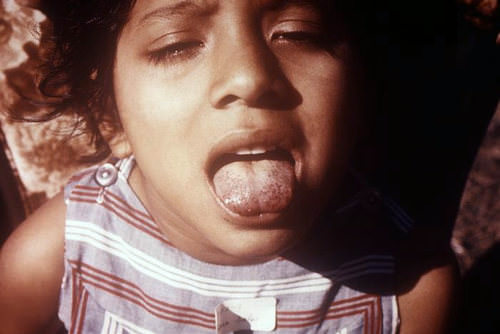
::观景点The spots on this girl's tongue are an early sign of vitamin C deficiency, which is also known as scurvy. This disorder, which may be fatal, is uncommon today, because foods high in vitamin C (including tomatoes, peppers, and citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and limes) are readily available. Scurvy was a well-known problem, however, on navy ships in the 1700s. It was said that scurvy caused more deaths in the British fleet than French and Spanish arms did! At that time, the cause of scurvy was unknown, and vitamins had not yet been discovered. Anecdotal evidence suggested that eating citrus fruits might cure scurvy, but no one knew for certain until 1747, when a Scottish naval physician named John Lind did an experiment to test the idea. Lind's experiment was one of the first clinical experiments in the history of medicine.
::这个女孩的舌头上的斑点是维生素C缺乏症的早期征兆,它也被称为腐烂。这种可能致命的疾病在今天并不常见,因为维生素C(包括西红柿、辣椒和柑橘、柠檬和石灰等柑橘等)含量高的食物随时可得。Scurvy在1700年代海军舰艇上是一个众所周知的问题。据说腐烂在英国舰队中造成的死亡比法国和西班牙舰队造成的死亡要多。当时,腐烂的原因并不为人所知,维生素尚未被发现。 传闻证据表明,吃柑橘水果可以治愈腐烂,但直到1747年苏格兰海军医生约翰·林德(John Lind)做了实验才知道这一点。 林德的实验是医学史上的第一个临床实验之一。What Is an Experiment?
::什么是实验?An experiment is a special type of scientific investigation that is performed under controlled conditions. Like all investigations, an experiment generates evidence to test a hypothesis . But unlike some other types of investigations, an experiment involves manipulating some factor in a system in order to see how it affects the outcome. Ideally, experiments also involve controlling as many other factors as possible in order to isolate the cause of the experimental results.
::实验是一种特殊类型的科学调查,在受控制的条件下进行。 与所有调查一样,实验产生证据来测试一种假设。 但与某些其他类型的调查不同,实验涉及在系统中操纵某种因素,以了解它如何影响结果。 理想的情况是,实验还涉及尽可能多的其他因素,以区分实验结果的原因。An experiment generally tests how one particular variable is affected by some other specific variable. The affected variable is called the dependent variable, or outcome variable. The variable that affects the dependent variable is called the independent variable . It is also called the manipulated variable because the researcher manipulates it. Any other variables that might also affect the dependent variable are held constant, or controlled, so that the effects of the independent variable are the only ones being measured.
::实验通常测试某个特定变量如何受到某些其他特定变量的影响。 受影响的变量称为从属变量, 或结果变量。 影响该从属变量的变量称为独立变量。 也称为被操纵变量, 因为研究者操纵了该变量。 任何其他可能影响该从属变量的变量都保持不变, 或被控制, 以便独立变量的效果是唯一被测量的变量。Lind's Scurvy Experiment
::林的斯康维实验Lind began his scurvy experiment on board a British ship after it had been at sea for two months. By then, sailors had started showing signs of scurvy. He chose 12 affected sailors and divided the group into six pairs. All 12 sailors received the same diet, but each pair also received a different daily supplement to their diet, as shown in the table .
::林德在一艘英国船只上开始了他的腐烂实验,该船在海上航行了两个月。 那时,水手们开始表现出腐烂的痕迹。 他选择了12名受影响的水手,并将他们分成六对。 所有12名水手都得到了同样的饮食,但每对水手的饮食每天也得到不同的补充,如表所示。Lind's Scurvy Experiment Pair of Subjects Daily Supplement to the Diet Received by this Pair
::这个对子收到每日补充《每日补充饮食》1 1 quart of cider 2 5 drops of sulfuric acid 3 6 spoons of vinegar 4 1 cup of seawater 5 2 oranges and 1 lemon 6 spicy paste and a drink of barley Lind's experiment ended after just five days, when the fresh citrus fruits ran out for pair number 5. The two sailors in this pair, however, had already fully recovered or greatly improved. The sailors in pair number 1 ( who received the quart of cider) also showed some improvement, but sailors in the other pairs showed none.
::林德的实验仅仅在五天后就结束了,当时新鲜柑橘水果用完了5对5的配对。 然而,这两对中的两名水手已经完全恢复或大大改进。 第一对水手(他们得到了苹果的四角架)也显示出了一些改善,但其他两对水手却没有表现出任何改善。Can you identify the independent and dependent variables in Lind's experiment?
::你能识别林德实验中 独立和依附的变量吗?The independent variable is the daily supplement received by the pairs. The dependent variable is the improvement or non-improvement of scurvy symptoms. Lind's results supported the citrus fruit cure for scurvy, and the treatment was soon adopted by the British navy with good results. The fact that scurvy is caused by a vitamin C deficiency was still not discovered until almost 200 years later.
::独立的变量是夫妇每天收到的补充品,从属变量是腐烂症状的改善或没有改善。 林德的研究结果支持柑橘类水果治愈腐烂,而治疗结果很快被英国海军采纳,结果良好。 维生素C缺乏症造成的腐烂直到近200年后才发现。Sampling
::抽样抽样Lind's scurvy experiment included just 12 subjects. By modern scientific standards, this is a very small sample. The sample in an experiment or other investigation consists of the individuals or events that are actually studied. It rarely includes the entire , because doing so would likely be impractical or even impossible.
::林德的潜伏实验只包括12个实验对象。根据现代科学标准,这是一个非常小的样本。实验或其他调查中的样本包括实际研究的个人或事件。它很少包括全部,因为这样做可能不切实际,甚至不可能。There are two types of errors that may occur when studying a sample instead of the entire population: chance error and bias.
::在研究抽样而不是整个人口时,可能会出现两类错误:误差和偏差。-
Chance error
is also called random error, and it's due to normal variation in a population.
T
he smaller the sample is, the greater the chance that it does not fairly represent the whole population. Chance error is mitigated by using a larger sample.
::偶然误差也被称为随机误差, 并且是由人群的正常变异造成的。 样本越小, 它不能公平代表整个人群的可能性越大。 使用更大的样本可以减少机会误差 。 -
Bias
occurs if the sample is not selected randomly with respect to a variable in the study. This problem is mitigated by taking care to choose a randomized sample.
::如果样本不是随机选取与研究中的变量有关的变量,就会出现偏差。 注意选择随机选取的样本可以缓解这一问题。
A reliable experiment must be designed to minimize both of these potential sources of error. You can see how they were addressed in another landmark experiment: the famous 1953 trial of Jonas Salk's newly developed polio vaccine . Salk's massive experiment has been called the "greatest public health experiment in history."
::必须设计一个可靠的实验来尽量减少这两个潜在的误差源。你可以看到另一个里程碑式的实验是如何解决的:著名的1953年Jonas Salk新研发的脊髓灰质炎疫苗试验。Salk的大规模实验被称为“历史上最伟大的公共卫生实验 ” 。Salk's Polio Vaccine Experiment
::Salk的脊髓灰质炎疫苗实验Imagine a nation-wide epidemic of a contagious, flu-like illness that attacks mainly children and often causes paralysis. That's exactly what happened in the U.S. during the first half of the 20th century. Starting in the early 1900s, there were repeated cycles of polio epidemics, and each seemed to be stronger than the one before. Many children ended up on life support in so-called "iron lungs" (see photo ), because their were paralyzed by the disease.
::想象一场全国性的传染性、类似流感的疾病流行病,这种疾病主要袭击儿童,并常常导致瘫痪。这正是20世纪上半叶发生在美国的情况。从1900年代初开始,小儿麻痹症流行病的周期反复发生,而且每个疾病似乎都比以前更严重。 许多儿童在所谓的“铁肺”(见照片)中最终依靠生命维持,因为他们因为疾病而瘫痪。This photo shows the iron lung ward in a California hospital in 1953, the same year that Salk undertook his nationwide vaccine experiment.
::这张照片展示了1953年加利福尼亚州一家医院的铁肺病房,Polio is caused by a , and there is still no cure for this potentially devastating illness. Fortunately, it can now be prevented with vaccines. The first polio vaccine was discovered by Jonas Salk in 1952. After testing the vaccine on himself and his family members to assess its safety, Salk undertook a massive experiment to test the effectiveness of the vaccine, using more than a million school children as subjects. It's hard to imagine a nationwide trial of an experimental vaccine using children as "guinea pigs" — and it would never happen today. However, in 1953, polio struck such fear in the hearts of parents that they accepted Salk's word that the vaccine was safe and gladly permitted their children to participate in the study.
::脊髓灰质炎是由一种潜在的毁灭性疾病引起的,而且这种潜在的疾病仍然没有治疗方法。幸运的是,现在可以用疫苗来预防。1952年,Jonas Salk发现了第一种小儿麻痹症疫苗。在对他本人和家人进行疫苗测试以评估其安全性之后,Salk进行了大规模实验,测试疫苗的有效性,使用100多万在校儿童作为科目。很难想象用儿童作为“guinea猪”来试验一种实验性疫苗,而这种试验在今天永远不会发生。然而,1953年,小儿麻痹症在父母的心中敲响了这样的恐惧,即他们接受了Salk的话,即疫苗是安全的,乐于允许他们的子女参加研究。Salk's experiment was very well designed. First, it included two very large, random samples of children — 600,000 in the treatment group and 600,000 in the nontreatment group. Using very large and randomized samples reduced the potential for chance error and bias in the experiment. Children in the treatment group were injected with the experimental polio vaccine. Children in the nontreatment group were injected with a harmless saline (salt water) solution. The saline injection was a placebo. A placebo is a "fake" treatment that actually has no effect on health. It is included in trials of vaccines and other medical treatments so subjects will not know if they have been placed in the treatment or nontreatment group. Use of a placebo helps researchers control for the placebo effect, which is a psychologically-based reaction to a treatment that occurs just because the subject is treated (even if the treatment has no real effect).
::Salk的实验设计得非常好。首先,它包括两个非常庞大的随机儿童样本——60万在治疗组,60万在非治疗组,60万在非治疗组;使用非常庞大和随机的样本减少了实验中出现偶然误差和偏差的可能性;治疗组的儿童注射了实验性小儿麻痹症疫苗;非治疗组的儿童注射了无害的盐碱(盐水)溶液;盐碱注射是一种安慰剂;安慰剂是一种“假”治疗,实际上对健康没有影响;安慰剂是一种“假”治疗,在疫苗和其他医疗实验中也包括在内,因此患者不会知道他们是否被置于治疗或非治疗组;使用安慰剂帮助研究人员控制安慰剂效应,这是对治疗对象(即使治疗没有实际效果)引起的治疗的一种心理反应。Experiments in which a placebo is used are generally blind experiments, because the subjects are "blind" to their experimental group. Experimenting blindly helps prevent bias in the experiment. Often, even the researchers do not know which subjects are in each group. This type of experiment is called a double-blind experiment, because bo th subjects and researchers are "blind" to which subjects are in each group. D ouble-blind experiments are now considered the gold standard for clinical trials of vaccines, therapeutic drugs , and other medical treatments. Salk's vaccine trial was a double-blind experiment.
::使用安慰剂的实验一般都是盲实验, 因为实验对象与其实验组是“ 盲的” 。 盲实验有助于防止实验中的偏差。 通常, 即使是研究人员也不知道每个实验组中的哪个实验对象。 这种实验被称为双盲实验, 因为实验对象和研究人员都是“盲的 ” , 每个实验组中都有。 双盲实验现在被视为疫苗、 治疗药物和其他医疗临床试验的黄金标准。 Salk的疫苗试验是一种双盲实验。Salk's polio vaccine proved to be highly successful. Analysis of data from his study revealed that the vaccine was 80 to 90 percent effective in preventing polio. Almost overnight, Salk was hailed as a national hero. He appeared on the cover of Time magazine and was invited to the White House. Within a few years, millions of children had received the polio vaccine. By 1961, the incidence of polio in the U.S. had been reduced by 96 percent.
::Salk的脊髓灰质炎疫苗证明非常成功。对研究数据的分析显示,疫苗在预防脊髓灰质炎方面有80%至90%的效果。几乎一夜之间,Salk被誉为民族英雄。他在时代杂志的封面上登上,并被邀请到白宫。几年内,数百万儿童获得了脊髓灰质炎疫苗。1961年,美国脊灰质炎发病率下降了96%。Limits on Experimentation
::试验限制It is not possible, practical, or ethical in all investigations for scientists to manipulate variables to test outcomes, although this method often yields the most reliable findings. As a result, many ideas cannot be tested by experimentation.
::在所有调查中,科学家不可能、实际或合乎道德地操纵变量来测试结果,尽管这种方法往往得出最可靠的结论。 结果,许多想法无法通过实验来测试。E xperiments cannot be used, for example, to test ideas about what our ancestors ate millions of years ago, because it is impossible to study those populations directly. Researchers must rely instead on indirect evidence, such as detailed observations of their fossilized teeth. It is similarly impossible to use experiments to study the extent to which long-term cigarette smoking contributes to lung , since it is unethical to expose human subjects to harmful cigarette smoke. Researchers may use large observational studies of people who are already smokers, with nonsmokers as controls, to look for correlations between smoking habits and lung cancer.
::举例来说,实验不能用来检验关于我们祖先数以百万计年前所吃东西的想法,因为不可能直接研究这些人口。研究人员必须依靠间接证据,例如对其化石化牙齿的详细观察。同样,也不可能利用实验来研究长期吸烟对肺部的贡献程度,因为暴露人体受有害烟雾的影响是不道德的。研究人员可能利用对已经吸烟者的大量观察研究,用非吸烟者作为控制手段,寻找吸烟习惯与肺癌之间的关系。Feature: Human Biology in the News
::特著:《新闻》中的人类生物学Lind undertook his experiment to test the effects of citrus fruits on scurvy at a time when seamen were dying by the thousands from this nutritional disease as they explored the world. Today's explorers are astronauts in space, and their nutrition is also crucial to the success of their missions. For astronauts in space, maintaining good nutrition can be challenging. One problem is that astronauts tend to eat less while in space. Not only are they very busy on their missions, but they may also get tired of the space food rations. Another problem is the environment of space itself. Factors such as microgravity and higher radiation exposure can have major effects on human health, and they can require nutritional adjustments to help counteract them. A novel way of studying astronaut nutrition and health is provided by identical twin astronauts Scott and Mark Kelly, pictured .
::林德在水手们在探索世界时,由于这种营养疾病而死亡的数千名海员正死于这种营养疾病。今天的探险家是太空中的宇航员,他们的营养也是他们任务成功的关键。对于太空中的宇航员来说,保持良好的营养可能具有挑战性。一个问题在于宇航员在太空期间往往吃得较少。他们不仅在飞行任务中非常忙碌,而且还可能厌倦空间食物配给。另一个问题是空间环境本身。微重力和高辐射照射等因素可能对人类健康产生重大影响,他们需要营养调整来帮助他们战胜这些疾病。同样的两位宇航员斯科特和马克·凯利(Scott and Mark Kelly)为研究宇航员的营养和健康提供了一种新的方法。Astronauts Mark and Scott Kelly at the Johnson Space Center.
::Johnson航天中心的宇航员Mark和Scott KellyThe Kelly brothers are the first identical twin astronauts , but twin studies are nothing new. Scientists have used identical (homozygotic) twins as research subjects for many decades. Identical twins have the same genes , so any differences between them generally can be attributed to environmental influences, rather than genetic causes. Mark Kelly spent almost a full year on the International Space Station (ISS) between 2015 and 2016, while his twin brother Scott Kelly stayed on the ground, serving as a control in this experiment. You may have noticed a lot of media coverage of Mark Kelly's return to Earth in March 2016. His continuous sojourn in space was the longest of any American astronaut to date. NASA is learning a great deal about the effects of long-term space travel on the by measuring and comparing nutritional indicators and other health data between these twins. Watch this NASA video to learn more about NASA's nutritional experiments involving Mark and Scott .
::Kelly兄弟是第一个完全相同的双胞胎宇航员,但双胞胎研究并不是什么新鲜事。 科学家们用相同的双胞胎作为研究对象已有数十年了。 同龄双胞胎有着相同的基因,因此它们之间的任何差异一般都可归因于环境影响,而不是基因原因。 Mark Kelly在2015年至2016年期间在国际空间站(ISS)度过了将近整整一年的时间,而他的双胞胎兄弟Scott Kelly则留在地面上,作为这一实验的对照。你可能注意到许多媒体报道了Mark Kelly在2016年3月返回地球。他在太空中的持续逗留是迄今为止美国宇航员中时间最长的。 美国航天局正在通过测量和比较这些双胞胎之间的营养指标和其他健康数据来了解长期空间旅行的影响。 观看美国航天局的这段视频是为了更多地了解美国航天局涉及Mark和Scott的营养实验。Identical twins who were raised separately from birth make especially good subjects for studying the effects of genes versus the environment on human health, , and behavior. Watch the news report below to learn more. In the video, a researcher who specializes in studying twin pairs explains why they are so important as research subjects. She also shares some of her amazing findings.
::与出生分开抚养的同龄双胞胎为研究基因与环境对人类健康、 和行为的影响提供了特别好的科目。 观看下面的新闻报道学习更多。 在视频中,一位研究双胞胎的研究者专门研究双胞胎,解释了他们为什么像研究课题一样重要。她还分享了她的惊人发现。Summary
::摘要-
In 1747, John Lind undertook one of the first clinical experiments
when he
tested citrus fruits as a cure for scurvy.
::1747年,约翰·林德进行了首批临床实验之一,当时他测试柑橘水果,作为皮肤腐烂的治疗方法。 -
An experiment is a special type of scientific investigation that is performed under controlled conditions. It involves manipulating some factor (the independent, or manipulated, variable) in order to see how it affects some other factor (the dependent, or outcome, variable).
::实验是一种在受控制条件下进行的特别类型的科学调查,涉及操纵某些因素(独立因素或被操纵的变量),以便了解它如何影响其他一些因素(依附因素或结果变量)。 -
The sample in an experiment consists of the individuals or events that are actually studied. A reliable experiment must be designed to minimize two potential sources of sampling error: chance error, which may occur if the sample is too small; and bias, which may occur if the sample is not selected randomly.
::实验中的样本由实际研究的个人或事件组成,必须设计可靠的实验,以尽量减少两个可能的取样错误来源:概率错误,如果样本太小,可能发生;偏差,如果样本不是随机选取,则可能发生。 -
Jonas Salk's landmark public health experiment, in which he tested his new polio vaccine, addressed both
chance error and bias
by using very large random samples and
setting up
the test with a double-blind experimental design,
including
a placebo.
::Jonas Salk具有里程碑意义的公共卫生实验,他测试了脊髓灰质炎新疫苗,通过使用非常庞大的随机样本和采用双盲实验设计,包括安慰剂来进行测试,从而解决了偶然错误和偏差问题。 -
Well-done experiments are generally the most rigorous and reliable scientific investigations, but many ideas cannot be tested by experimentation. Manipulating variables to test outcomes is not possible, practical, or ethical in all investigations.
::良好的实验通常是最严格和最可靠的科学调查,但许多想法不能通过实验来测试。 在所有调查中,操纵变量来测试结果是不可能的、实际的或合乎道德的。
Review
::回顾1. How do experiments differ from other types of scientific investigations?
::1. 实验与其他类型的科学调查有何不同?2. Identify the independent and dependent variables in Salk's nationwide polio vaccine trial.
::2. 确定Salk全国小儿麻痹症疫苗试验的独立和依赖变量。3. Compare and contrast chance error and bias in sampling. How can each type of error be minimized?
::3. 比较和对比抽样中偶然误差和偏差:如何尽量减少每一种误差?4. What is the placebo effect? Explain how Salk's experimental design controlled for it.
::4. 安慰剂效应是什么?解释Salk的实验设计是如何控制的。5. Fill in the blanks. The _____________ variable is manipulated to see the effects on the ___________ variable.
::5. 填充空白: 变数被操纵以查看对 变数的影响 。6. True or False : In studies of identical twins, the independent variable is genetics.
::6. 真实或假:在对同父双胞胎的研究中,独立的变量是遗传学。7. True or False : Experiments cannot be done on humans.
::7. 真实或假:不能对人类进行实验。8. True or False : Larger sample sizes are generally better than smaller ones in scientific experiments.
::8. 真实或假:在科学实验中,较大样本的大小一般优于较小样本的大小。9. Answer the following questions about Lind’s scurvy experiment.
::9. 回答以下关于林德的潜伏实验的问题。a. Why do you think it was important that the sailors’ diets were all kept the same, other than the daily supplement?
::a. 为什么你认为,除了每日补充食品外,海员的饮食必须保持不变?b. Can you think of some factors other than diet that could have potentially been different between the sailors that might have affected the outcome of the experiment?
::b. 除了饮食以外,你能想到水手之间可能影响实验结果的可能不同因素吗?c. Why do you think the sailors who drank cider experienced some improvement in their scurvy symptoms?
:c) 为什么你认为那些喝苹果酒的水手的病状会有所好转?
10. Explain why double-blind experiments are considered to be more rigorous than regular blind experiments.
::10. 解释为什么双盲实验被认为比普通盲实验更为严格。11. Why are studies using identical twins so useful?
::11. 为什么使用同性双胞胎的研究如此有用?12. Do you think it is necessary to include a placebo (such as an injection with saline in a drug-testing experiment) in experiments that use animals? Why or why not?
::12. 你认为是否有必要在使用动物的实验中包括安慰剂(如在药物试验试验中注入盐碱)?为什么或为什么没有?Explore More
::探索更多Watch this TED talk, in which b iochemist Kary Mullis talks about experiments as the basis of modern science.
::观看TED的演讲, 生物化学家Kary Mullis在演讲中谈到实验是现代科学的基础。Check out this video to learn more about conducting scientific experiments:
::查看这段影片以了解更多关于进行科学实验的知识: -
Chance error
is also called random error, and it's due to normal variation in a population.
T
he smaller the sample is, the greater the chance that it does not fairly represent the whole population. Chance error is mitigated by using a larger sample.