5.7 变音
章节大纲
-
Mutant Cosplay
::变异者CosplayYou probably recognize these costumed comic fans as two of the four Teenage Mutant Ninja . Can a mutation really turn a into an anthropomorphic superhero? Of course not — but mutations can often result in other (more realistic) drastic changes in living things.
::你可能承认这些装扮的漫画粉丝是四个青少年变异者忍者中的两个。 一个变异真的能将一个变异变成一个人类形态超级英雄吗? 当然不会,但变异往往会导致生活的其他(更现实的)急剧变化。What Are Mutations?
::什么是变异?Mutations are random changes in the sequence of bases in or . The word mutation may make you think of the Ninja Turtles, but that's a misrepresentation of how most mutations work. First of all, e veryone has mutations. In fact, most people have dozens (or even hundreds!) of mutations in their DNA. Secondly, from an evolutionary perspective, mutations are essential. They are needed for evolution to occur because they are the ultimate source of all new in any .
::变异是基数序列的随机变化。 突变这个词可能让你想到忍者龟, 但这是对大多数变异是如何运作的曲解。 首先, 每个人都有变异。 事实上, 大多数人的DNA中有几十个变异( 甚至几百个! ) 。 其次, 从进化的角度来说, 变异是不可或缺的。 变异是进化需要的, 因为它们是任何新事物的最终来源 。Causes of Mutations
::变异原因Mutations have many possible causes. Some mutations seem to happen spontaneously, without any outside influence. They occur when errors are made during DNA replication or during the phase of . Other mutations are caused by environmental factors. Anything in the environment that can cause a mutation is known as a mutagen . Examples of mutagens are shown in the figure .
::变异有许多可能的原因。有些变异似乎自发发生,没有任何外部影响。当DNA复制过程中或DNA阶段出现错误时,就会发生。其他变异是由环境因素造成的。环境中任何可能导致变异的事物都被称为变异基因。图中显示了诱变性的例子。Examples of Mutagens. Types of mutagens include radiation, chemicals, and infectious agents. Do you know of other examples of each type of mutagen shown here?
::突变物的例子。 突变物的类型包括辐射、 化学和传染性物剂。 您知道这里显示的每一种突变物的其他例子吗 ?Types of Mutations
::变音类型Mutations come in a variety of types . Two major categories of mutations are germline mutations and somatic mutations .
::变异有多种类型,两种主要变异类型是子宫变异和体形变异。-
Germline mutations
occur in
gametes
(the sex cells), such as
eggs
and
. These mutations are especially significant because they can be transmitted to offspring, causing every
in the offspring
to
carry
those
mutations.
::雌激素突变发生在诸如卵和卵等交替细胞(性细胞)中。这些突变特别重要,因为它们可以传给后代,导致每个后代都携带这些突变。 -
Somatic mutations
occur in other cells of the body. These mutations may have little effect on the
organism
, because they are confined to just one cell and its
daughter cells
. Somatic mutations cannot be passed on to offspring.
::体外突变发生在身体的其他细胞中。这些突变可能对有机体没有多大影响,因为它们只局限在一个细胞及其子细胞中,不能将体外突变传给后代。
Mutations also differ in the way that the genetic material is changed. Mutations may change an entire , or they may alter just one or a few nucleotides .
::基因物质改变的方式也不同。 变异可能会改变整个过程,或者它们可能只改变一种或几种核糖核酸。Chromosomal Alterations
::染色体改变Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure. They occur when a section of a chromosome breaks off and rejoins incorrectly, or otherwise does not rejoin at all. Possible ways in which these mutations can occur are illustrated in the figure . Chromosomal alterations are very serious. They often result in the death of the organism in which they occur. If the organism survives, it may be affected in multiple ways. An example of a human disease caused by a chromosomal duplication is Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1 (CMT1). It is characterized by muscle weakness, as well as loss of muscle tissue and sensation. The most common cause of CMT1 is a duplication of part of chromosome 17.
::染色体的改变是改变染色体结构的突变,发生于染色体部分断裂、不正确重新加入或不重新加入时,这些突变可能发生的方式在图中说明。染色体的改变非常严重,往往导致发生变异的有机体死亡。如果生物体存活下来,它可能受到多种影响。染色体重复造成的人类疾病的例子之一是1型色体(CMT1)的Charcot-Marie-Tooth疾病,其特点是肌肉弱,肌肉组织和感觉丧失。CMT1最常见的原因就是17型染色体的一部分重复。Chromosomal alterations are major changes in the genetic material.
::染色体改变是基因物质的重大改变。Point Mutations
::点变数A point mutation is a change in a single nucleotide in DNA. This type of mutation is usually less serious than a chromosomal alteration. An example of a point mutation is a mutation that changes the codon UUU to the codon UCU. Point mutations can be silent, missense, or nonsense mutations, as described in the following . The effects of point mutations depend on how they change the .
::点突变是DNA中单核核酸的改变。 这种突变通常比染色体变异不严重。 点突变的一个例子是, 点突变会把Codon UUU改变为codon UCU。 点突变可以是静音、 missense 或无意义的突变, 如下文所述。 点突变的效果取决于它们如何改变 。Type Description Example Effect Silent mutated codon codes for the same amino acid CAA (glutamine) → CAG (glutamine) none Missense mutated codon codes for a different amino acid CAA (glutamine) → CCA (proline) variable Nonsense mutated codon is a premature stop codon CAA (glutamine) → UAA (stop) usually serious Frameshift Mutations
::框架图变变A frameshift mutation is a deletion or insertion of one or more nucleotides, changing the reading frame of the base sequence. Deletions remove nucleotides, and insertions add nucleotides. Consider the following sequence of bases in RNA:
::框架转移突变是指删除或插入一个或多个核核素,改变基序列的读数框架。删除去除核素,插入添加核素。考虑RNA中的以下基数序列:AUG-AAU-ACG-GCU = start-asparagine-threonine-alanine
::AUG-AAAU-ACG-GCU = 开始的paraggine-threonine-alineNow, assume that an insertion occurs in this sequence. Let’s say an A nucleotide is inserted after the start codon AUG. The sequence of bases becomes:
::现在,假设插入会在这个序列中发生。让我们假设一个核核酸是在开始“AUG ” 之后插入的。 基础的顺序如下:AUG-AAA-UAC-GGC-U = start-lysine-tyrosine-glycine
::AUG-AAAA-UAC-GGC-UEven though the rest of the sequence is unchanged, this insertion changes the reading frame and, therefore, all of the codons that follow it. As this example shows, a frameshift mutation can dramatically change how the codons in mRNA are read. This can have a drastic effect on the product.
::尽管其余的顺序没有变化, 但插入此顺序会改变阅读框架, 并因此改变随之而来的所有codon。 正如这个例子所显示的, 框架转换突变可以显著改变 mRNA 中的codon 是如何阅读的。 这可能会对产品产生巨大影响 。Effects of Mutations
::变异的影响The majority of mutations have neither negative nor positive effects on the organism in which they occur. These mutations are called neutral mutations . Examples include silent point mutations, which are neutral because they do not change the amino acids in the proteins they encode.
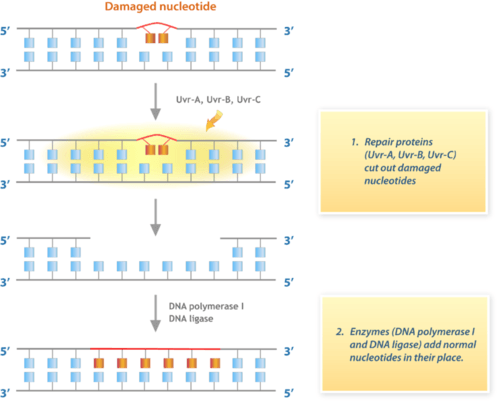
::大多数突变对发生突变的有机体没有消极或积极影响。 这些突变被称为中性突变。 例子包括静点突变,这些静点突变是中性的,因为它们不会改变所编码的蛋白质中的氨基酸。Many other mutations have no effects on the organism because they are repaired before protein synthesis occurs. Cells have multiple repair mechanisms to fix mutations in DNA. One way DNA can be repaired is illustrated in the figure . If a cell’s DNA is permanently damaged and cannot be repaired, is likely prevented .
::许多其他突变对生物体没有影响,因为它们是在蛋白质合成发生之前修复的。 细胞有多种修复机制来修复DNA中的突变。 图中说明了可以修复DNA的一种方式。 如果细胞的DNA被永久损坏并且无法修复,那么可能就被阻止了。DNA Repair Pathway. This flow chart shows one way that damaged DNA is repaired in E. coli bacteria.
::DNA修复途径。这个流程图显示,在E.大肠菌细菌中,有一种方法可以修复受损的DNA。Beneficial Mutations
::受益性变异Some mutations — known as beneficial mutations — have a positive effect on the organism in which they occur. They generally code for new versions of proteins that help organisms adapt to their environment. If they increase an organism’s chances of surviving or reproducing, the mutations are likely to become more common over time. There are several well-known examples of beneficial mutations. Here are two such examples:
::一些突变被称作有益的突变,对发生突变的有机体具有积极影响,它们通常为有助于生物体适应环境的新形式的蛋白质编码,如果它们增加生物体存活或再生的机会,变异可能会随着时间的流逝而变得更为常见。-
Mutations have occurred in
that allow the bacteria to survive in the presence of
antibiotic
drugs
, leading to the evolution of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
::出现变异是因为细菌在有抗生素药物的情况下存活下来,导致抗生素抗菌菌株的演变。 -
A unique mutation is found in people in a small town in Italy. The mutation protects them from developing
atherosclerosis
, which is the dangerous buildup of fatty materials in
. The individual in which the mutation first appeared has even been identified!
::在意大利的一个小镇上,人们发现了一种独特的突变。突变保护了他们避免发展无缝硬化症,这是一种危险的脂肪材料堆积。 突变最初出现的人甚至被识别出来!
Harmful Mutations
::有害变异Imagine making a random change in a complicated machine, such as a car engine. There is a chance that the random change would result in a car that does not run well — or perhaps does not run at all. By the same token, a random change in a gene's DNA may result in the production of a protein that does not function normally... or may not function at all. Such mutations are likely to be harmful. Harmful mutations may cause or .
::想象一下在汽车引擎等复杂机器中随机改变。 随机改变有可能会导致汽车运行不顺利 — — 或者可能根本不运行。 同样, 基因DNA随机改变可能导致蛋白质的产生,而蛋白质的产生并不正常...或者可能完全不起作用。 这种突变可能有害。 有害的突变可能引发或引发 。-
A
genetic disorder
is a disease, syndrome, or other abnormal condition caused by a mutation in one or more
genes
, or by a chromosomal alteration. An example of of a genetic disorder is
cystic fibrosis
. A mutation in a single gene causes the body to produce thick, sticky
mucus
that clogs the
lungs
and blocks ducts in digestive
organs
.
::基因紊乱是指一种或多种基因的突变或染色体变异引起的疾病、综合症或其他异常情况,遗传紊乱的一个例子是细胞纤维化,单一基因的突变导致身体产生粘粘粘的厚粘粘性粘膜,将肺部和消化器官的管管堵塞。 -
Cancer
is a disease in which cells grow out of control and form abnormal masses of cells (called tumors). It is generally caused by mutations in genes that regulate the
. Because of the mutations, cells with damaged DNA are allowed to divide without restriction.
::癌症是一种细胞无法控制地生长并形成异常的细胞群(所谓的肿瘤)的疾病,一般是由调节肿瘤的基因突变引起的。 由于突变,DNA受损的细胞可以不受限制地分裂。
Feature: My Human Body
::特质:我的人体Inherited mutations are thought to play a role in roughly five to ten percent of all cancers. Specific mutations that cause many of the known hereditary cancers have been identified. Most of the mutations occur in genes that control the growth of cells or the repair of damaged DNA.
::遗传突变被认为在所有癌症中约占5-10%。 导致许多已知遗传癌的具体突变已经查明。 大部分突变发生在控制细胞生长或修复受损DNA的基因中。Genetic testing can be done to determine whether individuals have inherited specific cancer-causing mutations. Some of the most common inherited cancers for which genetic testing is available include hereditary breast and ovarian cancer, caused by mutations in genes called BRCA1 and BRCA2. Besides breast and ovarian cancers, mutations in these genes may also cause pancreatic and prostate cancers. Genetic testing is generally done on a small sample of body fluid or tissue , such as , saliva , or skin cells. The sample is analyzed by a lab that specializes in genetic testing, and it usually takes at least a few weeks to get the test results.
::遗传检测可以用来确定个人是否继承了特定的致癌突变,一些最常见的遗传性癌症可以进行遗传检测,包括遗传乳腺癌和卵巢癌,这些癌症是由基因基因突变引起的,称为BRCA1和BRCA2。除了乳癌和卵巢癌外,这些基因的突变还可能造成胰腺癌和前列腺癌。遗传检测一般对少量的体液或组织样本进行,如唾液或皮肤细胞。样本由专门进行遗传检测的实验室分析,通常至少需要几个星期才能获得检测结果。Should you get genetic testing to find out whether you have inherited a cancer-causing mutation? Such testing is not done routinely just to screen patients for risk of cancer. Instead, the tests are generally done only when the following three criteria are met:
::是否进行基因测试,以确定您是否继承了导致癌症的突变?这种测试并非例行进行,而只是为了检查病人是否有癌症风险。相反,通常只有在满足以下三个标准时才进行测试:-
The test can determine definitively whether a specific gene is mutation is present. This is the case with the BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations, for example.
::测试可以确定特定基因是否突变。 BRCA1 和 BRCA2 基因突变就属于这种情况。 -
The test results would be useful to help guide future medical care. For example, if you found out you had a mutation in the BRCA1 or BR
CA
2 gene, you might get more frequent breast and ovarian cancer screenings than are generally recommended.
::测试结果将有助于指导未来的医疗。 比如,如果你发现自己在BRCA1或BRCA2基因中有突变,你可能会得到比一般推荐的更频繁的乳腺癌和卵巢癌筛查。 -
You have a personal or family history that suggests you are at risk of an inherited cancer.
::你有个人或家庭历史 表明你面临遗传癌症的风险
Criterion number 3 is based, in turn, on such factors as:
::第3号标准反过来又以下列因素为依据:-
diagnosis of cancer at an unusually young age
::在异常年轻年龄诊断癌症 -
several different cancers occurring independently in the same individual
::在同一个人中独立出现数种不同的癌症 -
several close genetic relatives having the same type of cancer (such as a maternal grandmother, mother, and sister all having breast cancer)
::几个同类型癌症的近亲遗传亲属(如祖母、母亲和姐妹,他们都患有乳腺癌) -
cancer occurring in both organs in a set of paired organs (such as both
or both breasts)
::两种器官在一组配对器官(如双乳或双乳)中出现癌症
If you meet the criteria for genetic testing and are advised to undergo it, genetic counseling is highly recommended. A genetic counselor can help you understand what the results mean and how to make use of them to reduce your risk of developing cancer. For example, a positive test result that shows the presence of a mutation may not necessarily mean that you will develop cancer. It may depend on whether the gene is located on an autosome or sex chromosome , and whether the mutation is dominant or recessive . Lifestyle factors may also play a role in cancer risk even for hereditary cancers. Early detection can often be life saving if cancer does develop. Genetic counseling can also help you assess the chances that any children you may have will inherit the mutation.
::如果你符合基因测试的标准,并且建议你接受基因检测,那么遗传咨询是推荐的。遗传咨询师可以帮助你了解结果的含义以及如何利用结果来降低癌症发展的风险。例如,显示突变存在的积极测试结果不一定意味着你将发展癌症。这取决于基因是否位于一个自动或性染色体上,以及突变是主导性的还是休眠性的。生活方式因素也可能在癌症风险中起到一定作用,即使是遗传性癌症。早期发现通常可以挽救生命,如果癌症确实发展的话。遗传咨询也可以帮助你评估任何孩子继承突变的可能性。Summary
::摘要-
Mutations are random changes in the sequence of bases in DNA or RNA. Most people have multiple mutations in their DNA without ill effects. Mutations are the ultimate source of all new genetic variation in any species.
::变异是DNA或RNA中基数序列的随机变化。 大多数人的DNA中有多重突变,没有不良效果。 变异是任何物种所有新基因变异的最终来源。 -
Mutations may happen spontaneously during DNA replication or transcription. Other mutations are caused by environmental factors called mutagens. Mutagens include radiation, certain chemicals, and some infectious agents.
::在DNA复制或转录过程中,变异可能自发发生,其他变异是由称为变异的环境因素引起的,变异包括辐射、某些化学品和某些传染性物剂。 -
Germline mutations occur in gametes and may be passed on to offspring. Every cell in the offspring will then have the mutation. Somatic mutations occur in cells other than gametes and are confined to just one cell and its daughter cells. These mutations cannot be passed on to offspring.
::阳性突变发生在调子中, 并可能传给后代。 后代中的每一个细胞都会发生突变。 体性突变发生在除调子以外的细胞中, 并且只局限于一个细胞及其子细胞。 这些突变不能传给后代 。 -
Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure and usually affect the organism in multiple ways.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1
is an example of a chromosomal alteration in humans.
::染色体变化是变异,改变染色体结构,通常以多种方式影响生物体。 染色体变化是人类染色体变化的一个例子。 -
Point mutations are changes in a single nucleotide. The effects of point mutations depend on how they change the genetic code and may range from no effects to very serious effects.
::点突变是单核核酸的变化,点突变的影响取决于它们如何改变遗传编码,从无影响到非常严重的影响可能不一而足。 -
Frameshift mutations change the reading frame of the genetic code and are likely to have a drastic effect on the encoded protein.
::框架变异改变了遗传代码的读数框架,可能对编码蛋白质产生剧烈影响。 -
Many mutations are neutral and have no effect on the organism in which they occur. Some mutations are beneficial and improve fitness. An example is a mutation that confers antibiotic resistance in bacteria. Other mutations are harmful and decrease fitness, such as the mutations that cause genetic disorders or cancers.
::许多突变是中性的,对发生突变的有机体没有影响,有些突变有益、更健康,例如突变给细菌带来抗生素抗药性,其他突变有害、体质下降,如引起基因紊乱或癌症的突变。
Review
::回顾1. Define mutation.
::1. 界定突变。2. Identify causes of mutation.
::2. 查明突变的原因。3. Compare and contrast germline and somatic mutations.
::3. 比较和对比细菌和体突变。4. Describe chromosomal alterations, point mutations, and frameshift mutations. Identify the potential effects of each type of mutation.
::4. 描述染色体变化、点变异和轮廓变异,确定每一种变异的潜在影响。5. Why do many mutations have neutral effects?
::5. 为什么许多变异具有中性效应?6. Give one example of a beneficial mutation and one example of a harmful mutation.
::6. 举一个有益的突变的例子和一个有害的突变的例子。7. Why do you think that exposure to mutagens (such as cigarette smoke) can cause cancer?
::7. 为什么你认为接触诱变性物(如烟雾)会导致癌症?8. True or False: Mutations are always caused by exposure to toxic substances.
::8. 真实或虚假:变异总是由于接触有毒物质所致。9. True or False: Some mutations can make chromosomes longer or shorter.
::9. 真实或假:某些变异可使染色体变长或变短。10. Explain why the insertion or deletion of a single nucleotide can cause a frameshift mutation.
::10. 解释为什么插入或删除单核核酸会导致轮胎突变。11. Compare and contrast missense and nonsense mutations.
::11. 比较和对比误差和无稽的突变。12. A mutation that substitutes one nucleotide for another is called a ___________ mutation.
::12. 一种突变可以代替一种核核酸代替另一种核酸,这种突变称为突变。13. Which type of mutation is the most common cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1?
::13. 哪种突变是Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1型疾病最常见的原因?14. Explain why mutations are important to evolution.
::14. 解释为何突变对演变很重要。Explore More
::探索更多Radiation is all around us. It is a part of everyday life. But what exactly is it, and what does it do to your body? Check it out here:
::辐射环绕着我们。它是日常生活的一部分。但它到底是什么, 它对你的身体有什么影响?看看这里:You probably know that smoking kills, but what exactly does smoking do to your body? Learn more here:
::你可能知道吸烟会致命 但吸烟对身体到底有什么影响? -
Germline mutations
occur in
gametes
(the sex cells), such as
eggs
and
. These mutations are especially significant because they can be transmitted to offspring, causing every
in the offspring
to
carry
those
mutations.