5.11 性生殖、美化和游戏起源
章节大纲
-
All in the Family
::全体家庭This self-portrait of an 18th century artist and his family clearly illustrates an important point. Children in a family resemble their parents and each other, but the children never look exactly the same, unless they are identical twins. Each of the daughters in the painting inherited a unique combination of traits from the parents. In this concept, you will learn how this happens. It all begins with sex — sexual reproduction, that is.
::一位18世纪艺术家及其家人的这种自画像清楚地表明了一个重要点。家庭中的儿童与父母和他们彼此相似,但孩子的外表却一模一样,除非他们是完全相同的双胞胎。绘画中的每个女儿都继承了父母独有的特征组合。在这个概念中,你将了解这种情况是如何发生的。这一切都始于性——性生殖,即性生殖。Sexual Reproduction
::性生殖is the process by which organisms give rise to offspring. It is one of the defining characteristics of living things. Like many other organisms, human beings reproduce sexually. Sexual reproduction involves two parents. As you can see from the figure , in sexual reproduction, parents produce reproductive (sex) — called gametes — that unite to form an offspring. Gametes are haploid (or 1N) cells. This means they contain one copy of each in the . Gametes are produced by a type of called , which is described in detail below. The process in which two gametes unite is called . The fertilized cell that results is referred to as a zygote . A zygote is a diploid (or 2N) cell, which means it contains two copies of each chromosome. Thus, it has twice the number of chromosomes as a gamete.
::生物是产生后代的过程。它是生物的决定性特征之一。和许多其他生物一样,人类是性繁殖的。性繁殖涉及双亲。从图中可以看出,在性生殖中,父母生产生殖(性)——称为网友——以形成后代为单位。网友是杂交(或1N)细胞。这意味着它们包含每个细胞的复制件。网友是由一种称为“网友”的种类产生的,下文对此有详细说明。两个网友联合起来的过程被称为“zygote”。结果被称作“zygote”的受精细胞。一个zygote是一个dloid(或2N)细胞,这意味着它包含每个染色体的复制件。因此,它拥有一个游戏的染色体的两倍。Cycle of Sexual Reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves the production of haploid gametes by meiosis, followed by fertilization and the formation of a diploid zygote. The number of chromosomes in a gamete is represented by the letter N. Why does the zygote have 2N, or twice as many, chromosomes?
::性生殖周期:性生殖涉及通过中度生成杂交调子,然后是施肥和形成低脂的zygote, 调子中的染色体数量由字母N表示。 为什么zygote有2N, 或两倍的染色体?Meiosis
::诊断The process that produces haploid gametes is called meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. It occurs only in certain special cells of an organism. During meiosis, homologous (paired) chromosomes separate, and haploid cells form that have only one chromosome from each pair. The diagram gives an overview of meiosis.
::生成杂交调色板的过程被称为 meiosis。 Meisisis 是细胞分裂的一种类型, 染色体的数量会减半。 只有在某种生物的特殊细胞中才会发生。 在混合过程中, 共性染色体( paired) 染色体是分开的, 以及每对只有一种染色体的杂交细胞形式。 该图表给出了对称的共性概述 。Overview of Meiosis. During meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate and go to different daughter cells. This diagram shows just the nuclei of the cells. Notice the exchange of genetic material that occurs prior to the first cell division.
::Meisisis 概览。 在梅希松病期间, 同族染色体分离并进入不同的女儿细胞。 此图表只显示细胞的核。 注意在第一个细胞分裂之前发生的基因物质的交换 。As you can see in the meiosis diagram, two cell divisions occur during the overall process, producing a total of four haploid cells from one parent cell . The two cell divisions are called meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I begins after replicates during interphase . Meiosis II follows meiosis I without DNA replicating again. Both meiosis I and meiosis II occur in four phases, called prophase , metaphase , anaphase , and telophase . You may recognize these four phases from , the division of the nucleus that takes place during routine cell division of eukaryotic cells .
::从微缩图中可以看出,整个过程中出现两个细胞分解,从一个母细胞中共产生四个散状细胞。两个细胞分解称为“单细胞一”和“单细胞二”。两个细胞分解称为“单细胞一”和“单细胞二”。在中间阶段复制后开始。二是“单细胞二”,在不复制DNA的情况下跟踪“单细胞一”和“单细胞二”。二是四个阶段,即预阶段、元阶段、亚相阶段和“线状”。您可以辨别这四个阶段,即:在单细胞常规细胞分划期间发生的核分。Meiosis I
::诊断一The phases of Meiosis I are:
::Meisisid I的阶段是:-
Prophase I:
The
nuclear envelope
begins to break down, and the chromosomes condense.
Centrioles
start moving to opposite poles of the cell, and a
spindle
begins to form. Importantly,
homologous chromosomes
pair up, which is unique to prophase I. In prophase of mitosis and meiosis II, homologous chromosomes do not form pairs in this way. During prophase I, crossing-over occurs. The significance of crossing-over is discussed below.
::预期一:核包件开始破裂,染色体开始凝结。三联体开始向细胞对面的极点移动,脊柱开始形成。重要的是,同质染色体配对,这是前一阶段独有的。在三联体和梅氏病第二期的预期中,同质染色体不会以这种方式形成对子。在前一期,跨线会发生。下文将讨论跨线的意义。 -
Metaphase I:
Spindle fibers attach to the paired homologous chromosomes. The paired chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell. This occurs only in metaphase I. In metaphase of mitosis and meiosis II, it is sister chromatids that line up along the equator of the cell.
::元阶段一: 配对的同族染色体附着的斯宾德尔纤维。 配对的染色体排在细胞赤道一带。 这只在元阶段一发生。 在肾上腺素和梅氏二号元阶段, 姐妹染色体排在细胞赤道一带。 -
Anaphase I:
Spindle fibers shorten, and the chromosomes of each homologous pair start to separate from each other. One chromosome of each pair moves toward one pole of the cell, and the other chromosome moves toward the opposite pole.
::分析阶段一:斯宾德尔纤维缩短,每对同父异父异母的染色体开始分离。每对同父异母的染色体有一个染色体移向细胞的一根杆,另一个染色体移向对立杆。 -
Telophase I and
Cytokinesis
:
The spindle breaks down, and new nuclear membranes form. The
cytoplasm
of the cell divides, and two haploid
daughter cells
result. The daughter cells each have a random assortment of chromosomes, with one from each homologous pair. Both daughter cells go on to meiosis II.
::Teloprophic I 和 Cytokinesis : 脊椎破裂, 新的核膜形式。 细胞分裂的细胞图层和两个手动女儿细胞的结果。 女儿细胞各有染色体的随机分布, 每对同父异母的染色体各有一个。 两个女儿细胞都进入二号间歇。
Meiosis II
::诊断二The phases of meiosis II are:
::诊断第二阶段是:-
Prophase II:
The nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle begins to form in each haploid daughter cell from meiosis I. The centrioles also start to separate.
::第二阶段:核封套破裂,脊椎开始从中度I 的每个软体女儿细胞中形成。中间体也开始分离。 -
Metaphase II:
Spindle fibers line up the sister chromatids of each chromosome along the equator of the cell.
::代号二:斯宾德尔纤维排列在细胞赤道沿线每个染色体的姐妹色谱。 -
Anaphase II:
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
::分析阶段二:姐妹染色体分离,移到对极。 -
Telophase II and Cytokinesis:
The spindle breaks down, and new nuclear membranes form. The cytoplasm of each cell divides, and four haploid cells result. Each cell has a unique combination of chromosomes.
::电波II和Cytokinesis: 螺旋断裂, 新的核膜形式。 每个细胞的细胞分裂和四个手动细胞结果。 每个细胞都有独特的染色体组合。
Gametogenesis
::游戏起源At the end of meiosis, four haploid cells have been produced, but the cells are not yet gametes. The cells need to develop before they become mature gametes capable of fertilization. The of haploid cells into gametes is called . It differs between males and females.
::盘旋结束时,已经生产了四个手动细胞,但细胞还不是网格。细胞在成为成熟的能够施肥的网格之前需要发育。将机动细胞称为网格。男女差别很大。-
A gamete produced by a male is called a
,
and the process that produces a mature sperm is
called
spermatogenesis
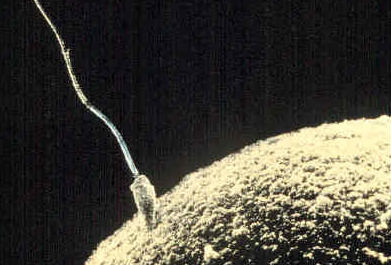
. During this process, a sperm cell grows a tail and gains the ability to “swim,” like the human sperm cell shown in the figure
.
::由男性制作的调子被称为“一个 ” , 产生成熟精子的过程被称为“精子产生 ” 。 在这一过程中,精子细胞长出尾巴,并获得与图中显示的人类精子细胞一样的“游泳”能力。 -
A gamete produced by a female is called an
egg
,
and t
he process that produces a mature egg is called
oogenesis
, during which just one functional egg is produced. The other three haploid cells that result from me
iosis
are called
polar bodies
, and they disintegrate. The single egg is a very large cell, as you can see from the human egg also shown in the figure
.
::由雌性生成的果子被称作鸡蛋,而产出成熟蛋的过程被称作 " 产卵 " ,在这一过程中,只生产出一个功能性的蛋。其他三个由梅氏病生成的手动细胞被称作极体,它们分解。单蛋是一个非常大的细胞,从图中可以看到,从人类的蛋中也可以看到这一点。
A human sperm is a tiny cell with a tail. A human egg is much larger. Both cells are mature haploid gametes that are capable of fertilization. What process is shown in this photograph?
::人类精子是带有尾巴的小细胞。 人类蛋要大得多。 两个细胞都是成熟的、 能够施肥的杂交组合体。 这张照片显示了什么过程 ?Sexual Reproduction and Genetic Variation
::性生殖和遗传变异"It takes two to tango" might be a euphemism for sexual reproduction. Requiring two individuals to produce offspring, however, is also the main drawback of this way of reproducing, because it requires extra steps — and often a certain amount of luck — to successfully reproduce with a partner. On the other hand, sexual reproduction greatly increases the potential for in offspring, which increases the likelihood that the resulting offspring will have genetic advantages. In fact, each offspring produced is almost guaranteed to be genetically unique, differing from both parents and from any other offspring. Sexual reproduction increases genetic variation in a number of ways:
::“探戈需要两个时间”可能是性生殖的一种委婉说法。 但是,要求两个人生子也是这种再生方式的主要缺点,因为它需要额外的步骤,而且往往需要一定的运气,才能与伴侣成功繁殖。另一方面,性生殖大大增加了后代的潜力,这增加了后代获得遗传优势的可能性。事实上,每个后代几乎都保证遗传上的独特性,与父母和任何其他后代不同。性生殖以多种方式增加遗传变异:-
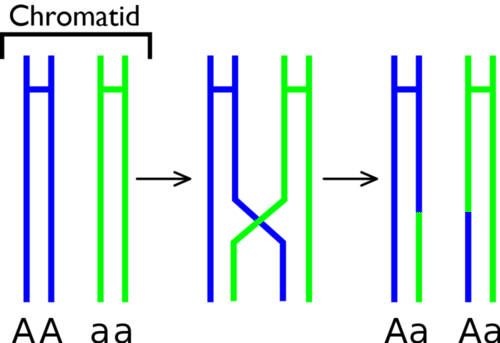
When homologous chromosomes pair up during meiosis I, crossing-over can occur.
Crossing-over
is the exchange of
genetic material
between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes. It results in new combinations of
genes
on each chromosome. This is called
recombination
. You can see how it happens in the figure
.
::当同族染色体在美化一期间配对时,可能发生交叉。交叉是同族染色体的非姐妹染色体染色体之间的基因材料交换。它导致每种染色体的基因新组合。这叫做重组。你可以从数字中看到它是如何发生的。 -
When cells divide during meiosis, homologous chromosomes are randomly distributed to daughter cells, and different chromosomes segregate independently of each other. This is called
independent assortment
. It results in gametes that have unique combinations of chromosomes.
::当细胞在美化过程中分裂时,同族染色体会随机分布到女儿的细胞中,而不同的染色体会彼此独立分离。这被称为独立分类。它导致有独特的染色体组合的调子。 -
In sexual reproduction, two gametes unite to produce an offspring. But which two of the millions of possible gametes will it be? This is a matter of chance, and it's obviously another source of genetic variation in offspring.
::在性生殖中,两个调子合在一起产生一个后代。但是,在几百万种可能的调子中,哪一个是可能的?这是一个偶然问题,而且显然是后代遗传变异的另一个来源。
Crossing-over and recombination in meiosis I increase genetic variation in gametes.
::甲型脑膜炎的交叉和再组合I会增加复位数的遗传变异。All of these mechanisms — crossing over , independent assortment, and the random union of gametes — work together to result in an amazing range of potential genetic variation. Each human couple, for example, has the potential to produce more than 64 trillion genetically unique children. No wonder we are all different!
::所有这些机制——跨越、独立的组合和任意组合——共同努力,导致一系列惊人的潜在基因变异,例如,每对人类夫妇都有可能产生超过64万亿个基因独特的儿童,难怪我们都不同。Summary
::摘要-
In sexual reproduction, two parents produce gametes that unite in the process of fertilization to form a single-celled zygote. Gametes are haploid cells with one copy of each of the 23 chromosomes, and the zygote is a diploid cell with two
copies of each of the 23 chromosomes.
::在性生殖方面,双亲生产在受精过程中结合形成单细胞zygote的调子;双胞胎是单细胞细胞,每23个染色体各一份;双胞胎是浸泡细胞,每23个染色体各两份。 -
Meiosis is the type of cell division that produces four haploid daughter cells that may become gametes. Meiosis occurs in two stages, called meiosis I and meiosis II, each of which occurs in four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase).
::Meisisis 是一种细胞分裂型,可产生4个可能变成游戏的散发女儿细胞。 Meisis 分两个阶段发生,称为 meisisis I 和 meisis II, 每一个阶段分四个阶段( 预阶段、 元阶段、 周期阶段和 调频阶段 ) 。 -
Meiosis is followed by gametogenesis, the process during which the haploid daughter cells change into mature gametes. Males produce gametes called sperm in a process known as spermatogenesis, and females produce gametes called eggs in the process known as oogenesis.
::美化之后是游戏起源,在这个过程里,手动女儿细胞变成了成熟的调子。 雄性在被称为精子起源的过程里生产被称为精子的调子,而雌性则在被称为卵起源的过程里生产被称为卵的调子。 -
Sexual reproduction produces genetically unique offspring. Crossing-over, independent assortment, and the random union of gametes work together to result in an amazing
range
of potential genetic variation.
::性生殖产生基因上独特的后代。 交叉、独立的组合和随机的调子结合共同产生惊人的潜在基因变异。
Review
::回顾1. Explain how sexual reproduction happens at the cellular level.
::1. 解释性生殖在细胞层面是如何发生的。2. Summarize what happens during meiosis.
::2. 概述在流行病期间发生的情况。3. Compare and contrast gametogenesis in males and females.
::3. 比较和对比男性和女性的游戏起源。4. Explain the mechanisms that increase genetic variation in the offspring produced by sexual reproduction.
::4. 解释哪些机制会增加性生殖所产生后代的遗传变异。5. Why do gametes need to be haploid? What would happen to the chromosome number after fertilization if they were diploid?
::5. 为什么调子需要杂乱无章?如果是杂乱无章,在施肥后染色体数会怎样?6. Describe one difference between prophase I of meiosis and prophase of mitosis.
::6. 描述前期一级疾病和前期性疾病之间的一个区别。7. Do all of the chromosomes that you got from your mother go into one of your gametes? Why or why not?
::7. 你从母亲那里得到的所有染色体 是否都进入你的发色板?8. True or False: Crossing-over is the exchange of genetic material between sister chromatids.
::8. 真实或假:交叉是指姐妹染色体之间基因材料的交换。9. True or False: Human sperm are haploid.
::9. 真实或假:人类精子是杂乱无章的。10. True or False: Sister chromatids separate from each other during meiosis I.
::10. 真实的或假的:姐妹染色体在甲状腺结膜结膜结膜结膜结膜结膜1期间彼此分离。11. How many cells are produced after a single cell goes through meiosis?
::11. 在单细胞经历经线性硬化后,有多少细胞生产出来?12. Which stage of meiosis (prophase I or II; metaphase I or II; anaphase I or II; telophase I or II) best fits the descriptions below? Choose only one for each description.
::12. 哪个医疗阶段(第一或二期;第一或二元阶段;第一或二期;第一或二期;第一或二期;第一或二期;第一或二期)最符合以下描述?为每个描述选择一个。a. Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell.
::a. 细胞赤道一带的同质染色体对称。b. Sister chromatids separate.
::b. 姐妹染色体分开。c. Homologous chromosomes separate from each other.
::c. 相互分离的同族染色体。Explore More
::探索更多A special type of cell division known as meiosis is responsible for your uniqueness. Learn more here:
::一种特殊类型的细胞分裂,叫做梅伊松, 负责您的独特性。 在此学习更多 :Check out this video to learn more about Down Syndrome:
::查看这段影片以了解更多唐氏综合症: -
Prophase I:
The
nuclear envelope
begins to break down, and the chromosomes condense.
Centrioles
start moving to opposite poles of the cell, and a
spindle
begins to form. Importantly,
homologous chromosomes
pair up, which is unique to prophase I. In prophase of mitosis and meiosis II, homologous chromosomes do not form pairs in this way. During prophase I, crossing-over occurs. The significance of crossing-over is discussed below.